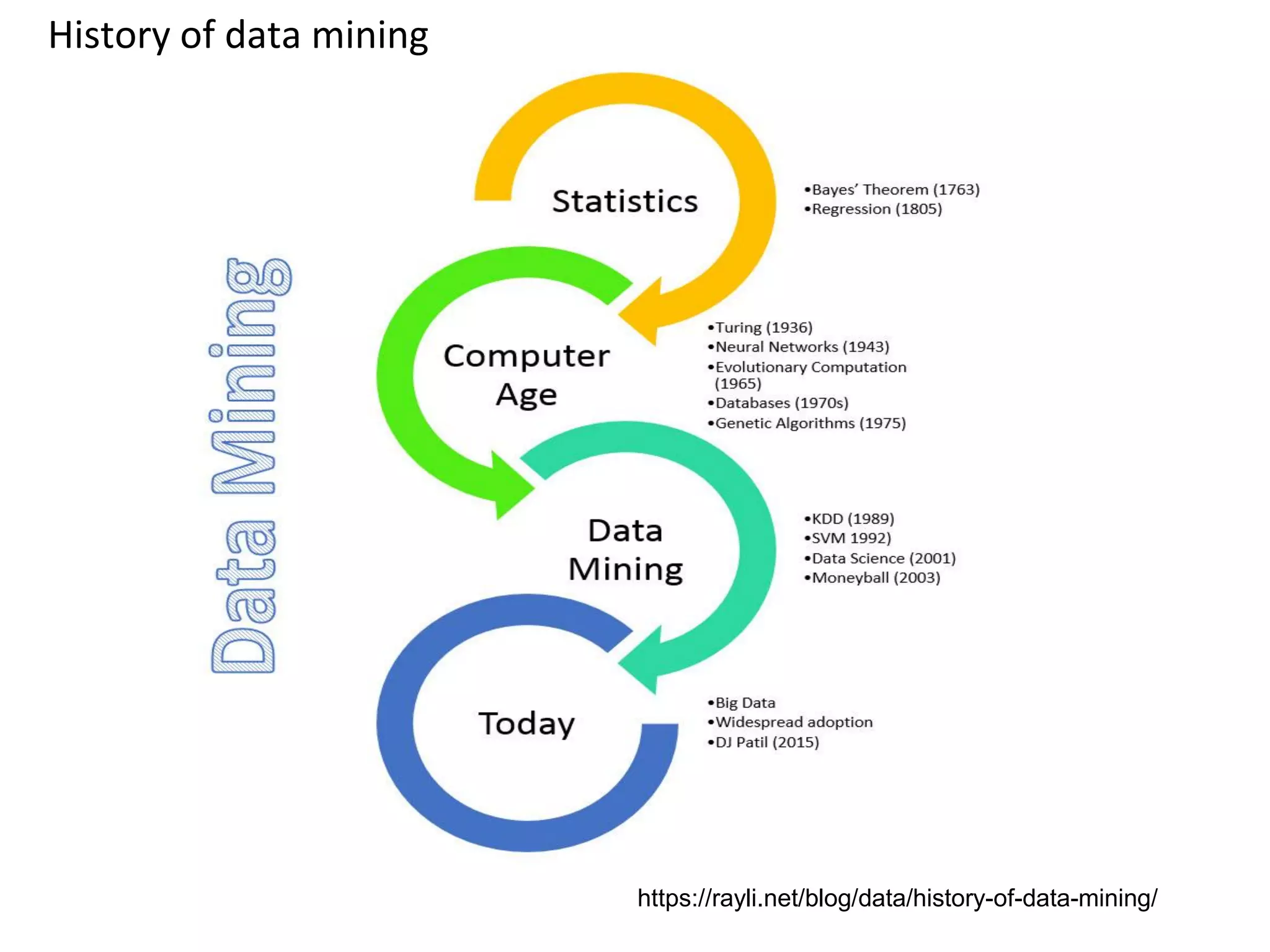
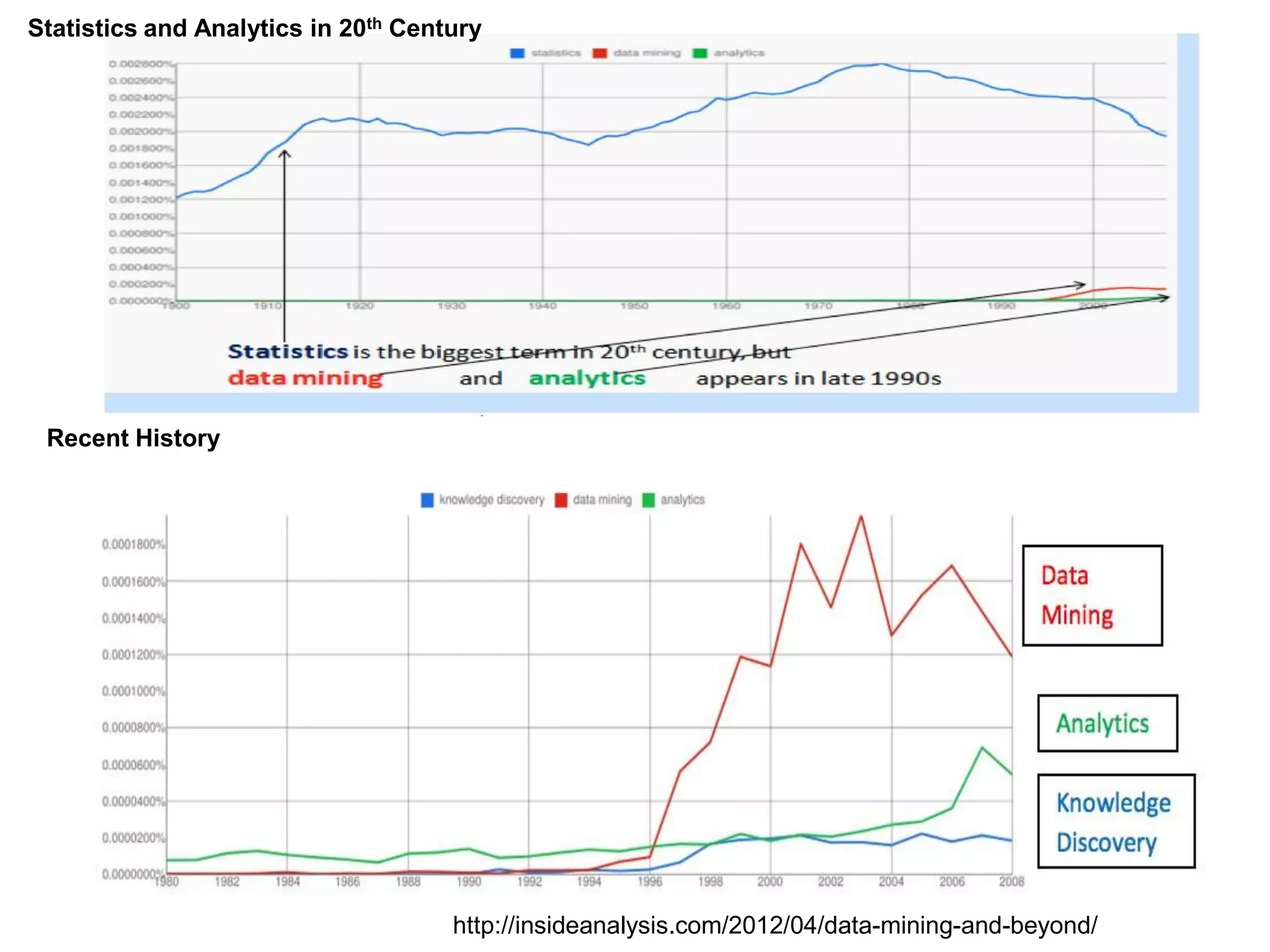
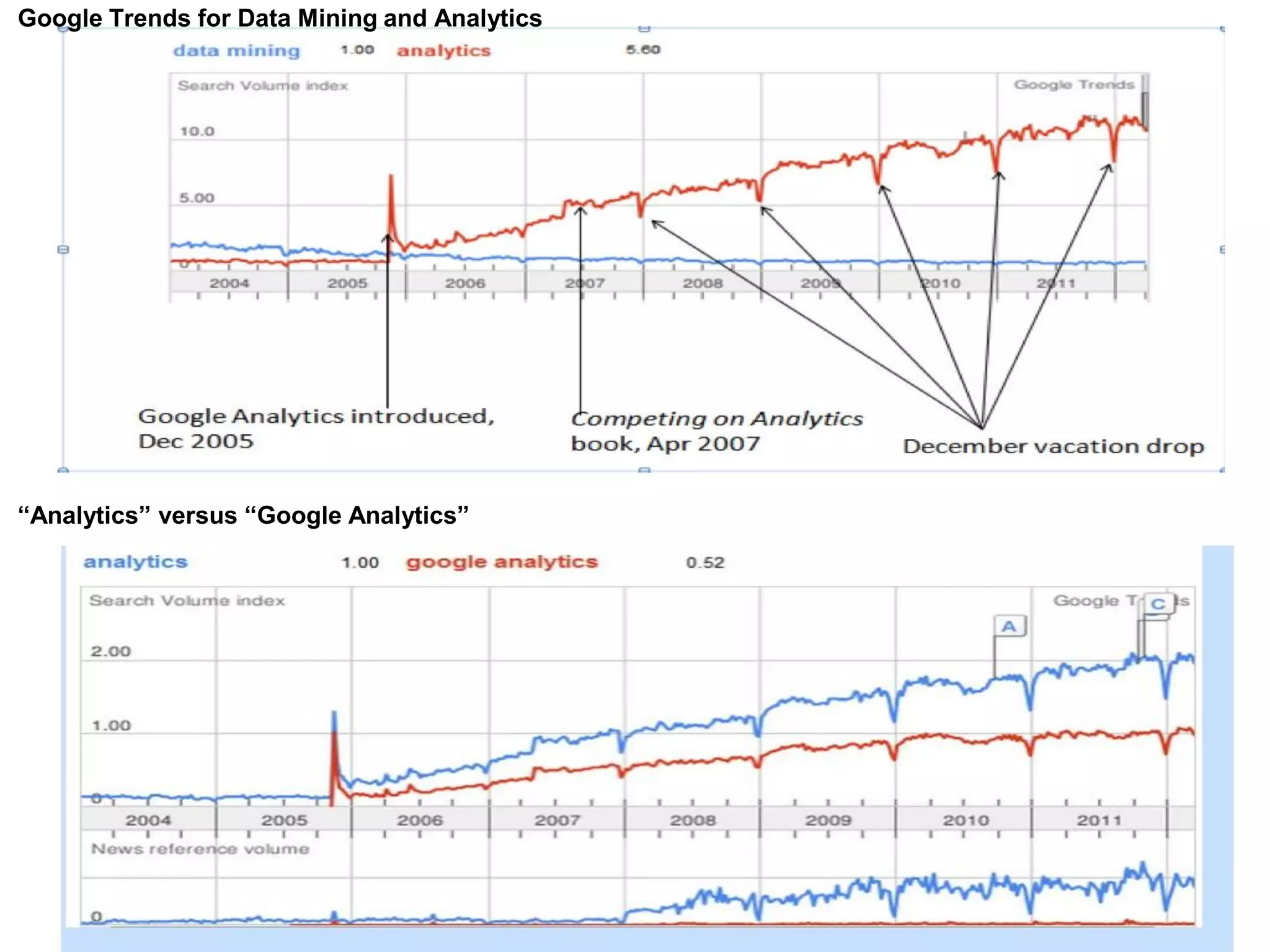
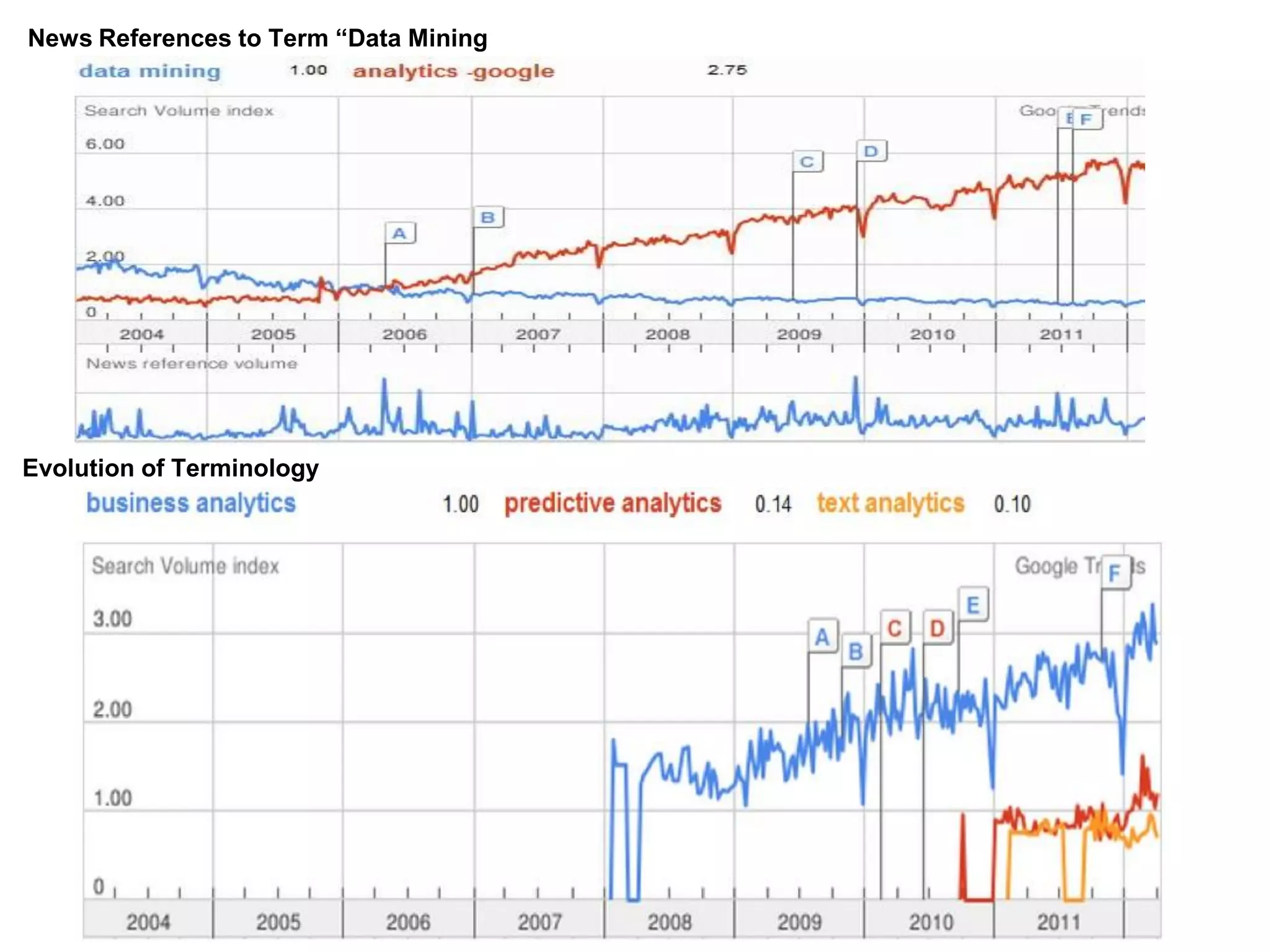
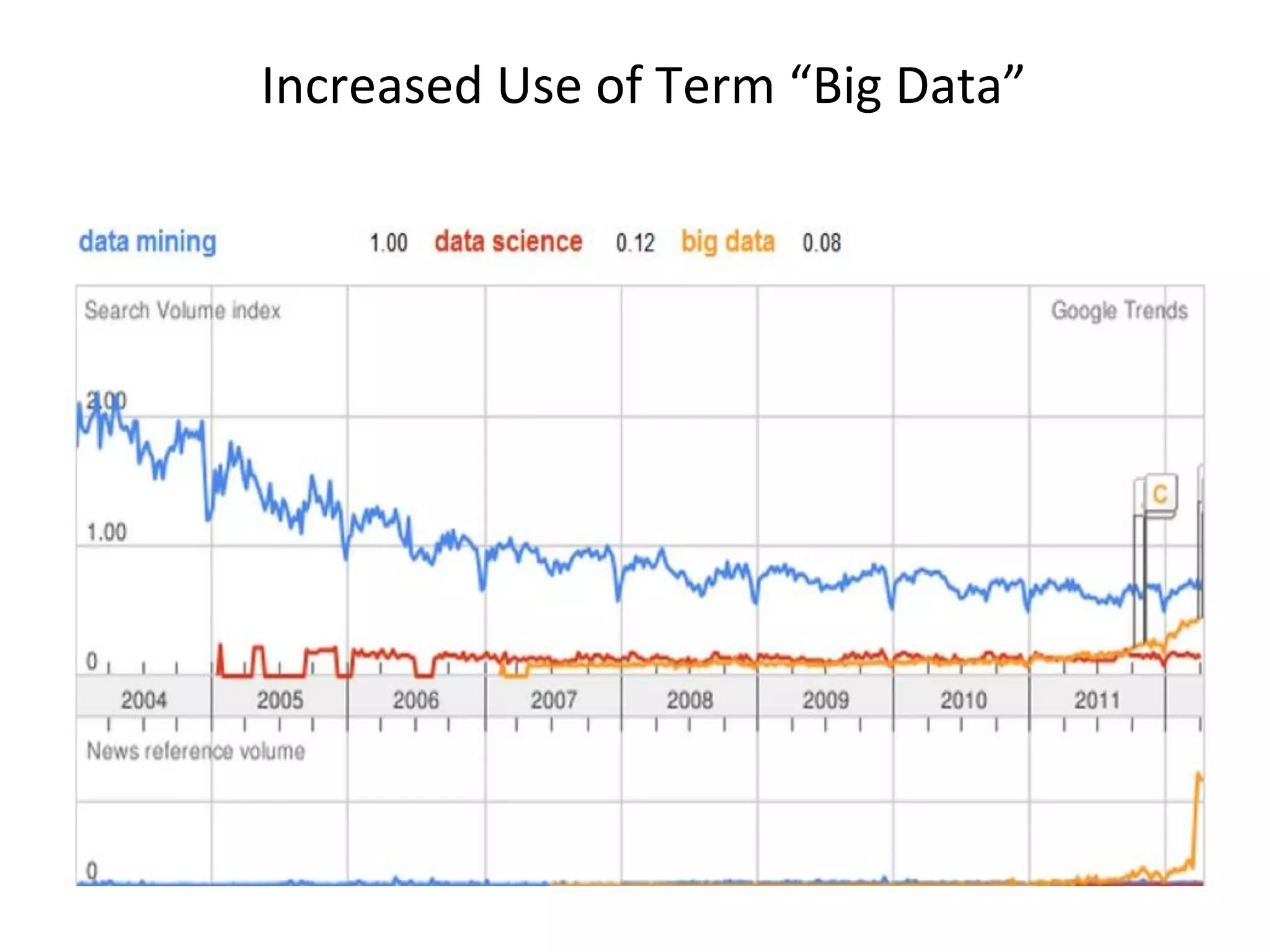
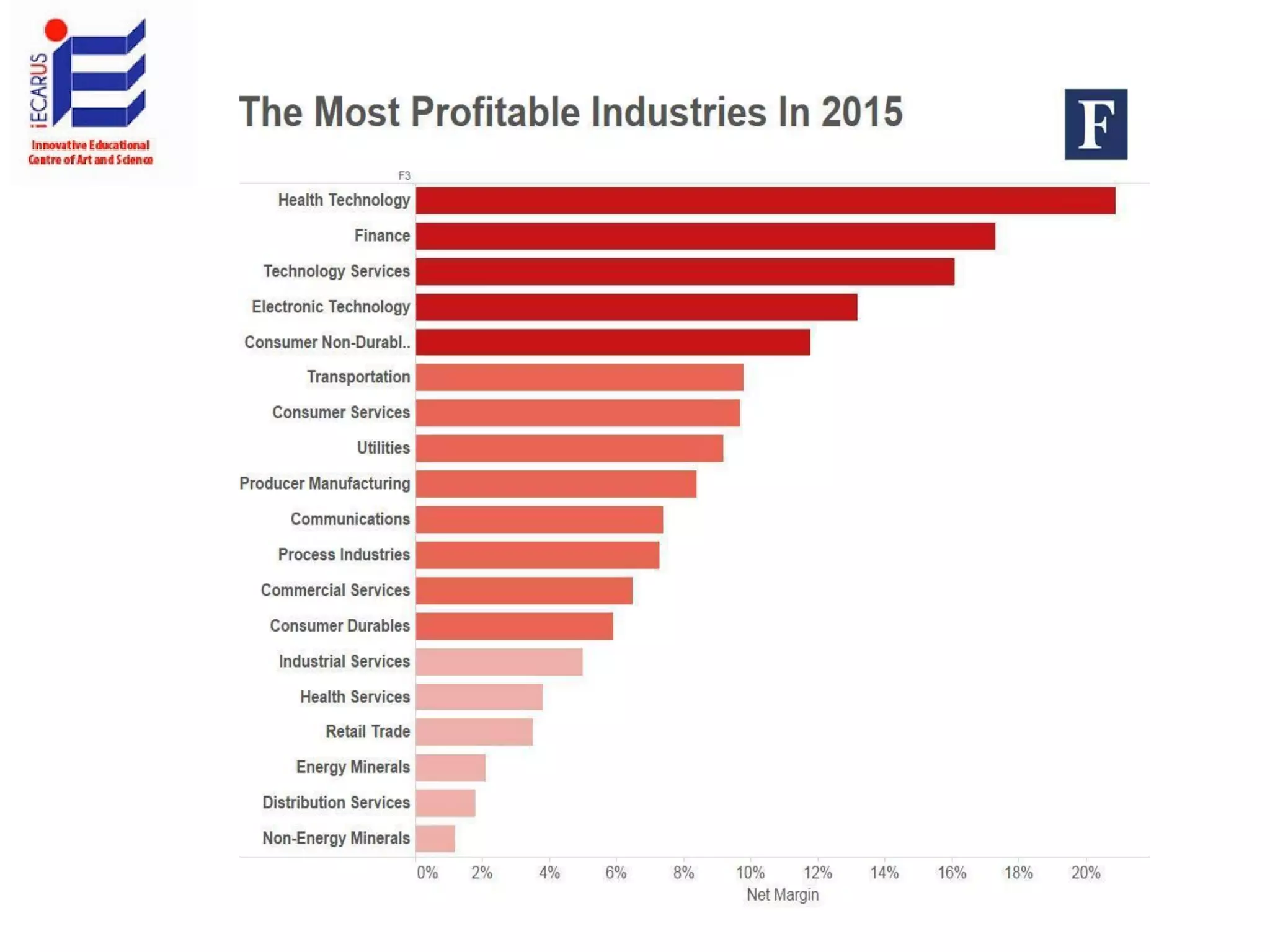
