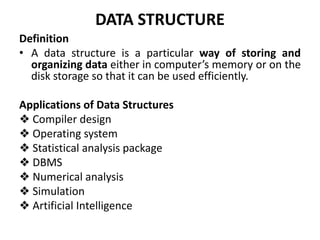
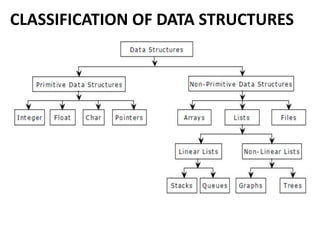
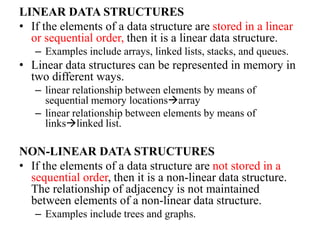
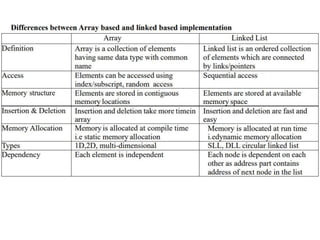
The document discusses data structures and algorithms. It aims to understand abstract data types (ADTs) and their implementation, apply sorting and searching techniques, and learn algorithm design. It covers linear data structures like arrays and linked lists, and non-linear structures like trees and graphs. Specifically, it describes the list ADT and implementations using arrays and linked lists, discussing creation, insertion, deletion and other list operations.







![Declaration of Array:
#define maxsize 10
int list[maxsize], n ;
Creation of Array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1linkedlist-231027141005-691e7b6b/85/unit-1_Linked-list-pptx-12-320.jpg)

![Insert Operation: Insert operation is used to insert an element at
particular position in the existing list.
void Insert( )
{
int i,data,pos;
printf("nEnter the data to be inserted:t");scanf("%d",&data);
printf("nEnter the position at which element to be inserted:t");
scanf("%d",&pos);
if (pos>=n)
printf (“Array overflow”);
for (i = n-1; i >= pos-1 ; i--)
{
list[i+1] = list[i];
}
list[pos-1] = data;
n=n+1;
Display();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1linkedlist-231027141005-691e7b6b/85/unit-1_Linked-list-pptx-14-320.jpg)

![Deletion
void Delete( )
{
int i, pos ;
printf("nEnter the position of the data to be deleted:t");
scanf("%d",&pos);
printf("nThe data deleted is:t %d", list[pos-1]);
for(i=pos-1;i<n-1;i++)
{
list[i]=list[i+1];
}
n=n-1;
Display();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1linkedlist-231027141005-691e7b6b/85/unit-1_Linked-list-pptx-16-320.jpg)

![Search Operation:
Routine to search an element in the array:
void Search( )
{
int search,i;
printf("nEnter the element to be searched:t");
scanf("%d",&search);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(list[i]==search)
{
printf("Value is in the %d Position", i);
}
else
{
printf("Value %d is not in the list::", search);
continue;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1linkedlist-231027141005-691e7b6b/85/unit-1_Linked-list-pptx-18-320.jpg)