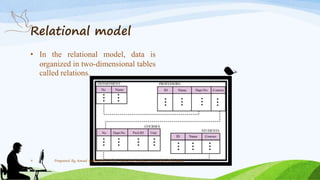
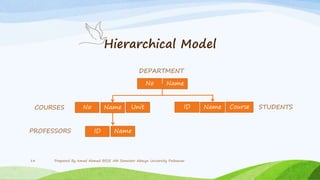
This document discusses different types of data models used in database management systems (DBMS), including record-based, relational, network, hierarchical, and entity-relationship (ER) models. It provides an overview of key concepts like data, information, databases, and data models. For each model type, it describes how data is organized and represented. For example, it explains that the relational model organizes data into two-dimensional tables with attributes and tuples, while the hierarchical model structures data in a tree configuration. The ER model views data as entities and relationships between entities.