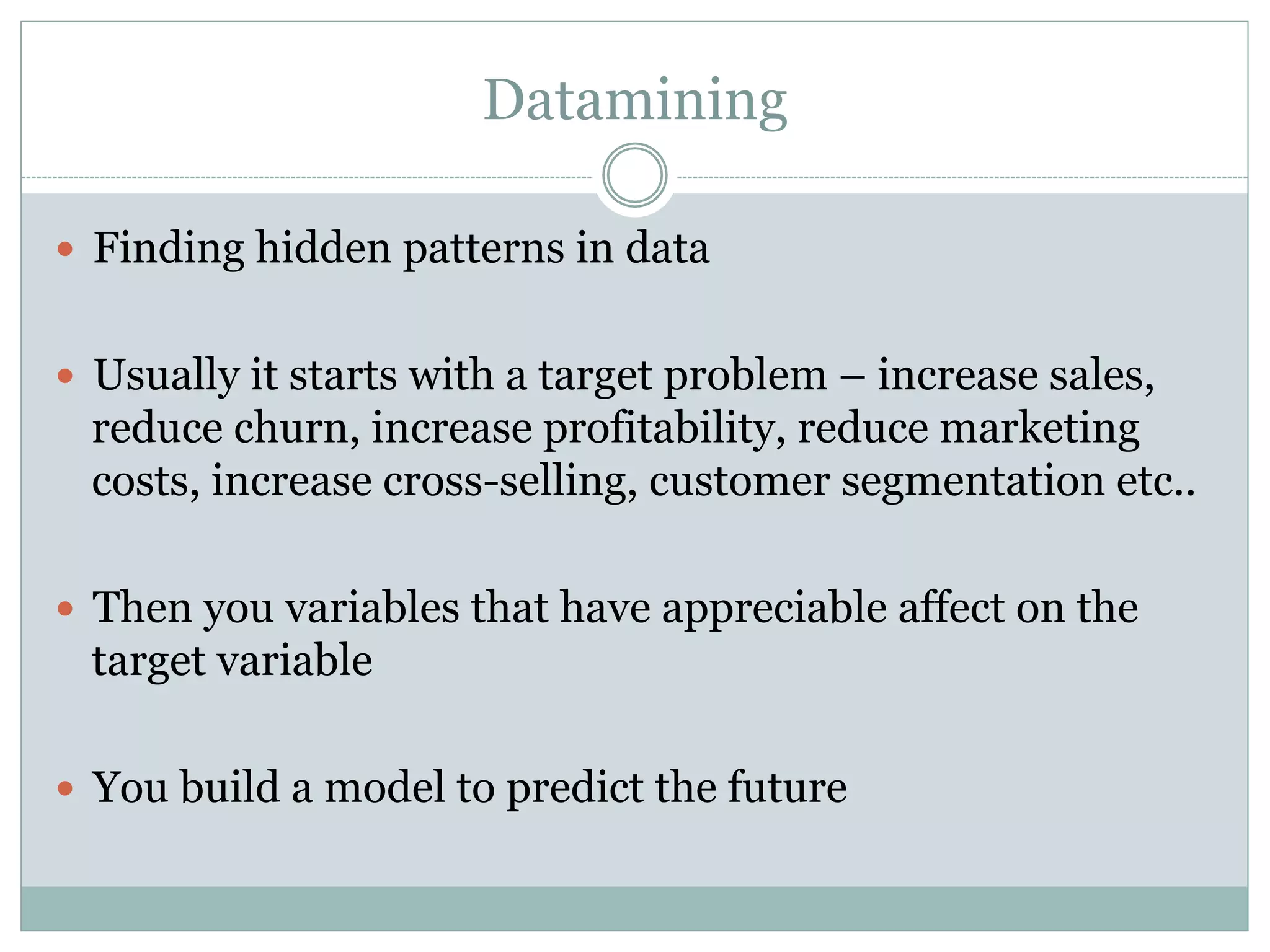
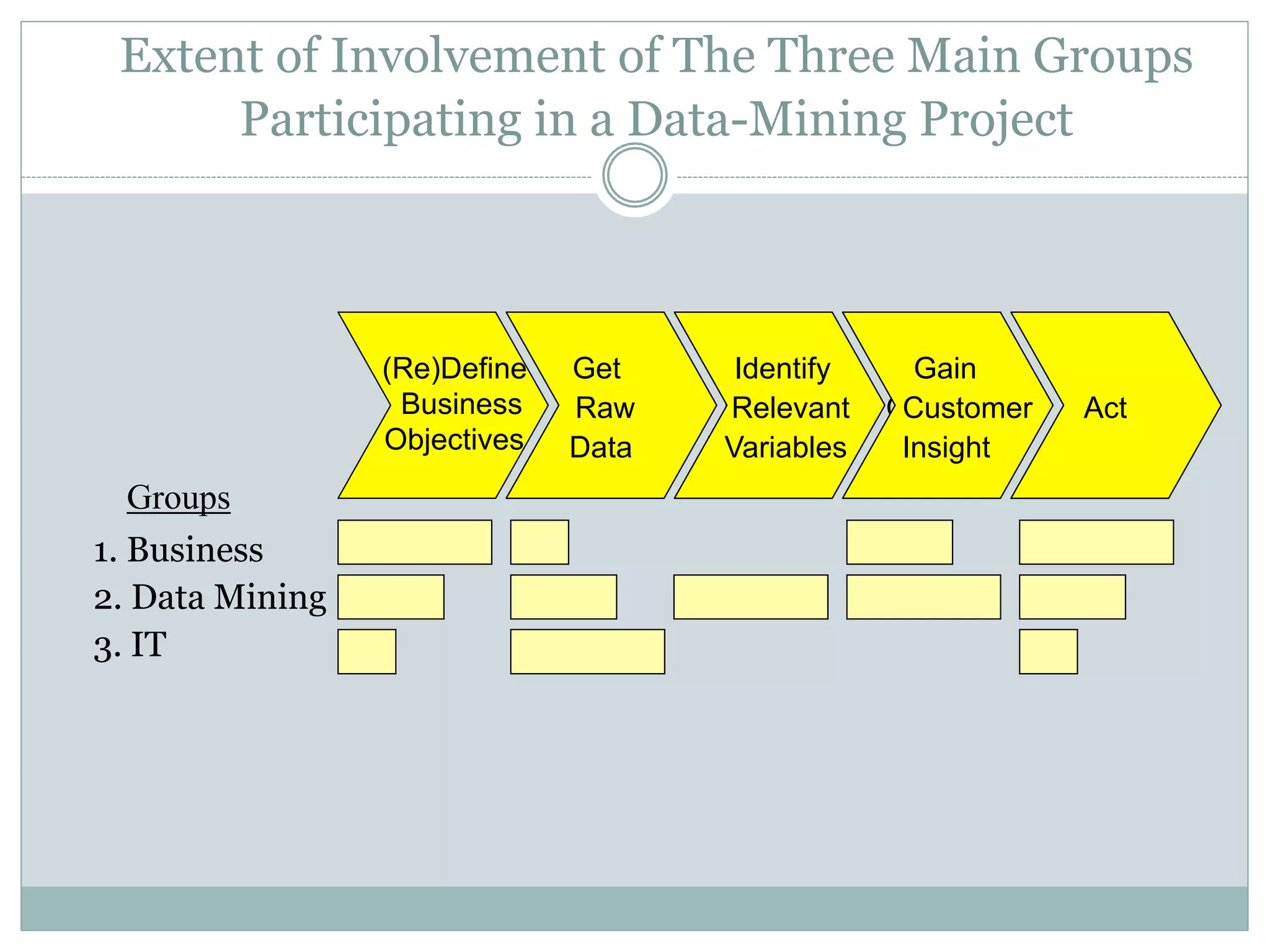
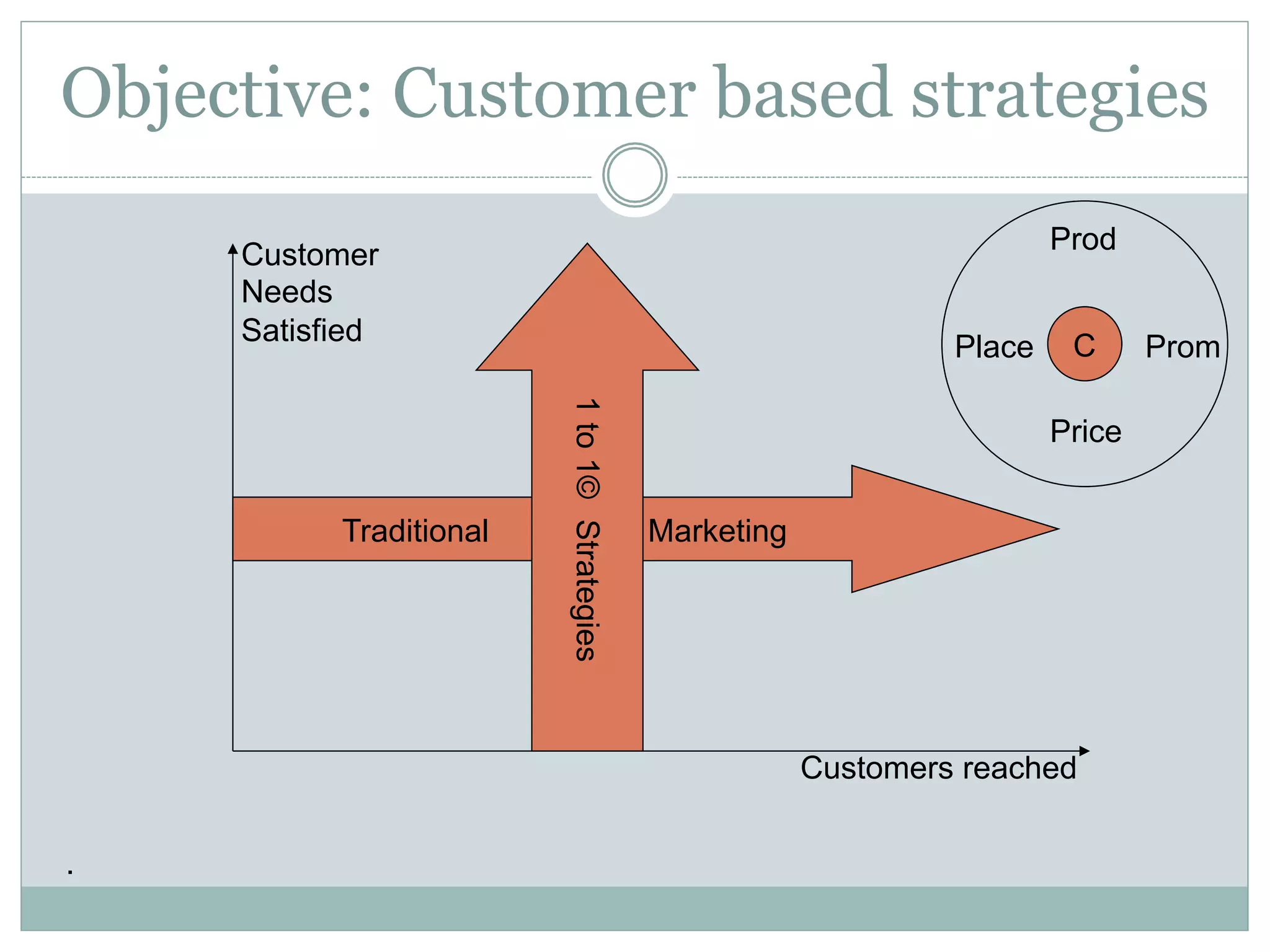
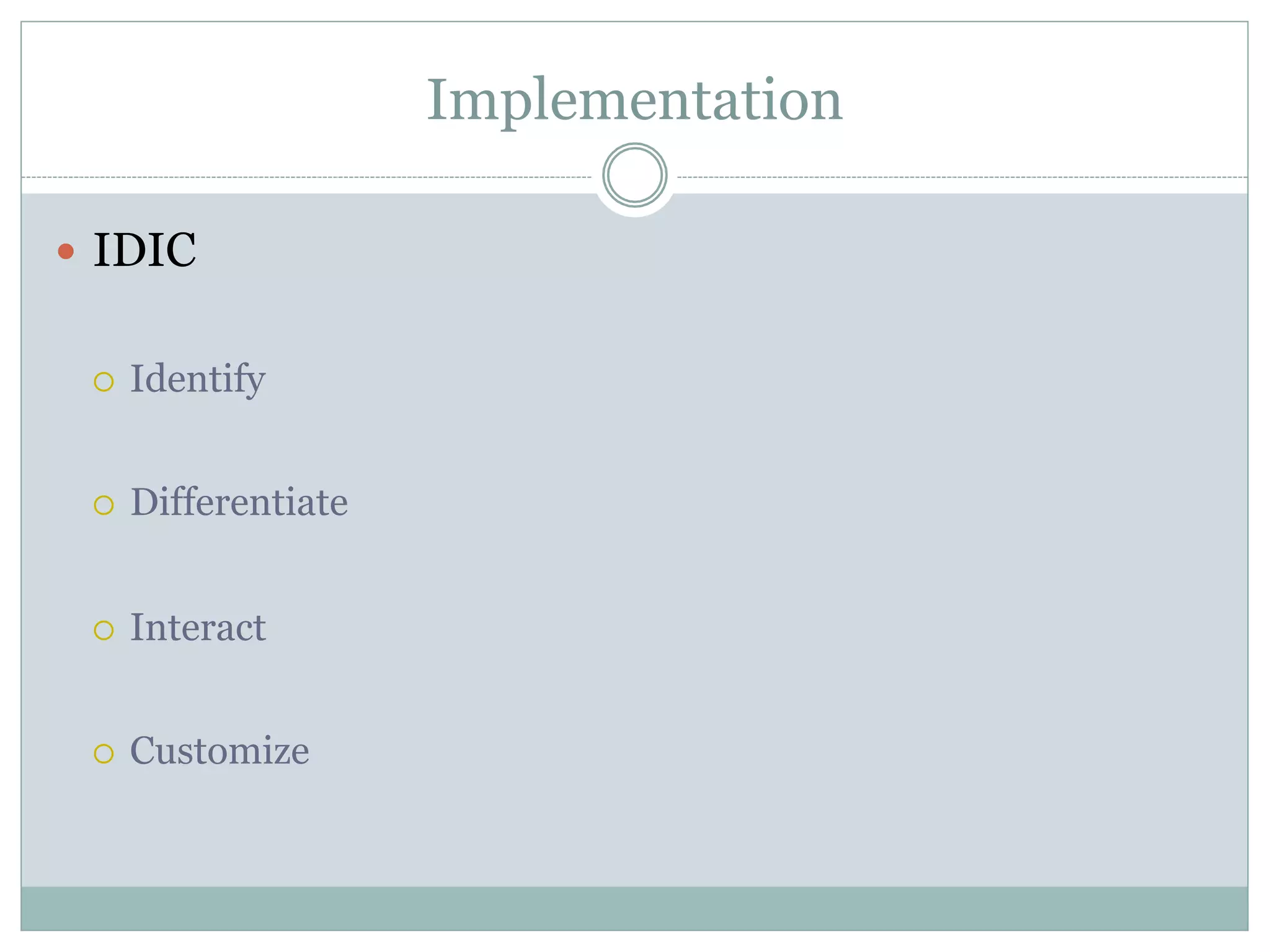
The document discusses the increasing reliance of companies on business analytics (BA) to gain a competitive edge, driven by the demand for analytical talent to translate data into actionable insights. It highlights the rapid growth of BA due to the low cost of data capture and the shift towards data-driven decision-making, emphasizing the importance of data-savvy managers. Additionally, it covers various data mining strategies used by major companies to improve customer engagement and business outcomes.