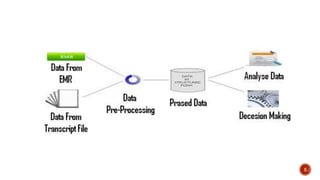
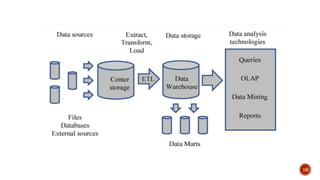
The document discusses clinical data mining and data warehousing. It begins by introducing clinical data mining as a process to analyze and interpret available clinical data for decision making and knowledge building. It then describes approaches to clinical data mining including data collection, pre-processing, parsing, and applying knowledge to create new databases and queries. The document also discusses online clinical data mining tools, advantages of data warehousing, challenges of clinical data warehousing, and applications of data mining such as creating electronic patient files and improving healthcare quality.