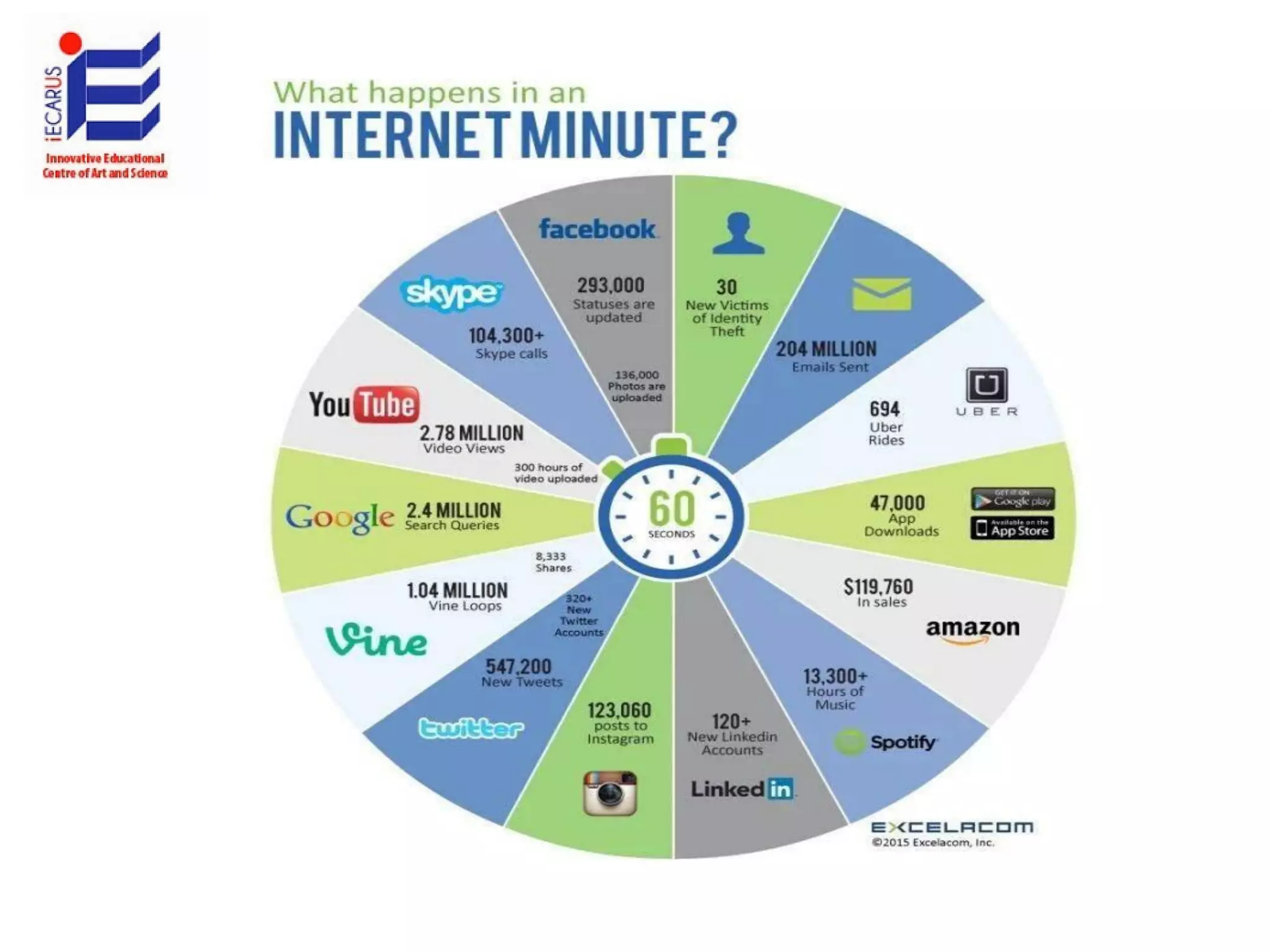
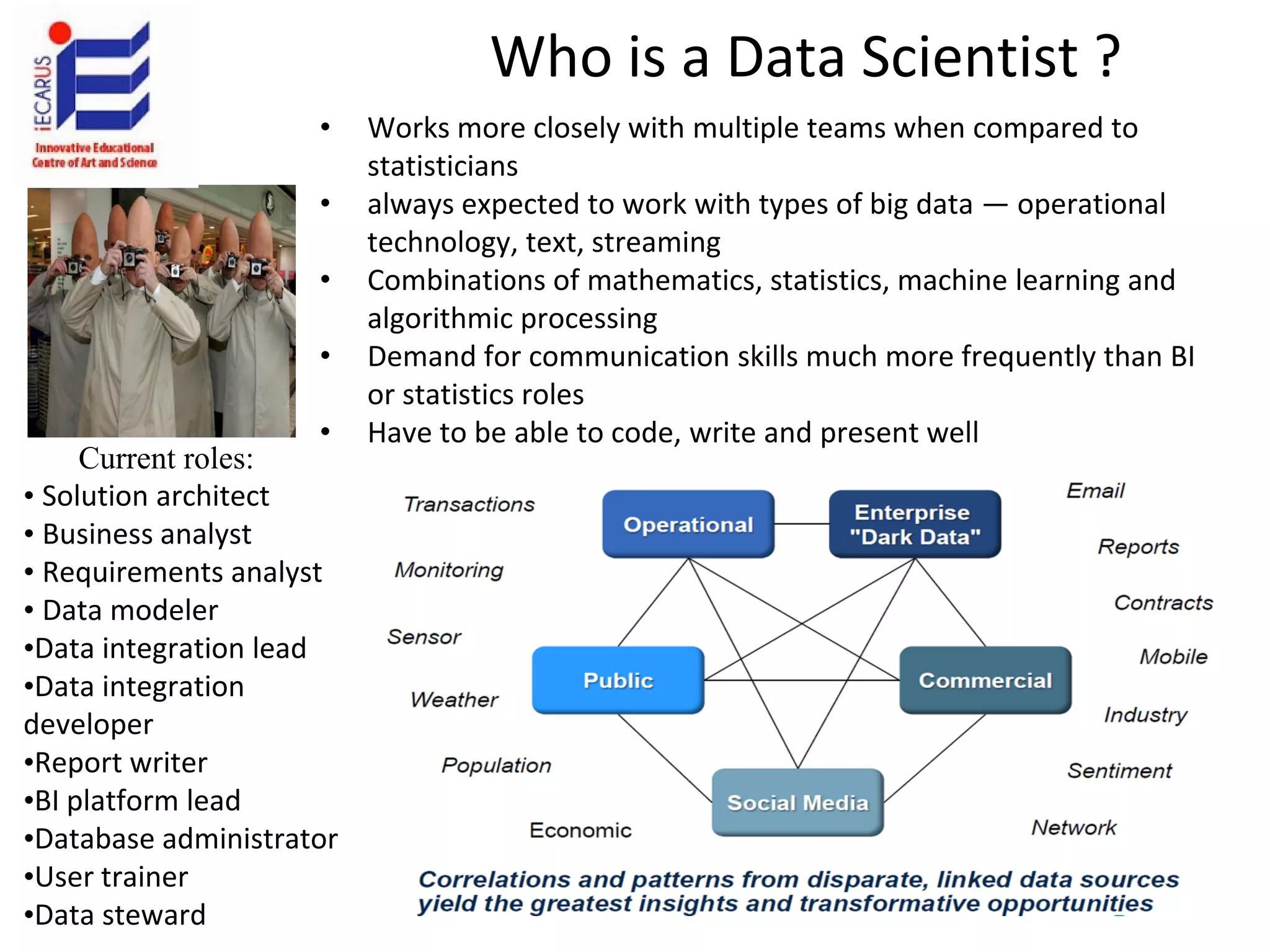
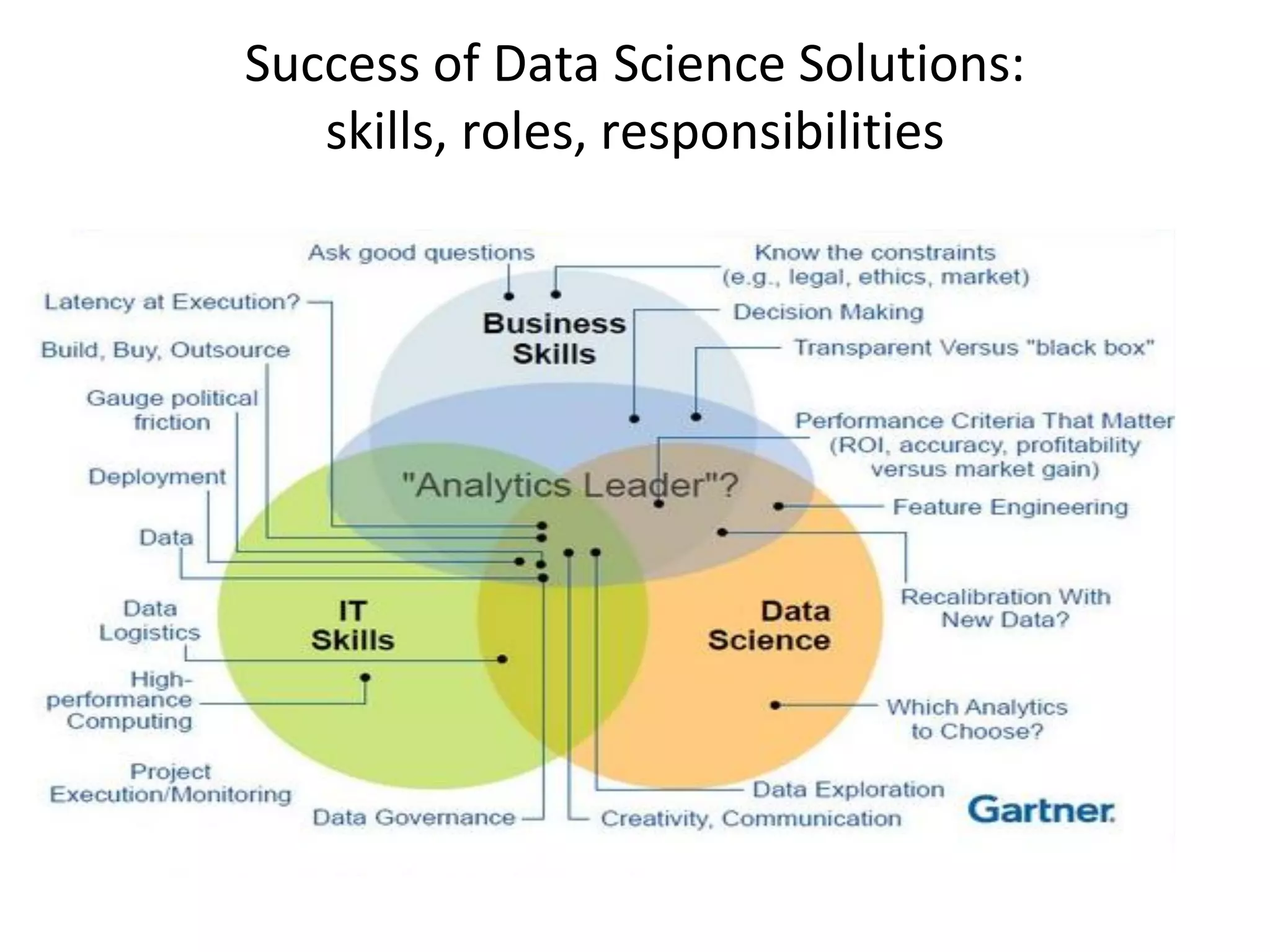
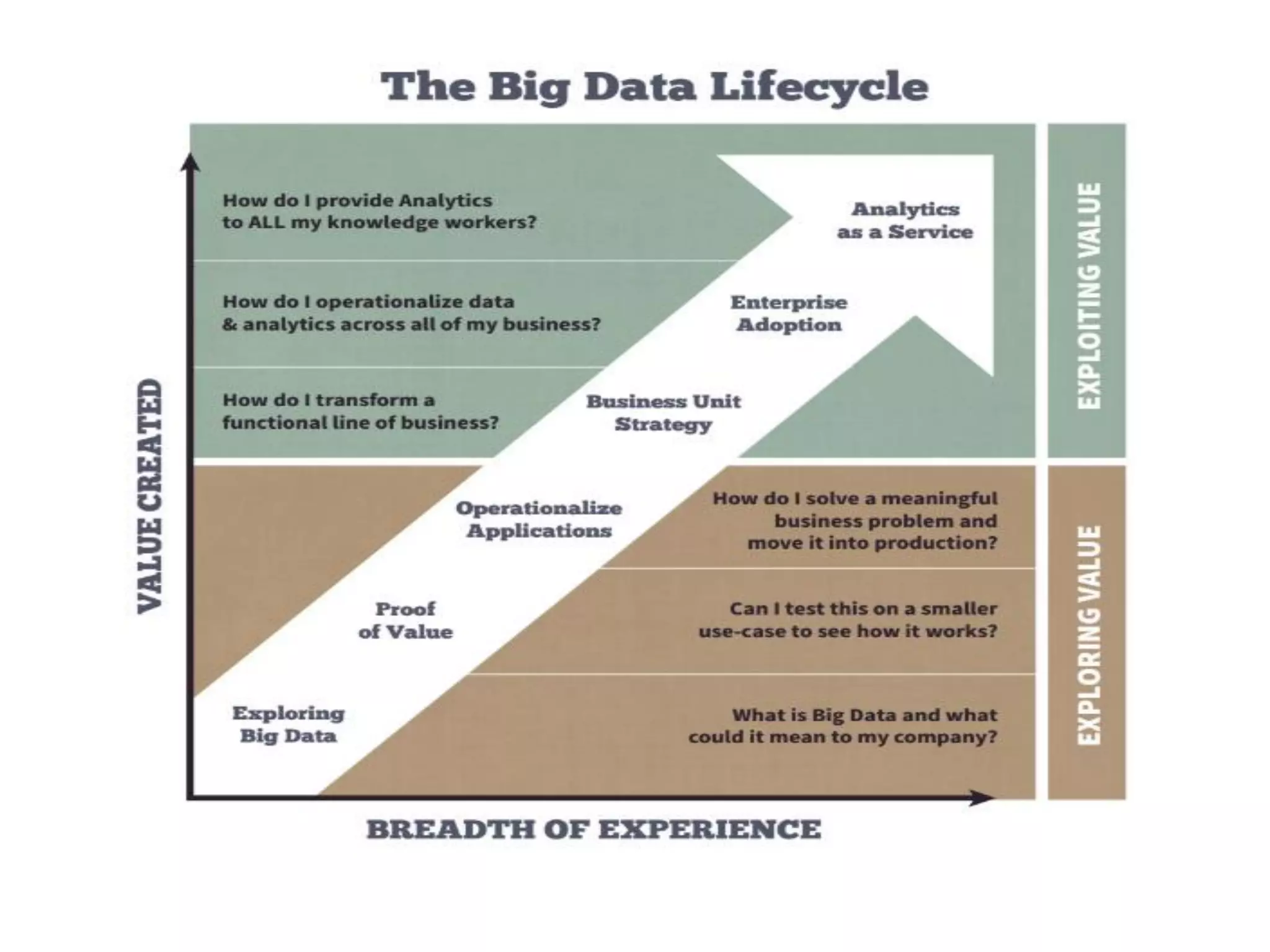
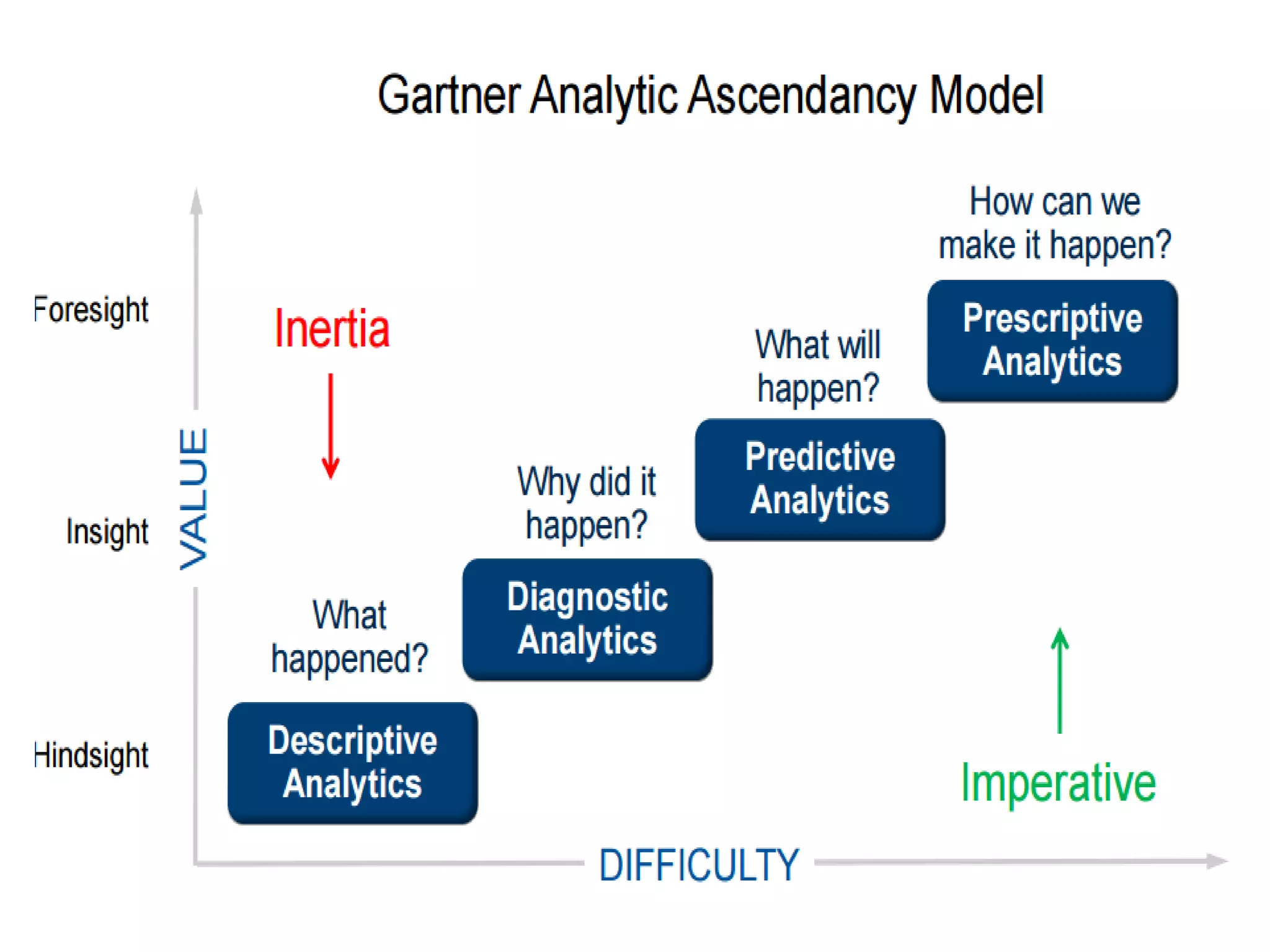
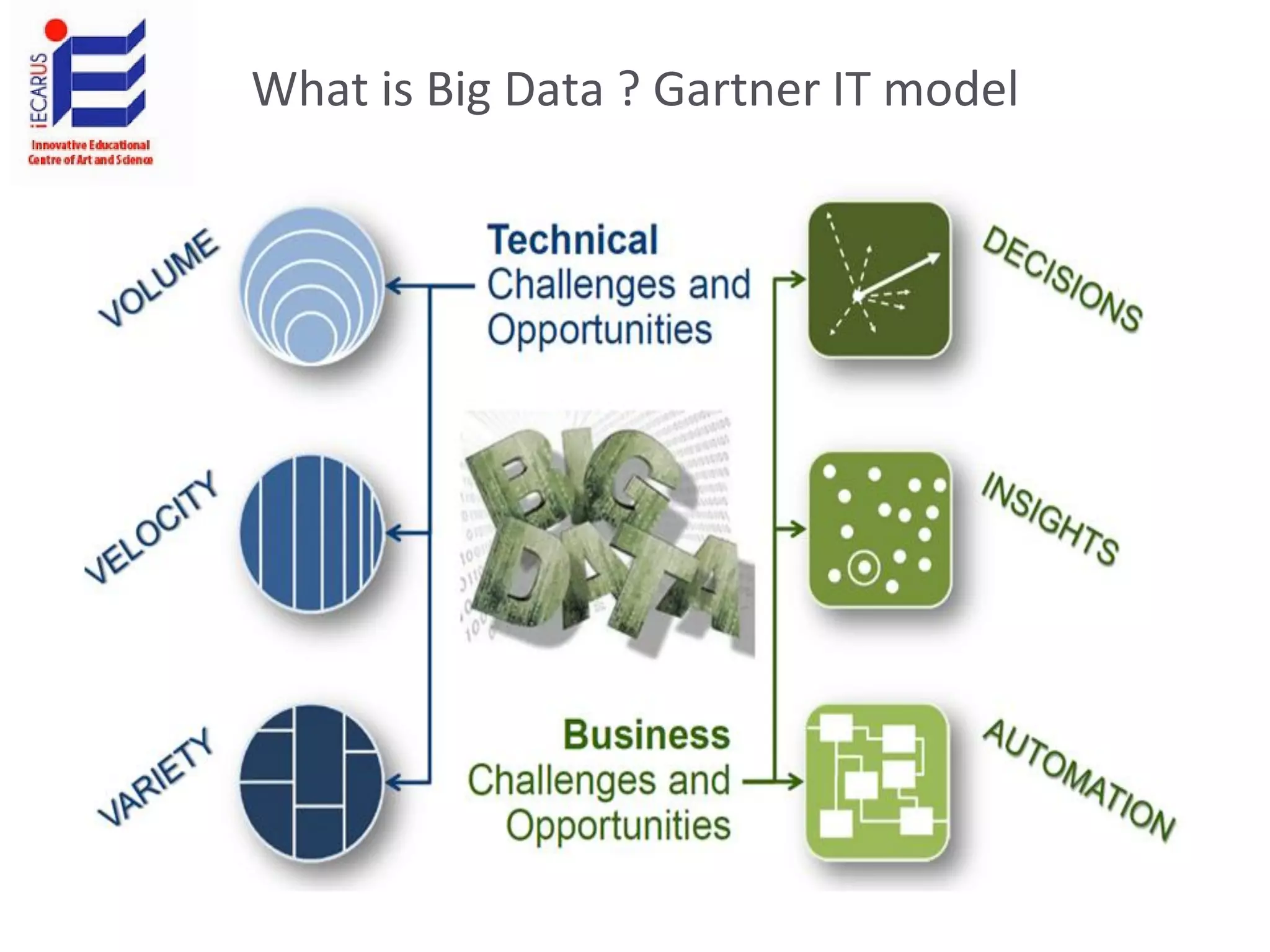
