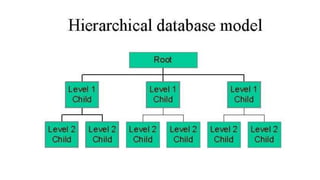
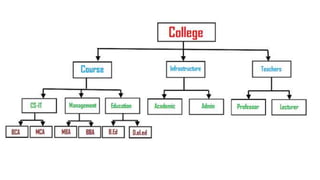
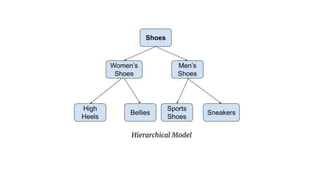
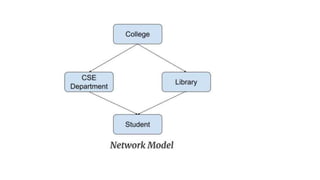
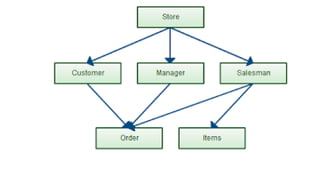
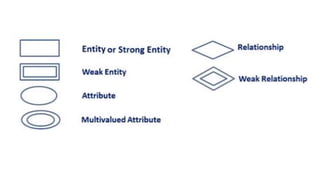
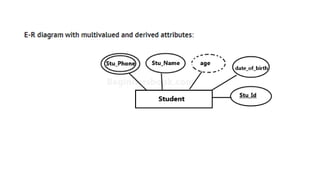
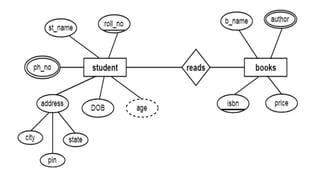
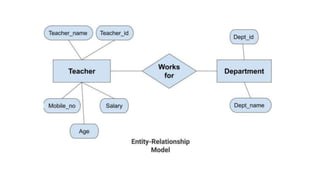
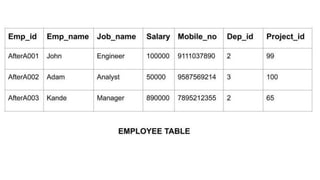
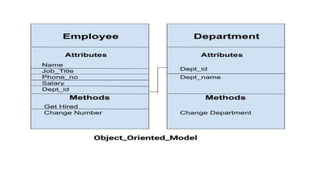
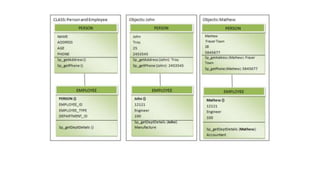
The document discusses different data models including hierarchical, network, entity-relationship, relational, and object-oriented models. It provides details on each model such as their structure, advantages, and disadvantages. The hierarchical model organizes data in a tree structure while the network model extends the hierarchical model by allowing a record to have more than one parent. The entity-relationship model represents data using entities, attributes, and relationships. The relational model stores data in tables and relations. Finally, the object-oriented model represents both data and relationships within a single object structure.