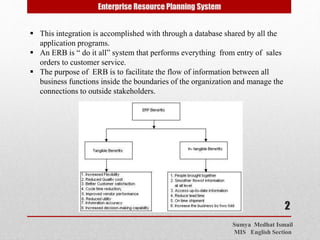
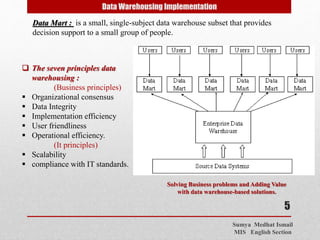
This document discusses Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems and data warehousing implementation. It defines ERP as software that integrates all functions of an organization, including development, manufacturing, sales and marketing. ERP offers solutions for all business functions and packages for organizations of various sizes and types. Implementing ERP is complex, expensive and time-consuming. The document also defines data warehousing as an integrated, subject-oriented database that supports decision making. It discusses factors to consider for data warehousing implementation such as available funding, management views, and corporate culture.