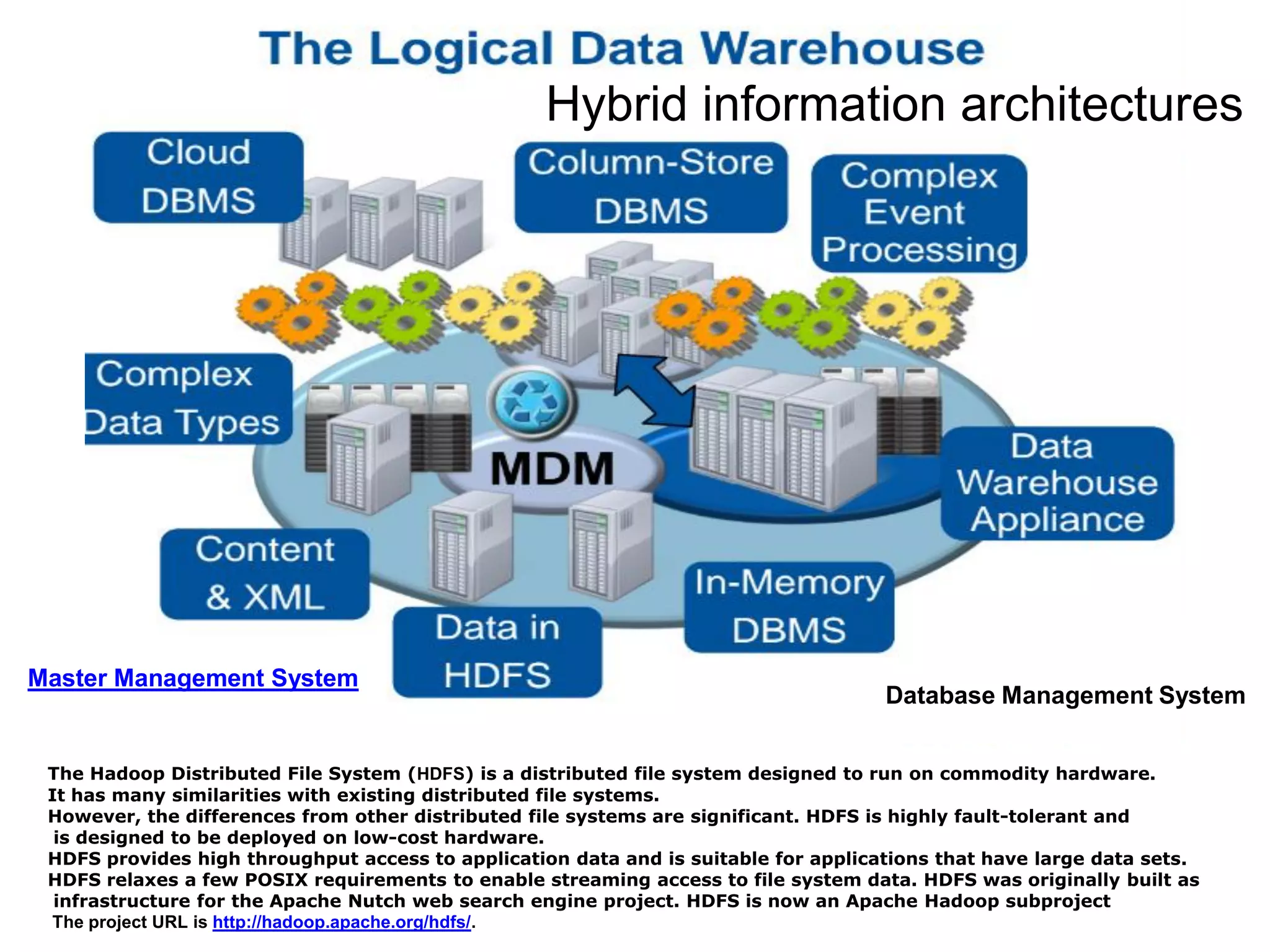
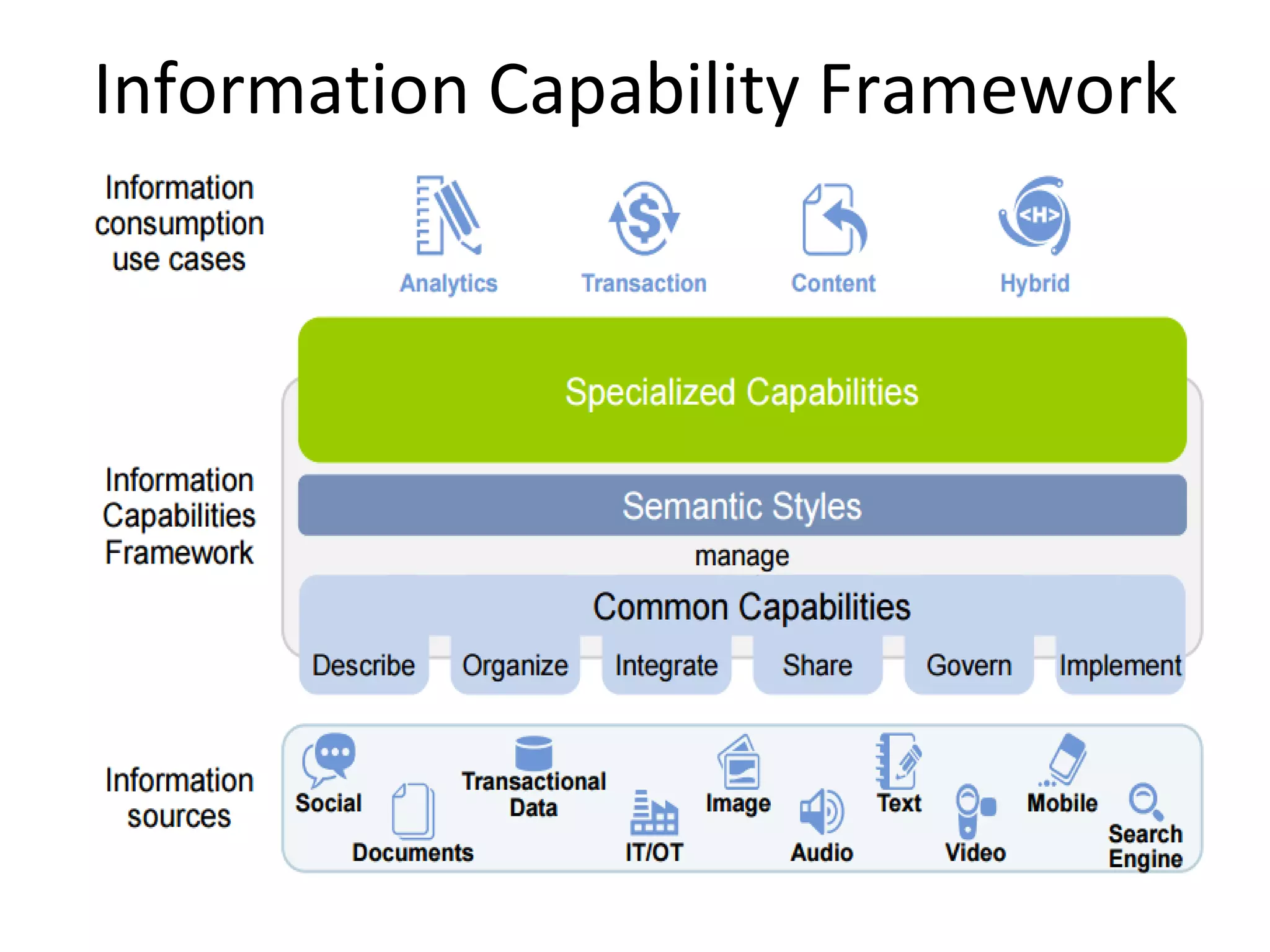
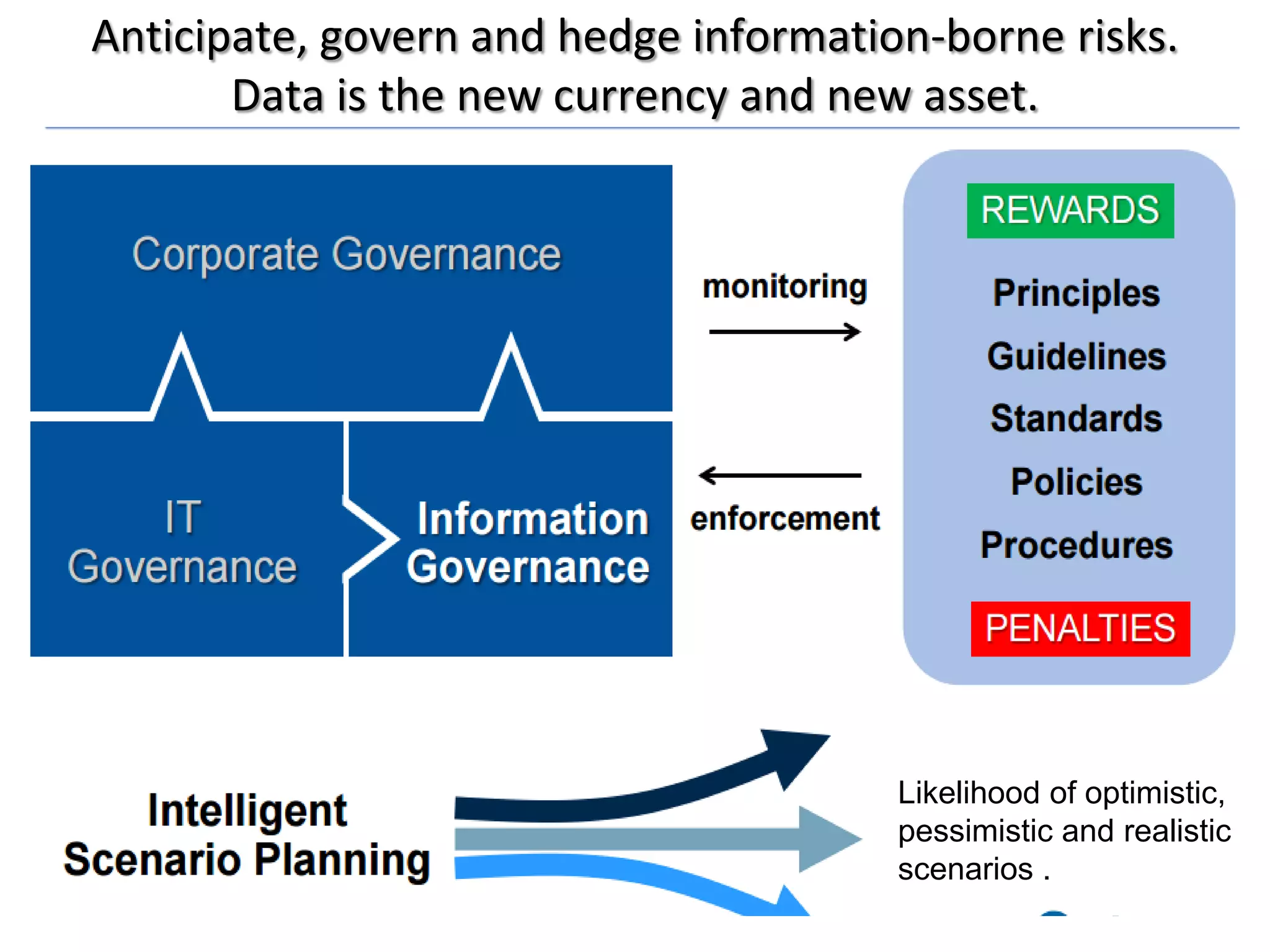
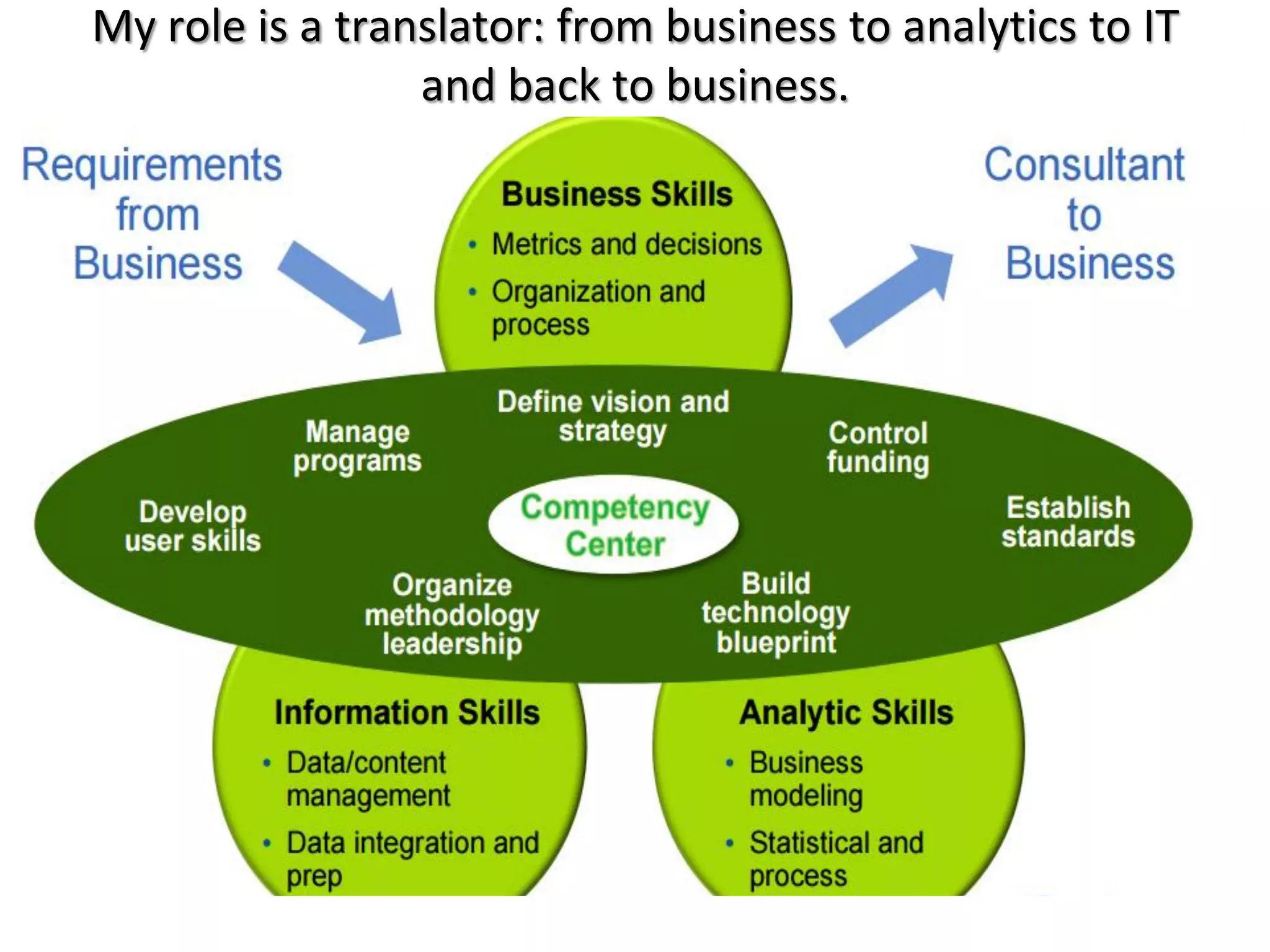
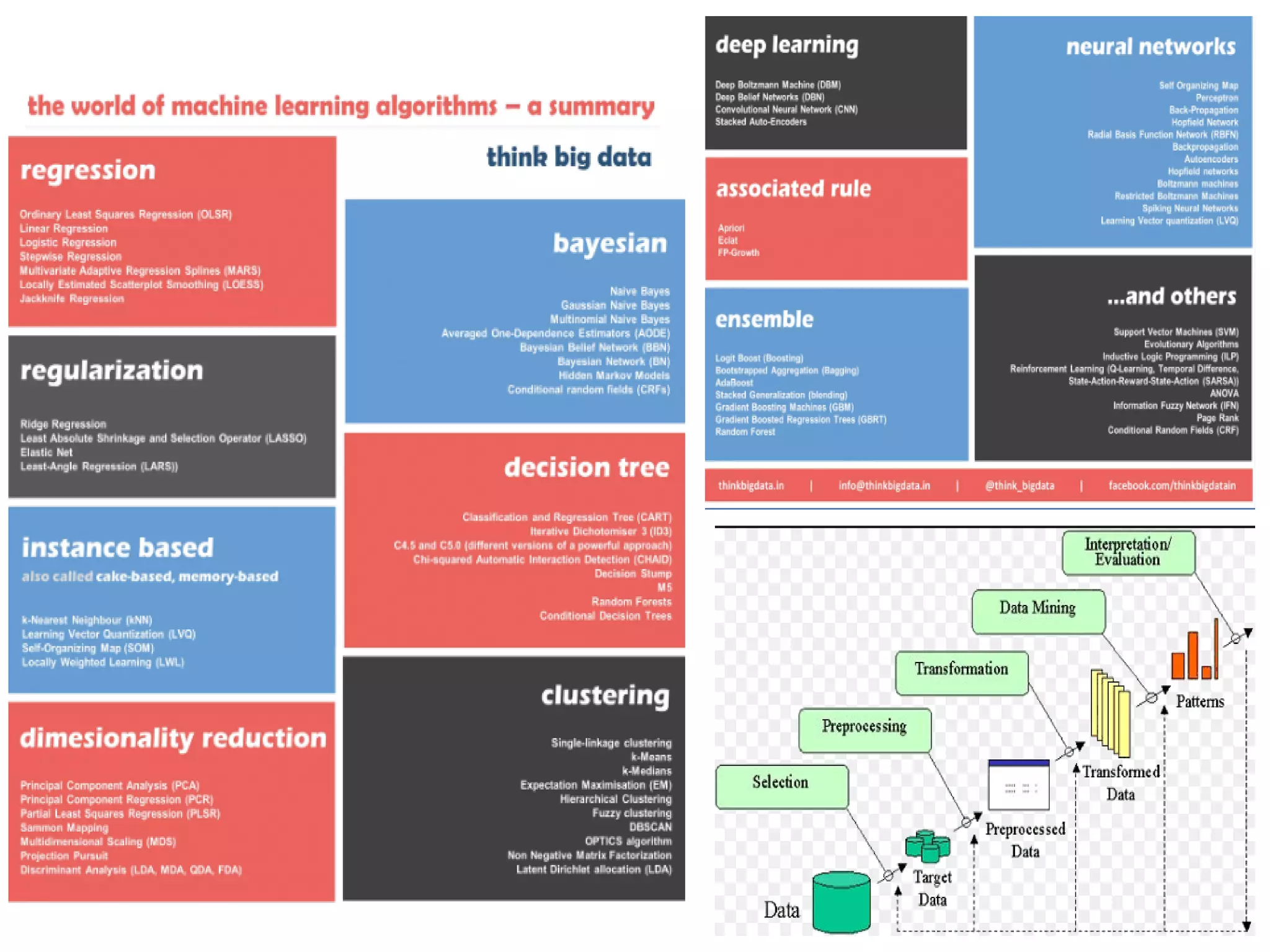
