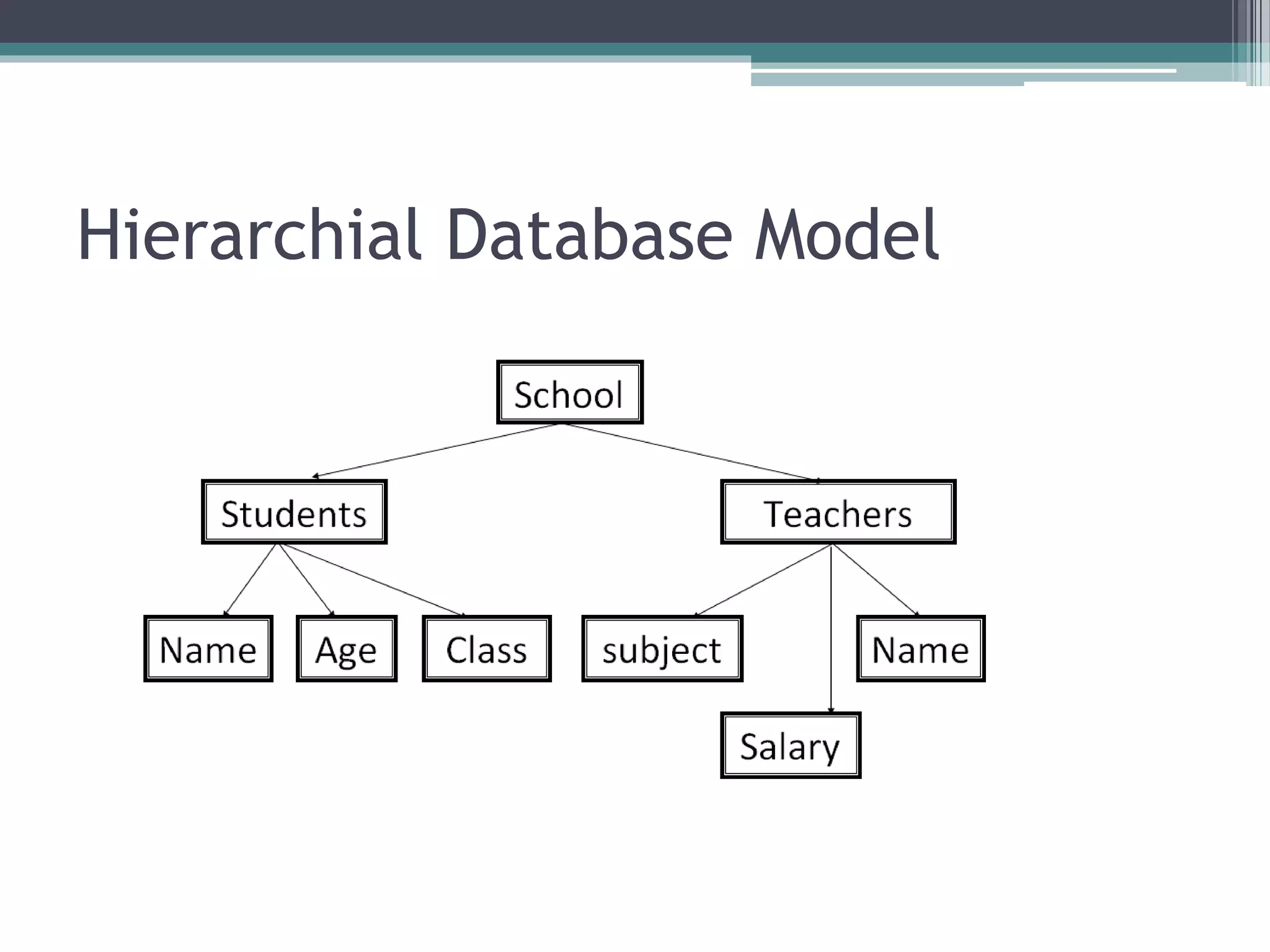
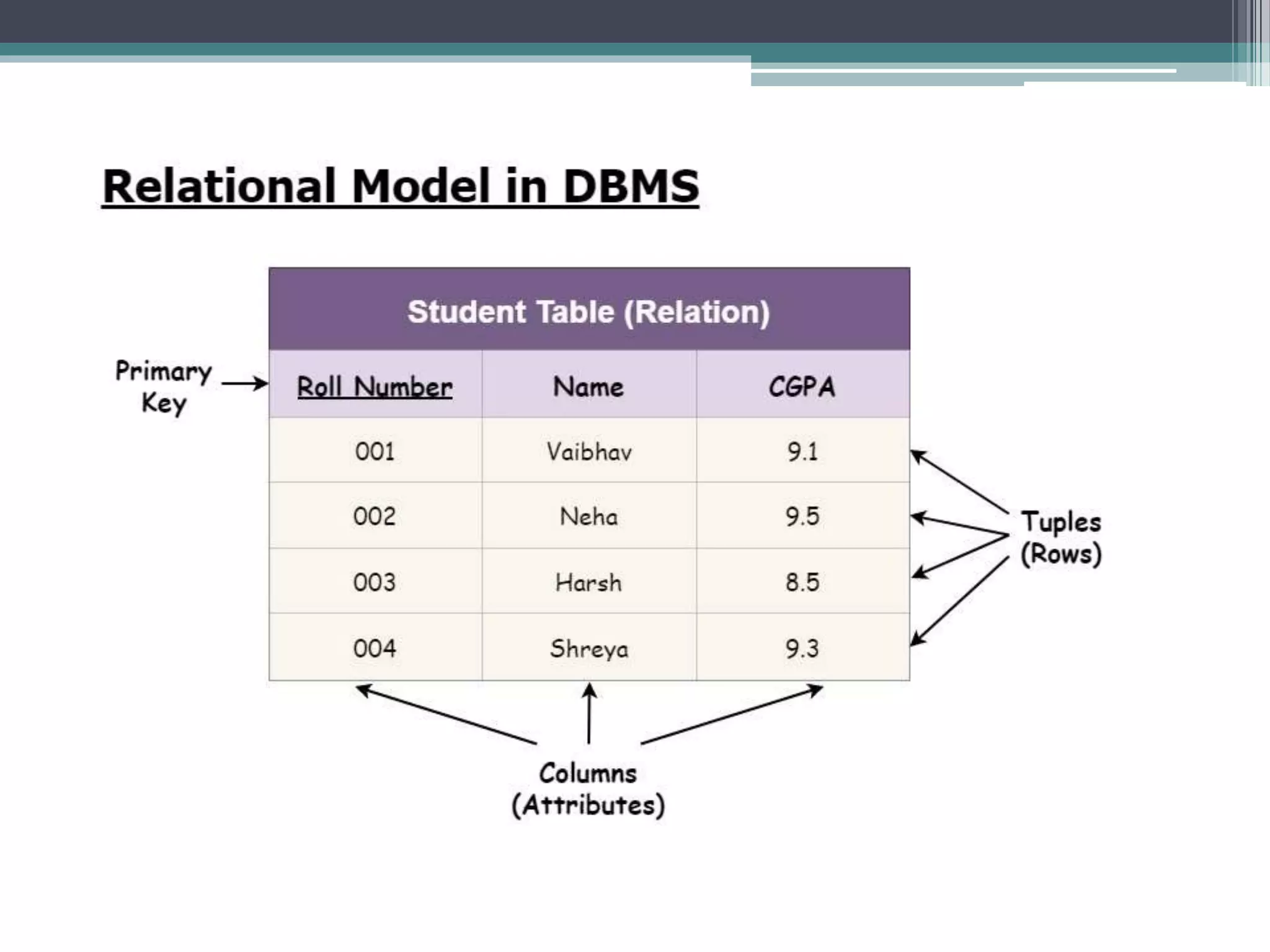
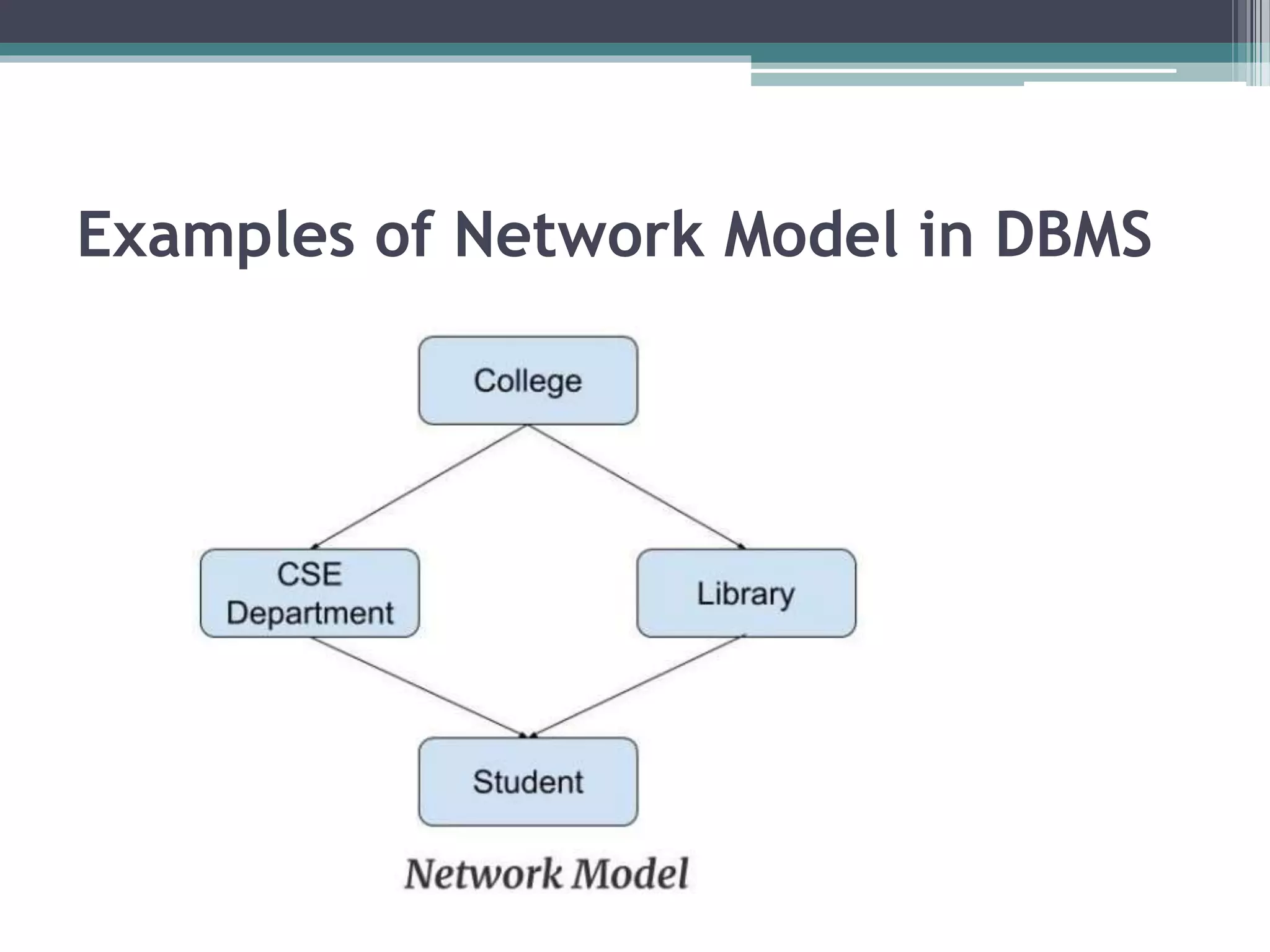
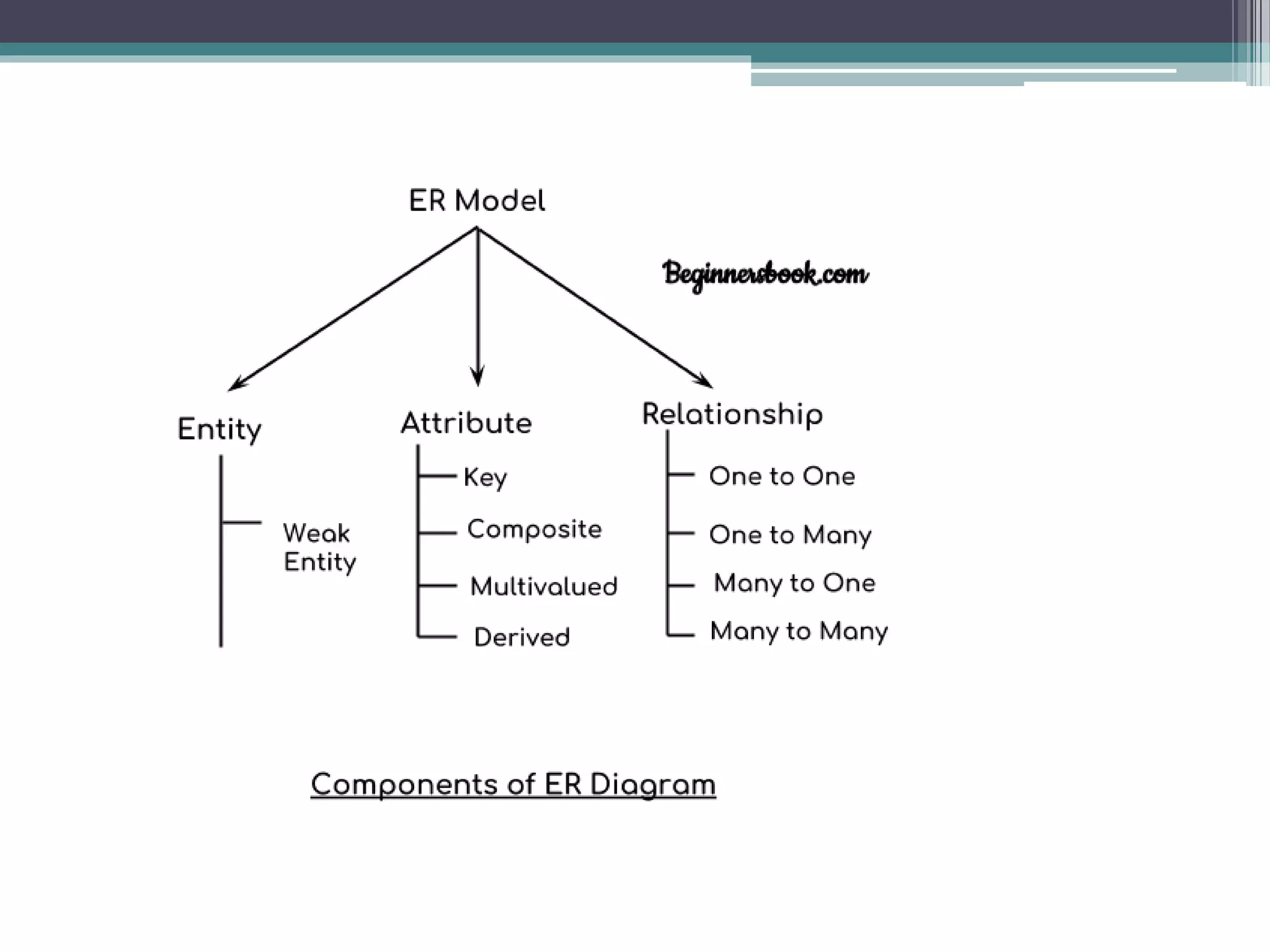
The document discusses different types of database models including relational, hierarchical, network, and entity-relationship models. The hierarchical model stores data in a tree-like structure, with parent-child relationships, while the network model represents many-to-many relationships in a graph structure. The relational model stores data in tables and defines important concepts like attributes, tuples, and columns. The entity-relationship model diagrams entities, attributes, and the relationships between entities.