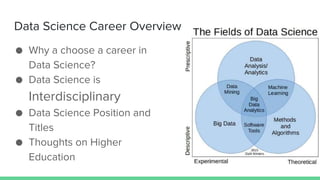
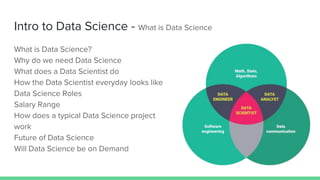
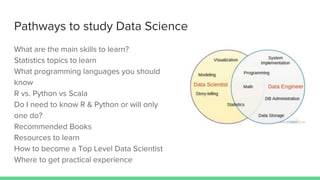
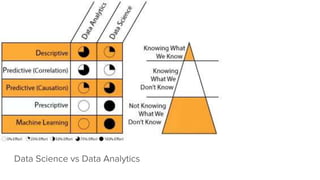
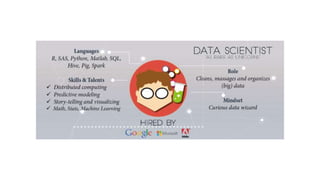
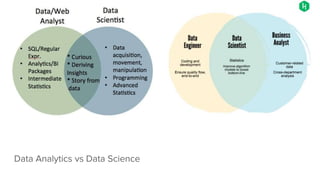
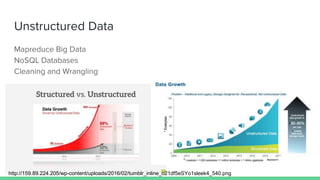
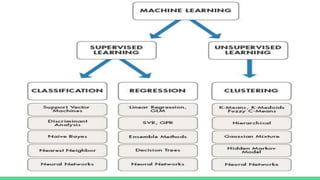
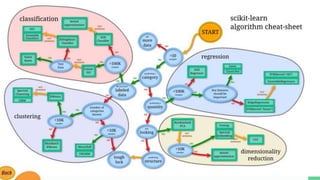
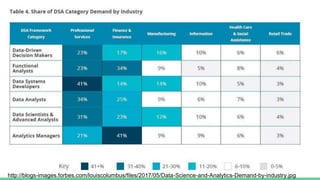
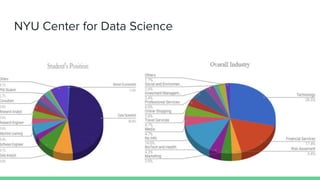
The document provides an overview of a course on careers in data science. It discusses frequently asked questions about the field, the job market and demand for data scientists. It defines the roles of data scientists and how their day-to-day work and responsibilities differ from data analysts and business intelligence professionals. The document also addresses prerequisites for becoming a data scientist, recommended skills to learn, and pathways for gaining practical experience in the field.