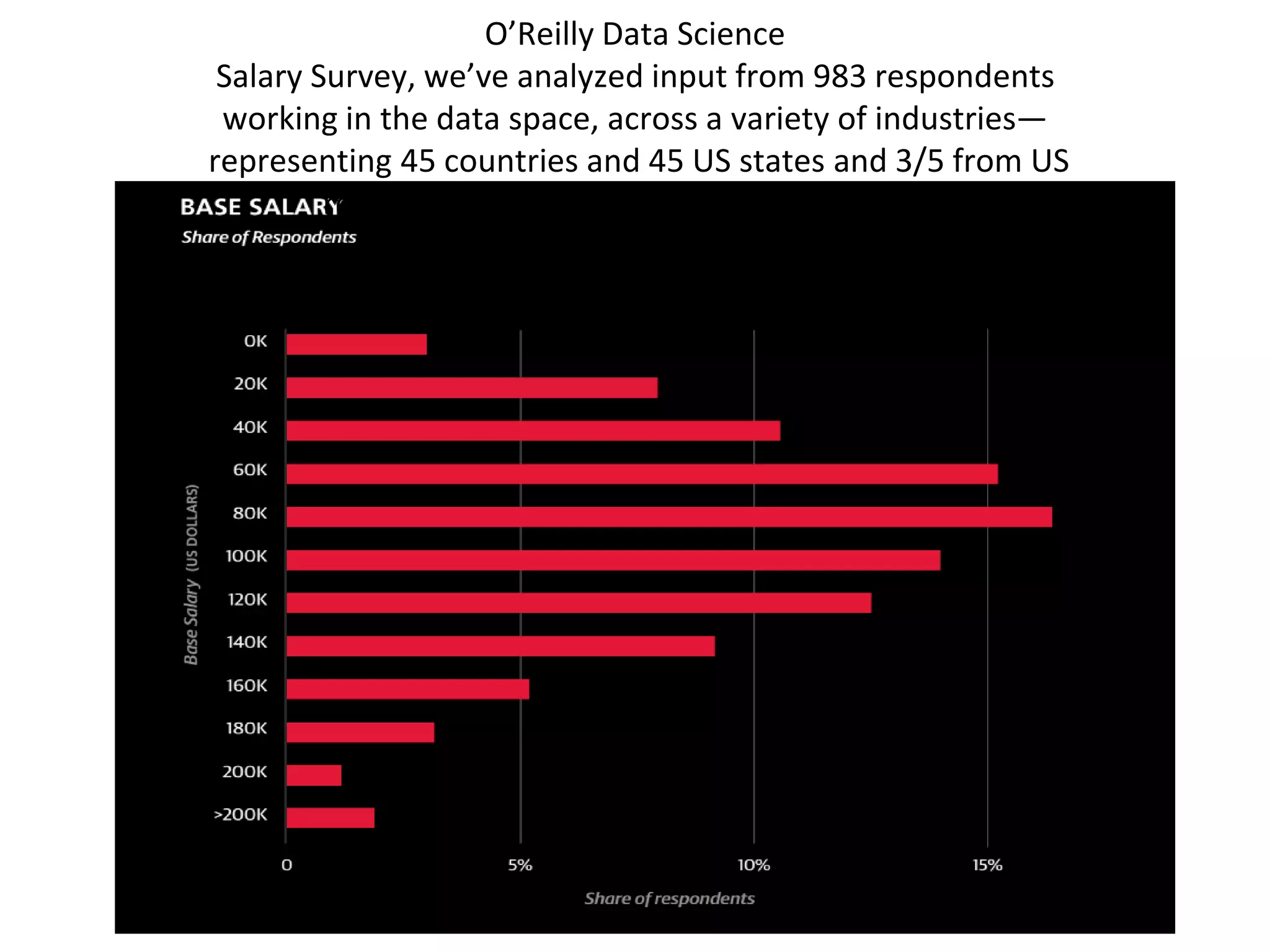
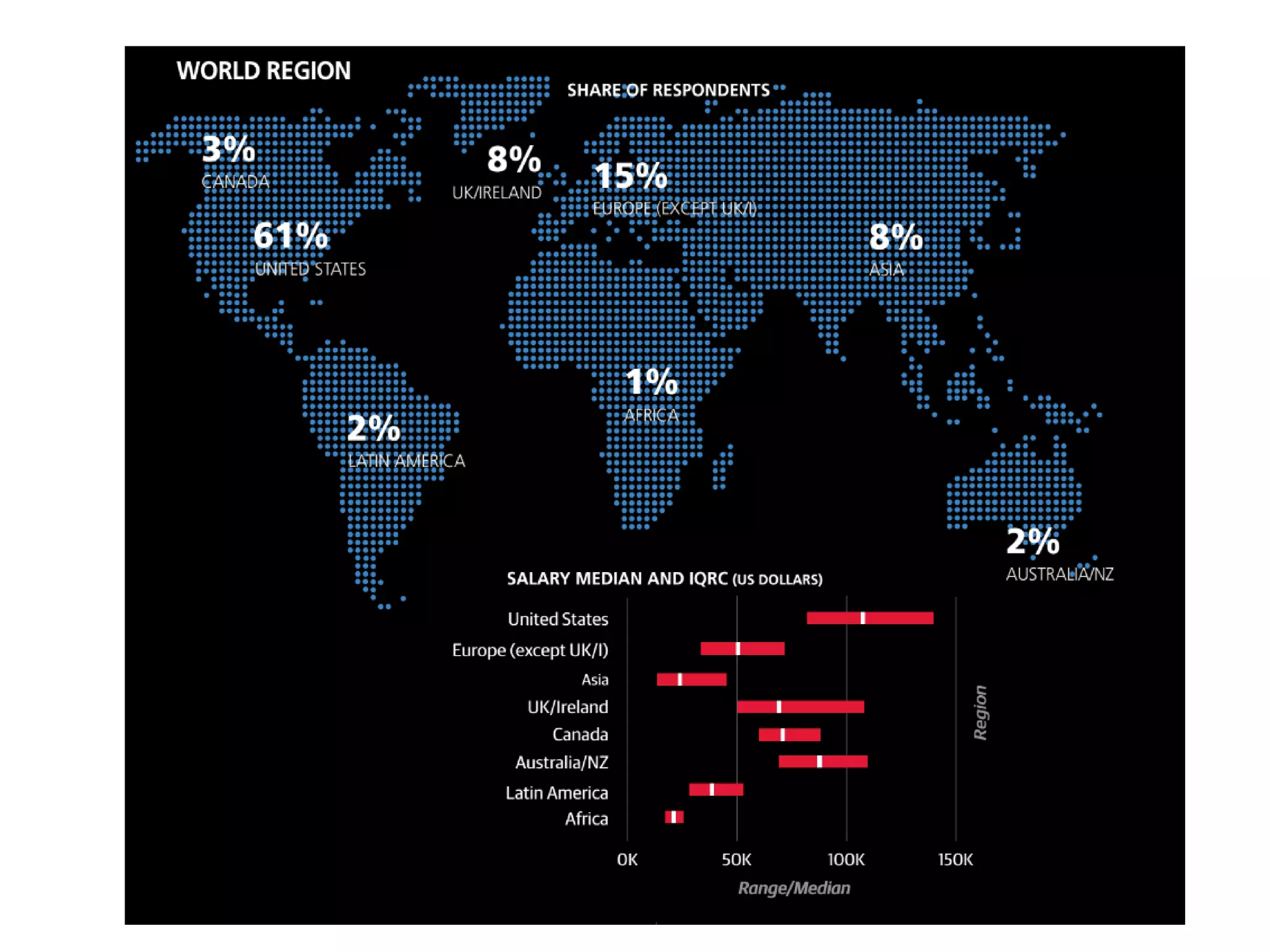
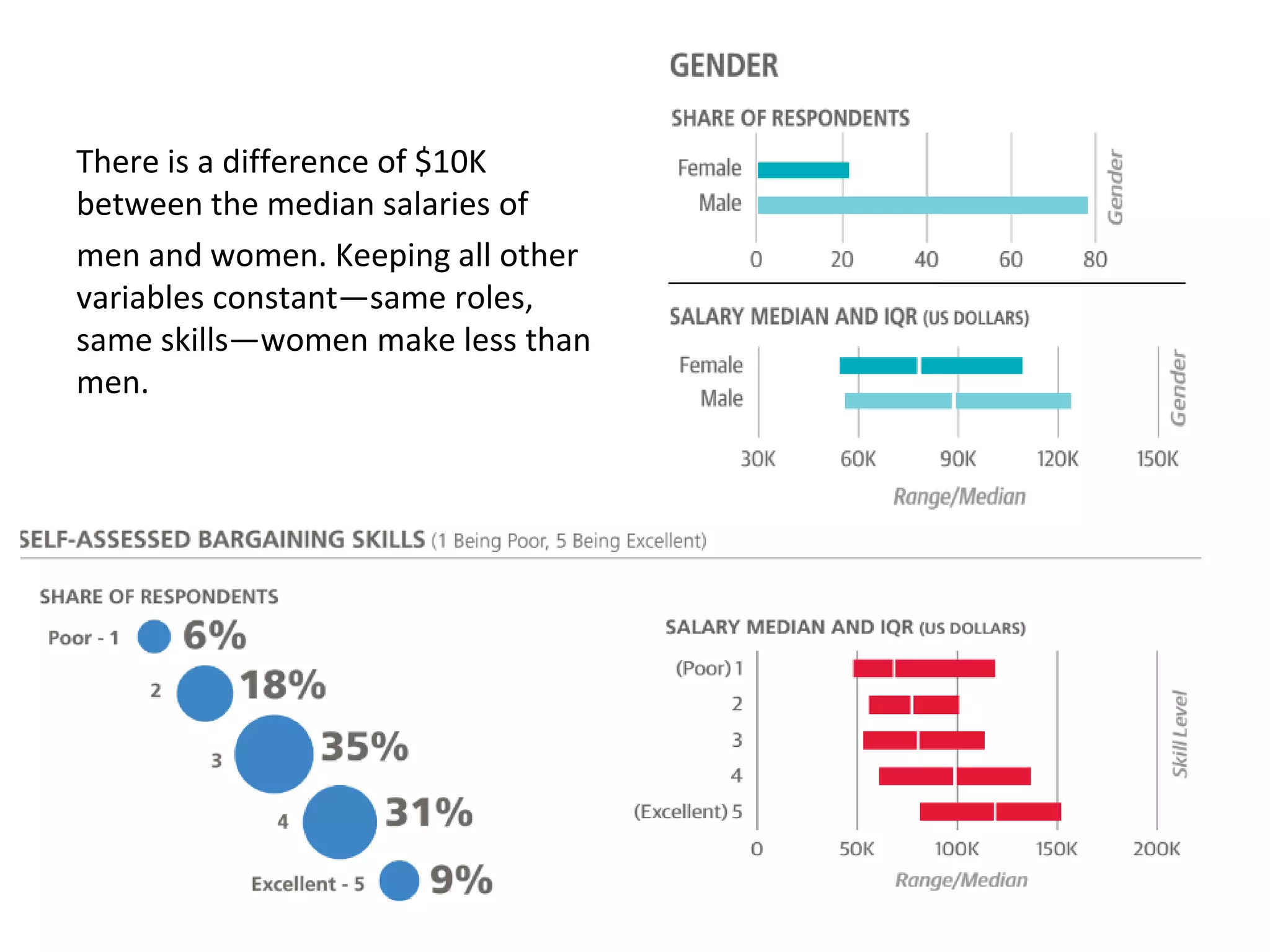
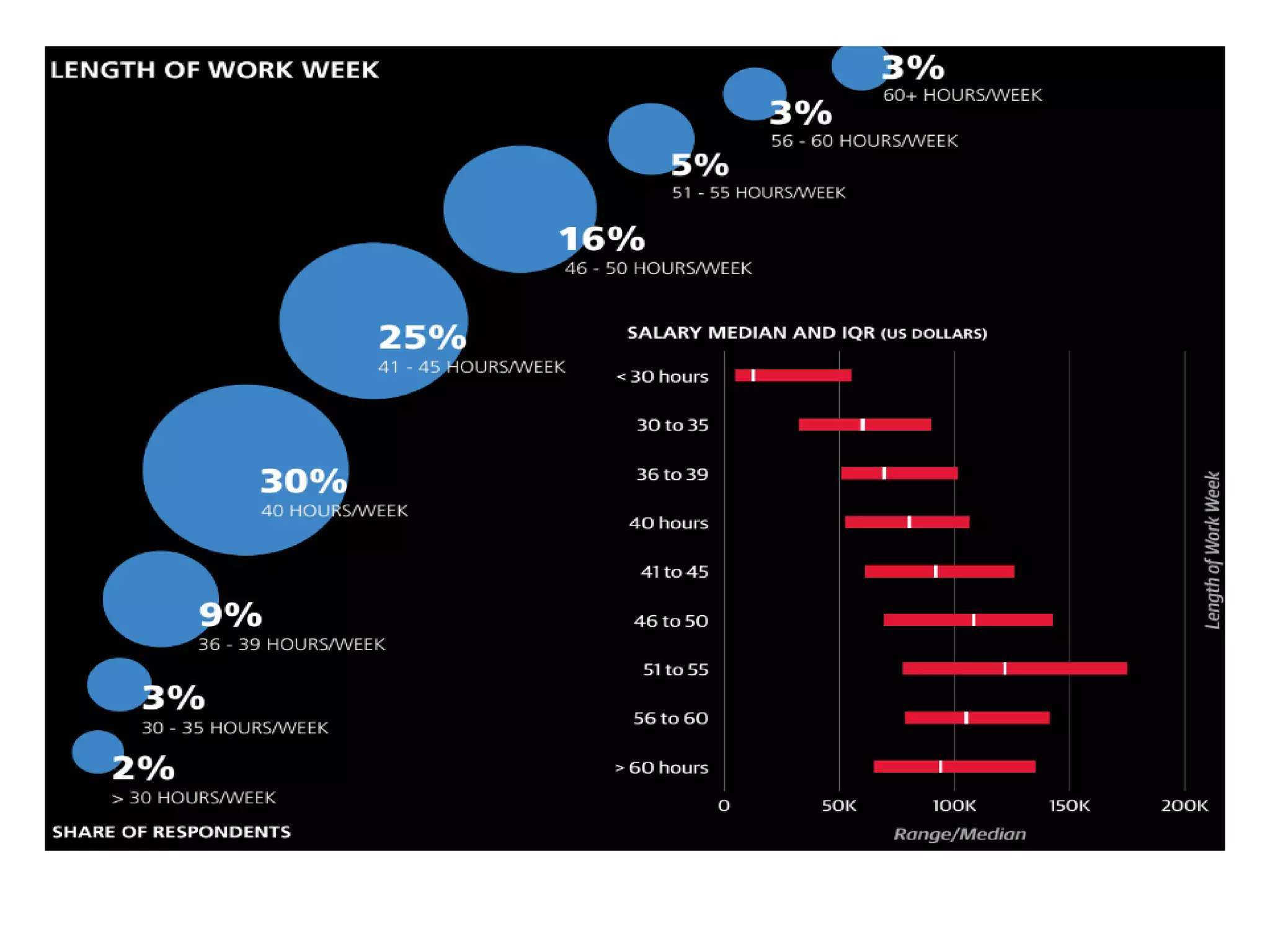
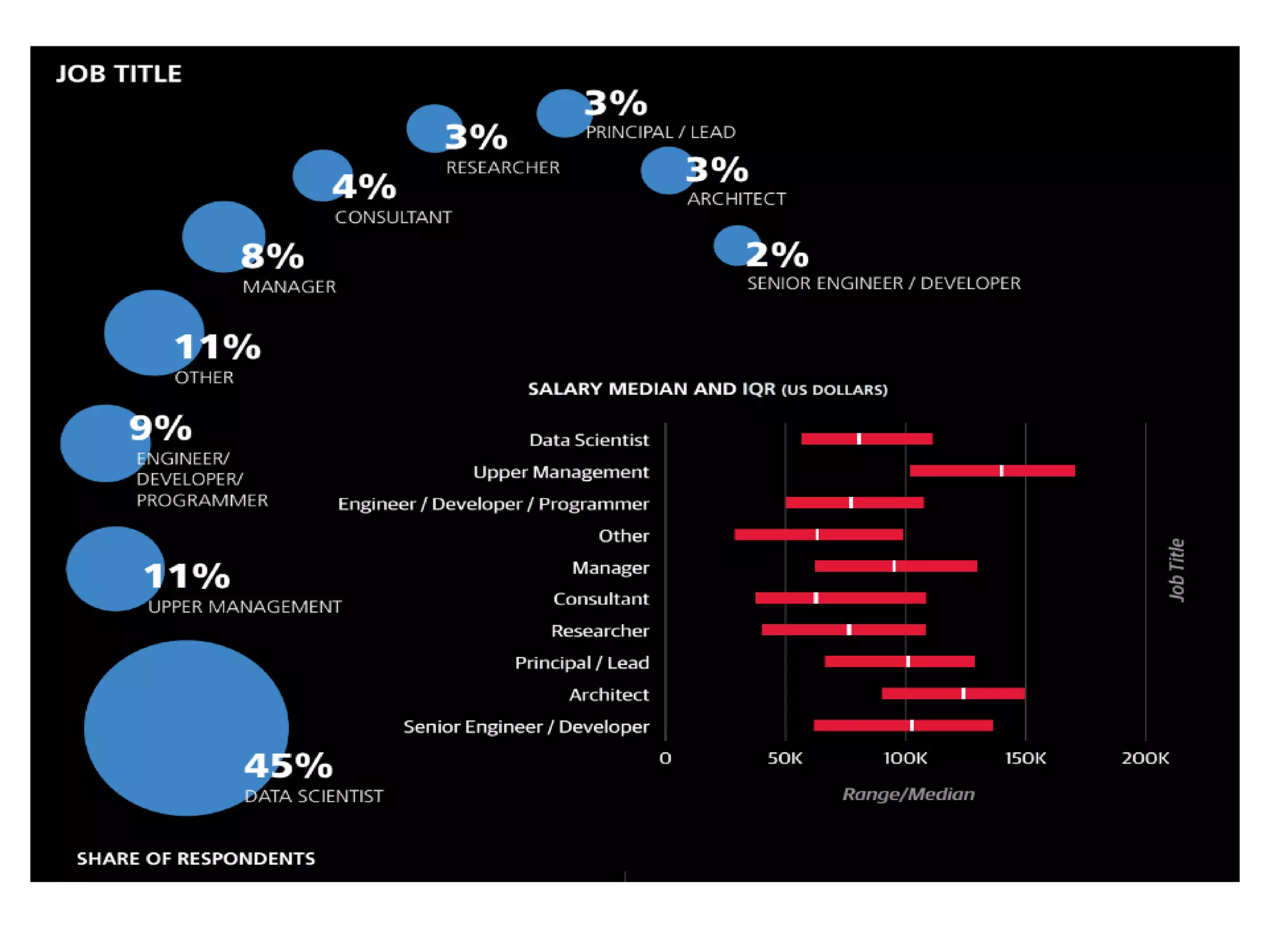
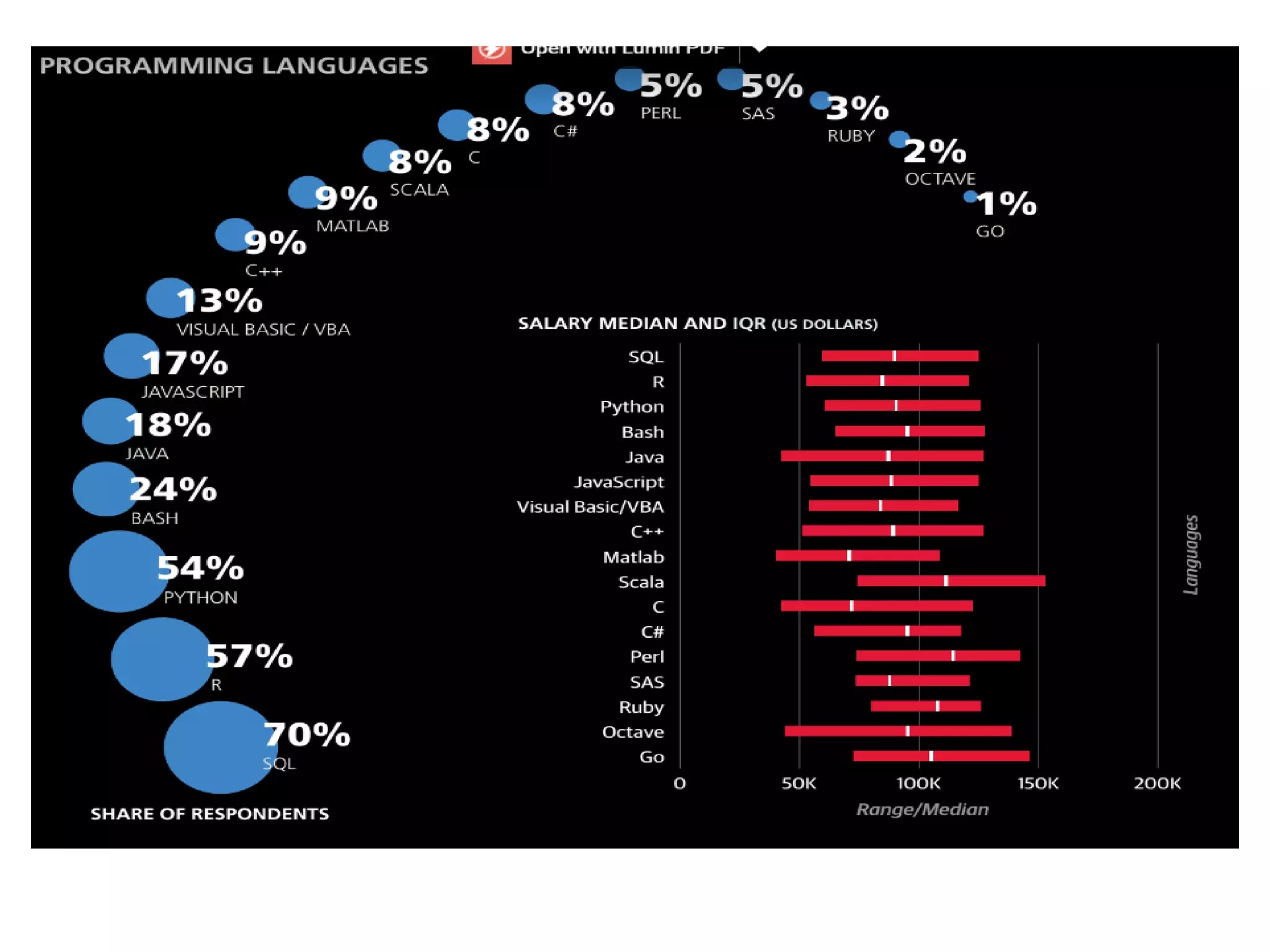
