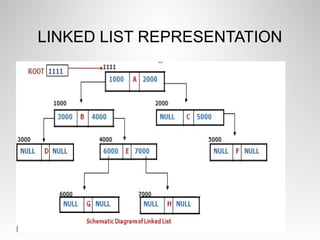
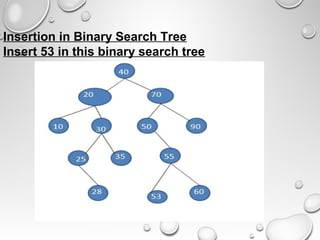
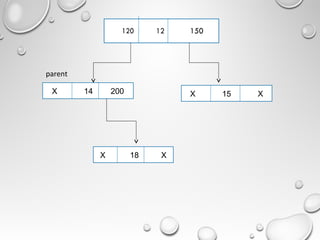
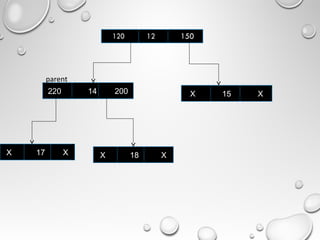
The document outlines a presentation on trees and binary trees. It discusses different tree types including binary trees, complete binary trees, and binary search trees. It covers tree traversal methods like preorder, inorder and postorder traversal. It also discusses representations of binary trees using arrays and linked lists and algorithms for insertion and deletion in binary search trees.