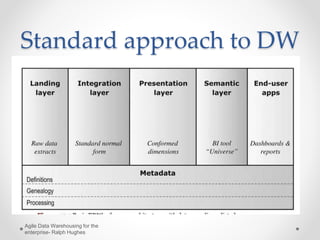
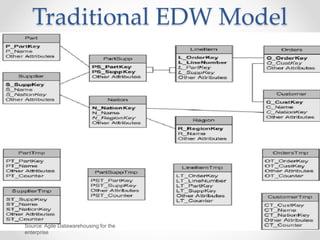
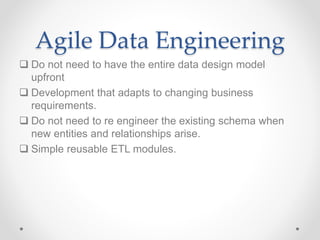
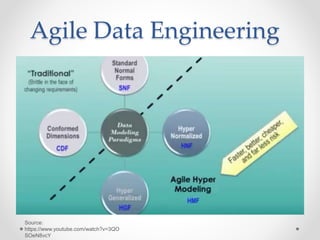
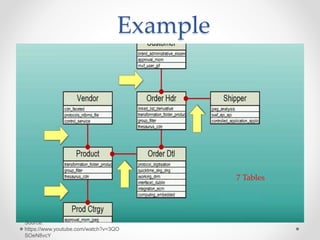
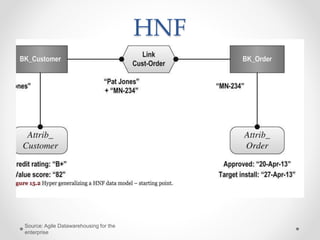
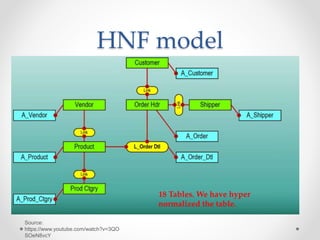
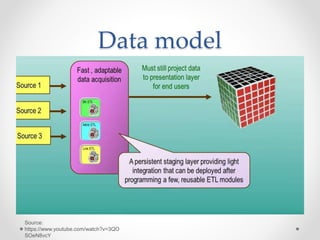
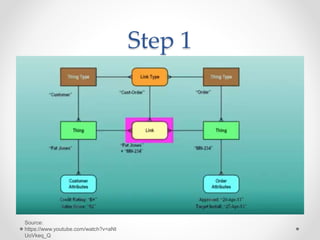
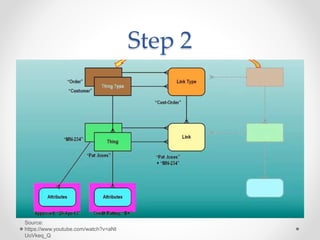
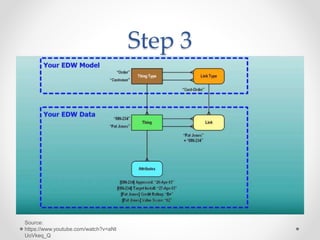
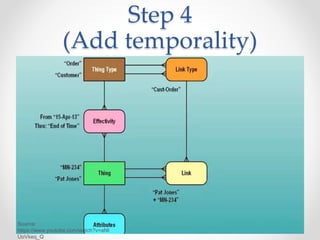
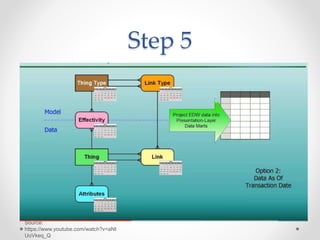
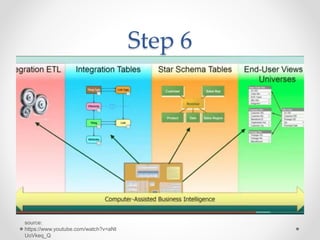
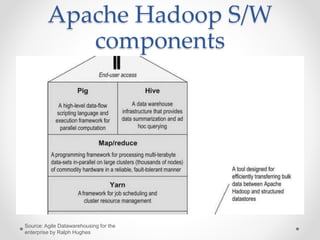
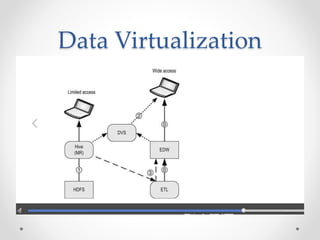
The document discusses agile approaches to data warehousing and big data technologies. It describes traditional data warehousing as brittle and costly to modify. An agile approach uses reusable ETL modules and a hyper-normalized integration layer to flexibly adapt to changing requirements. Big data technologies like Hadoop, NoSQL databases, and cloud-based data warehouses are also discussed as enabling flexible and cost-effective options for large and evolving data and analytics needs.