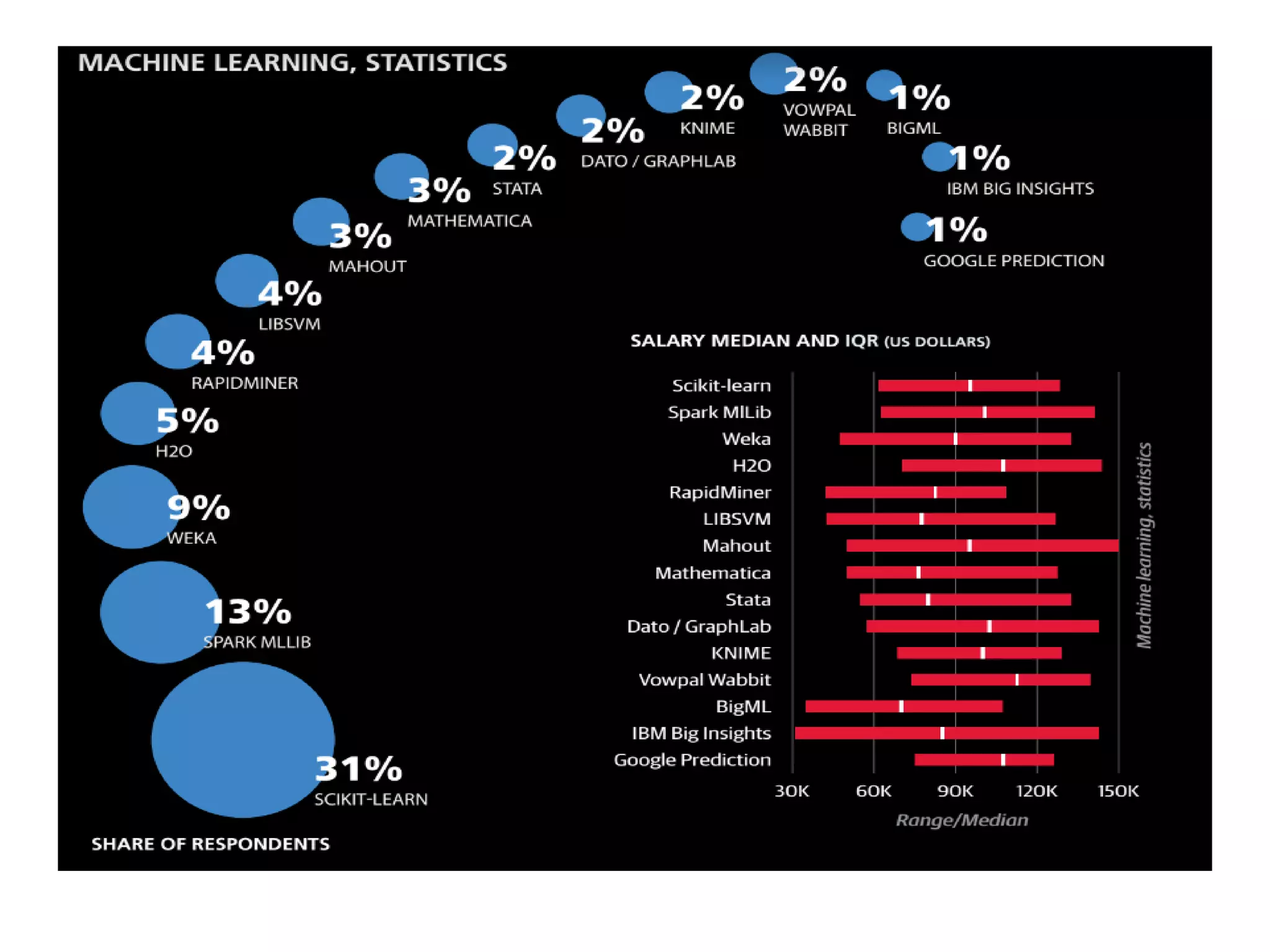
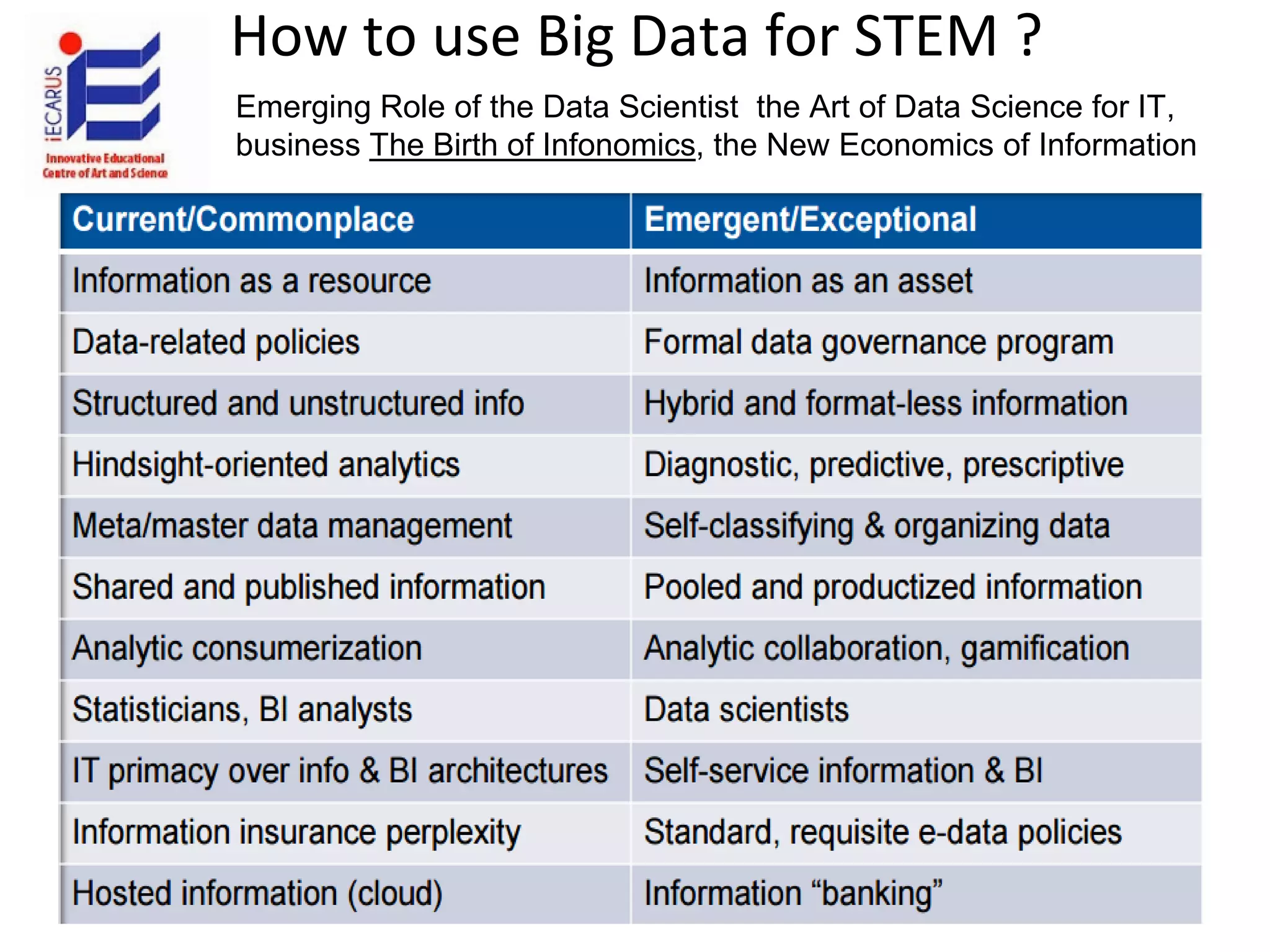
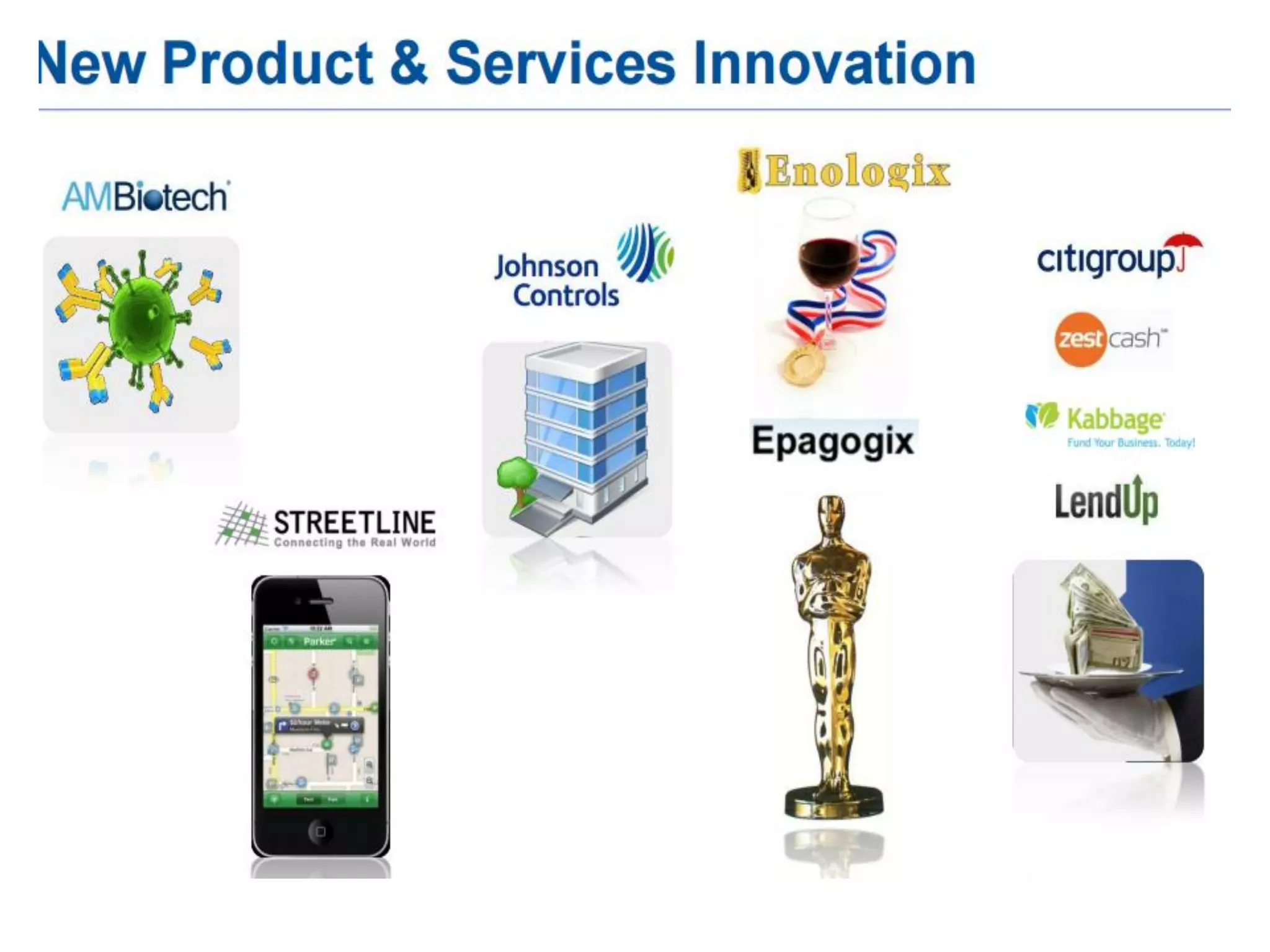
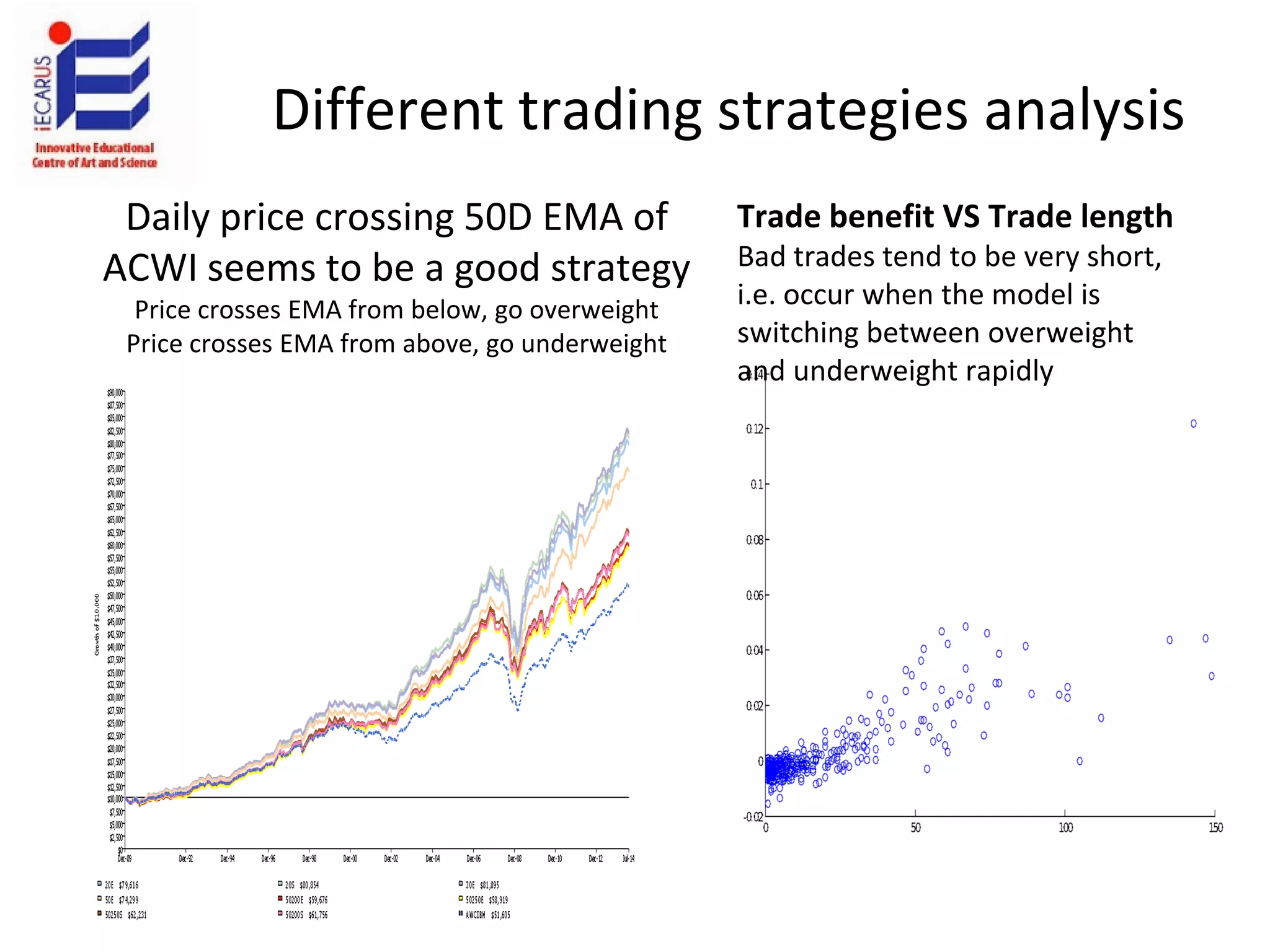
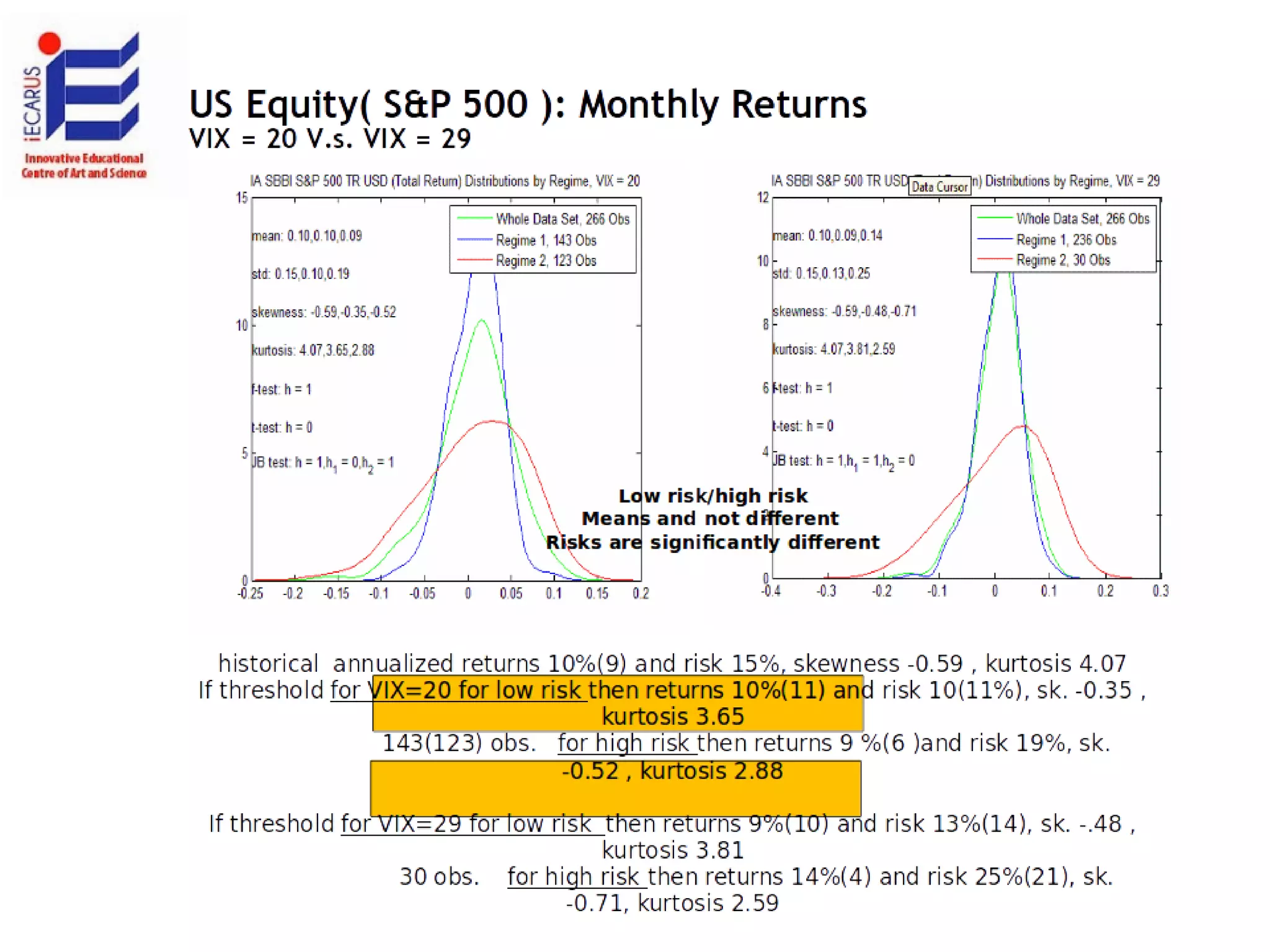
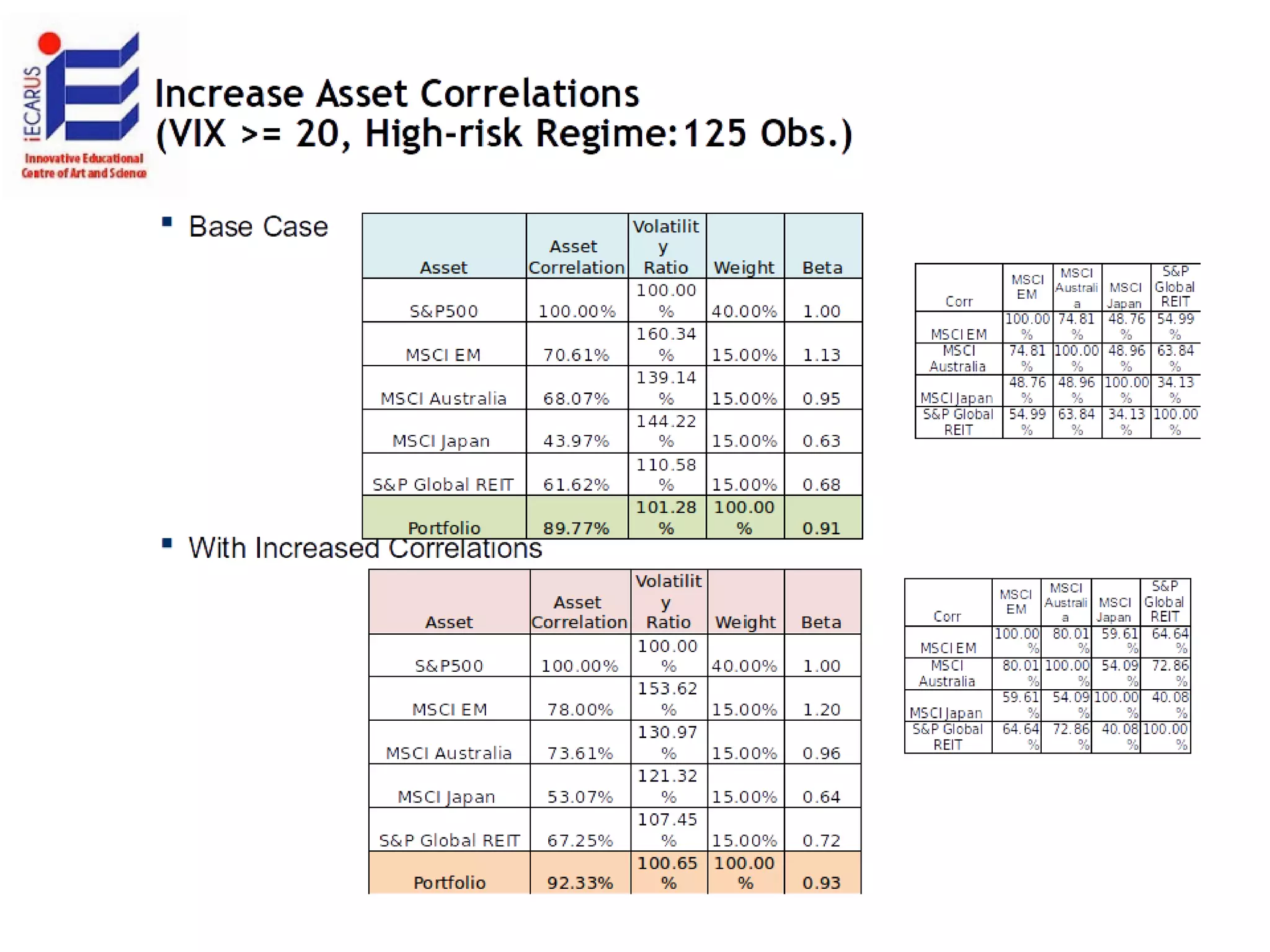
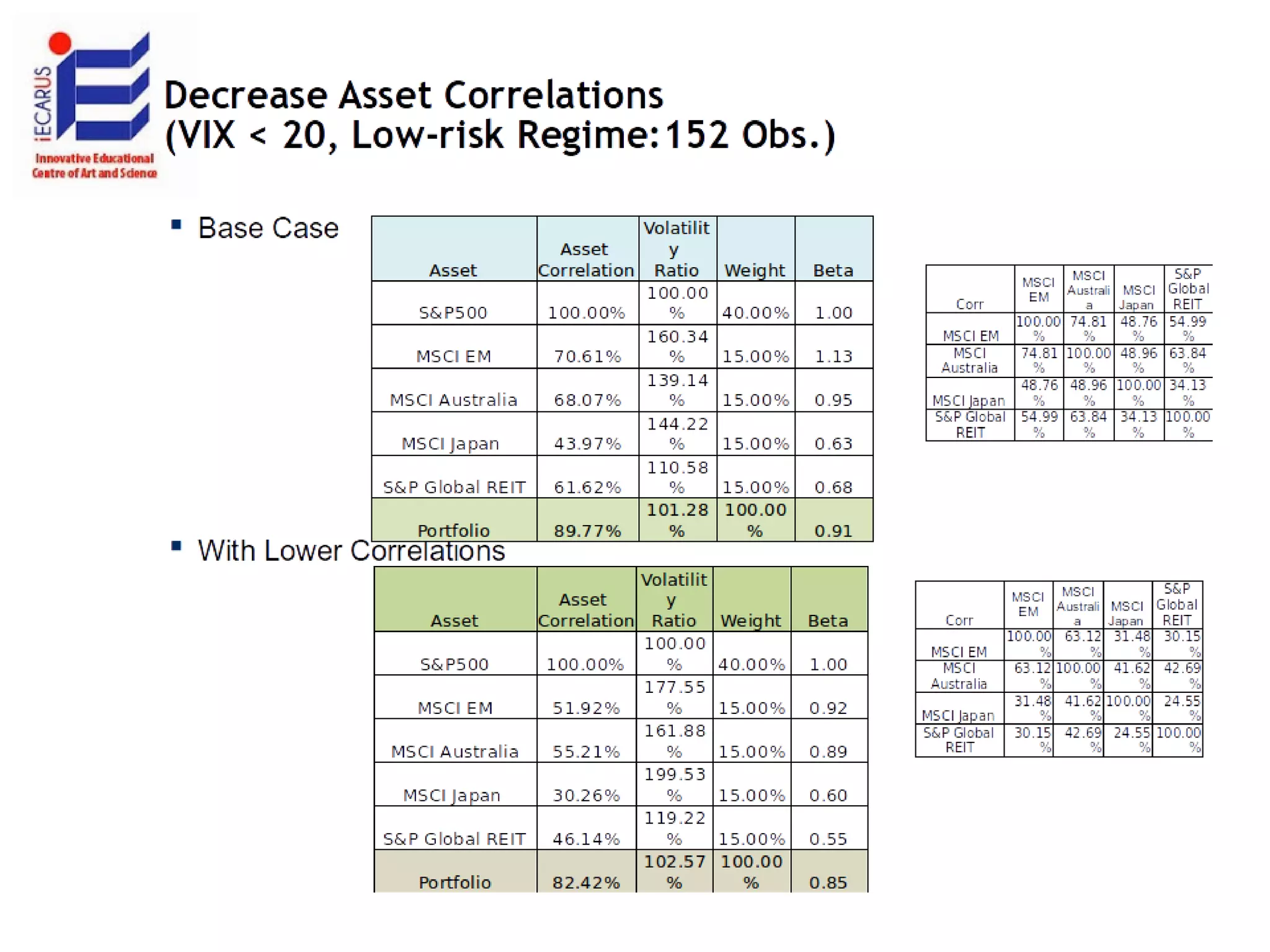
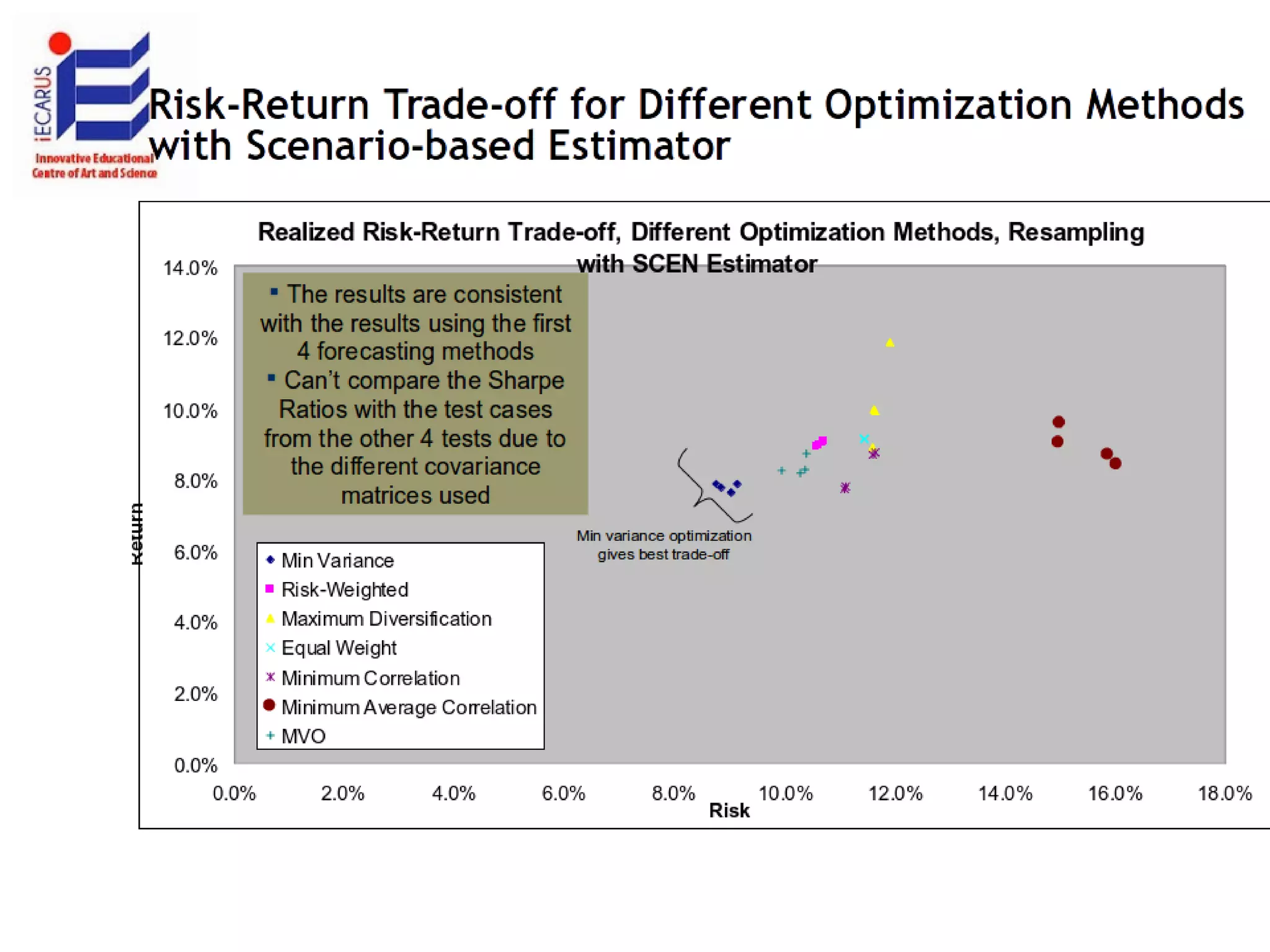
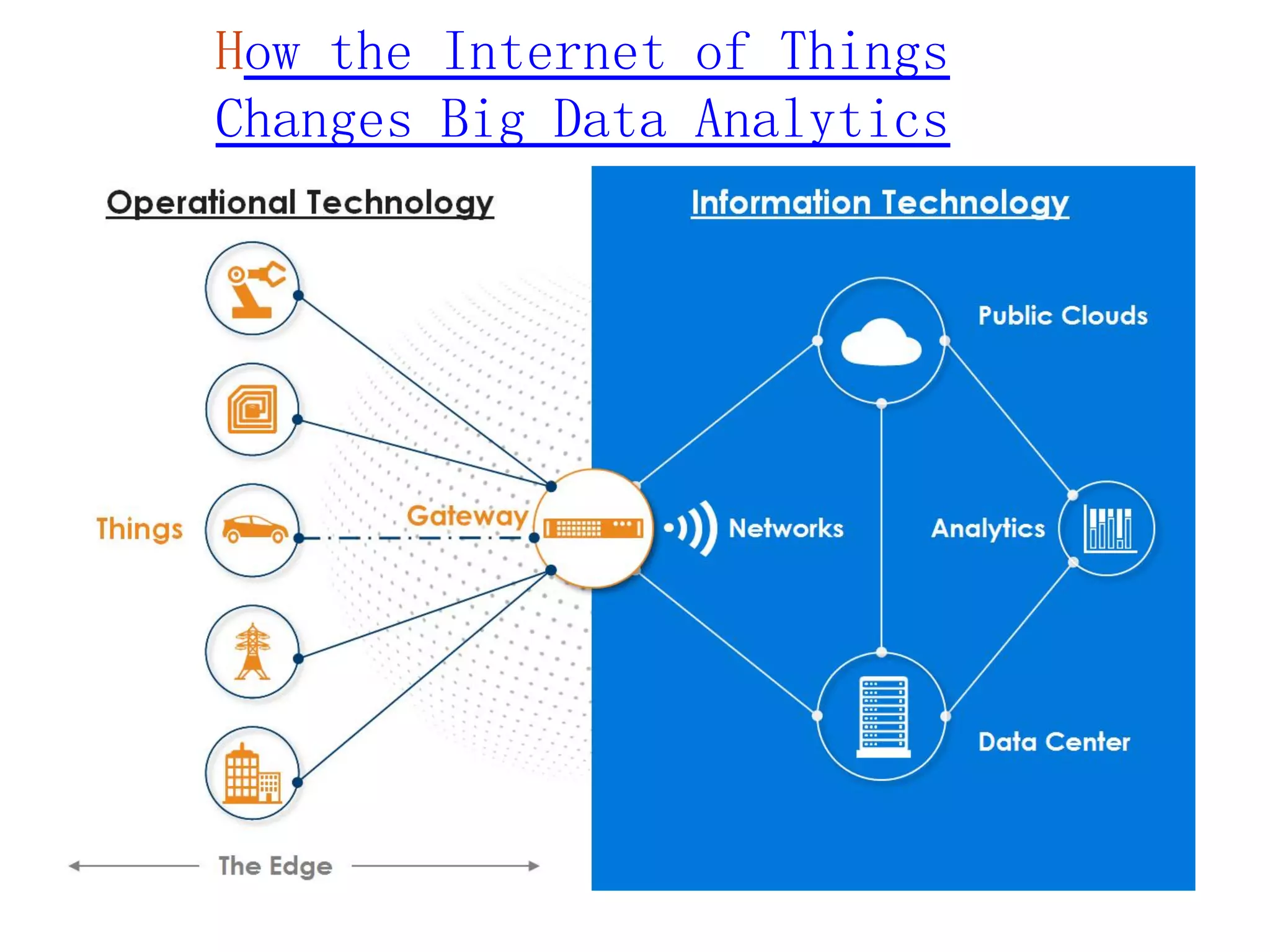
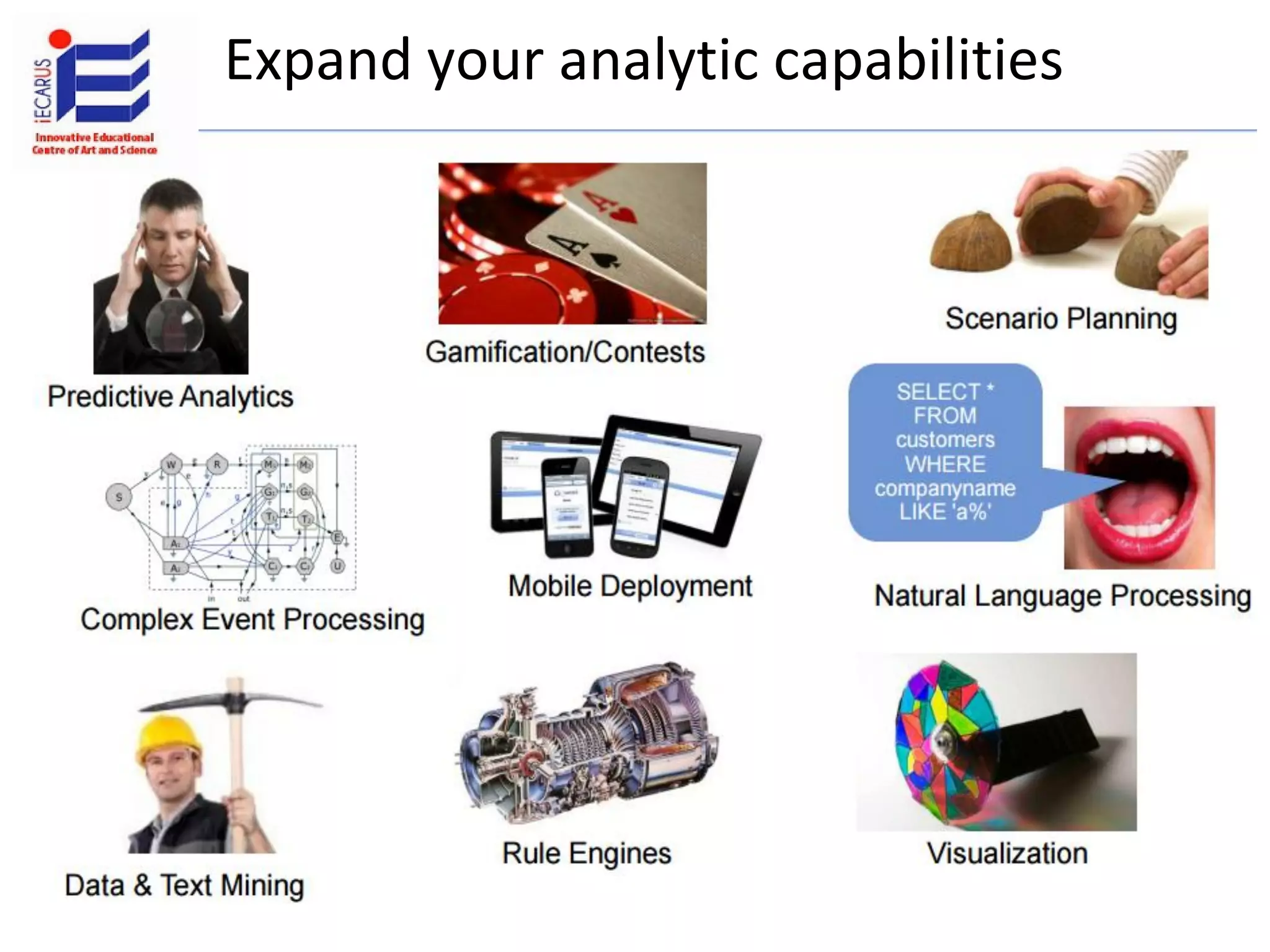
The document discusses the significance and future of big data and data science, emphasizing its role in transforming data into valuable products and insights for businesses. It highlights the evolving responsibilities of data scientists, the demand for their skills, and real-world applications of big data across various industries. Additionally, the document presents potential future scenarios for the data science field, including the integration of data science into organizational processes and the democratization of data expertise.