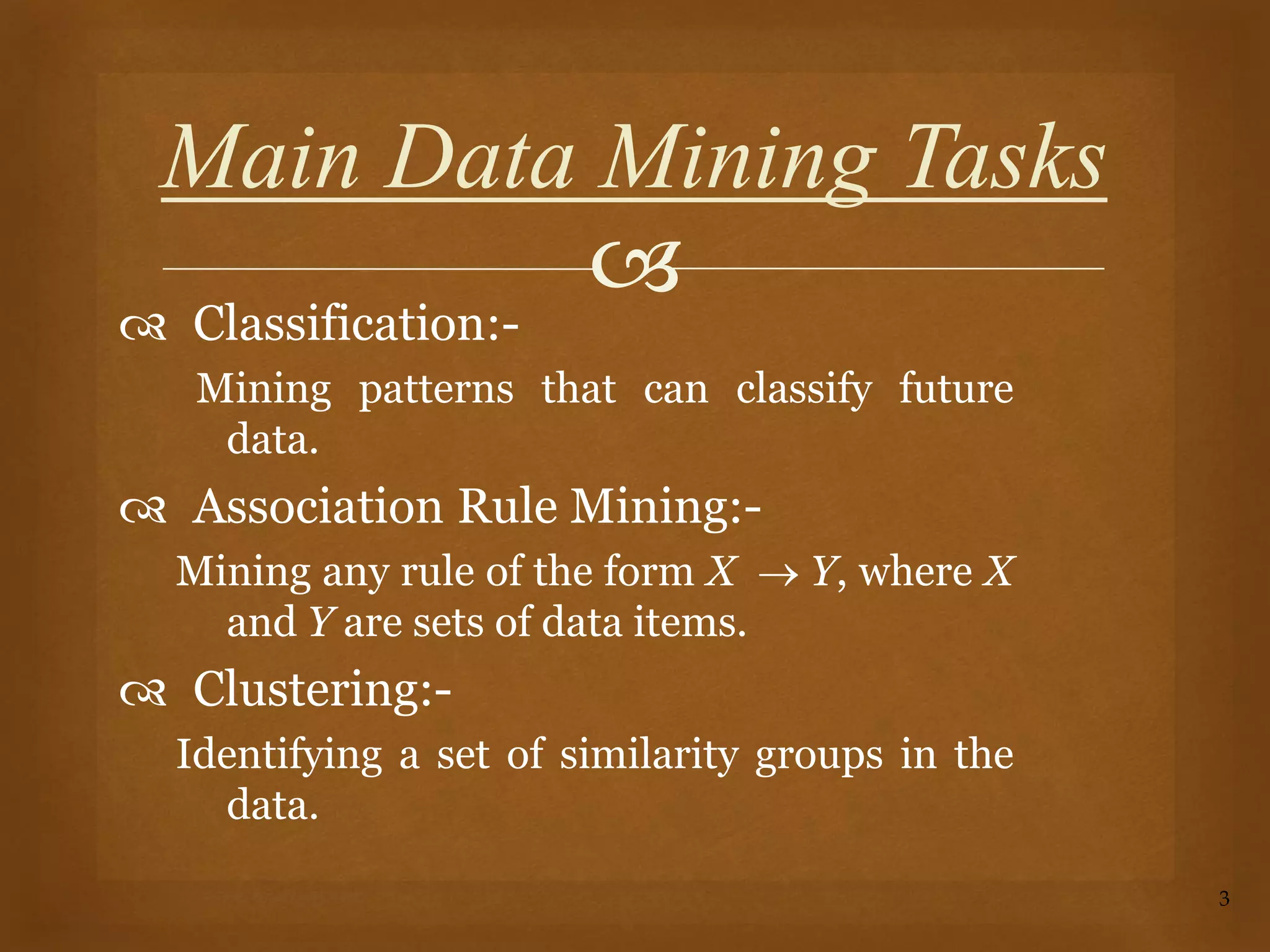
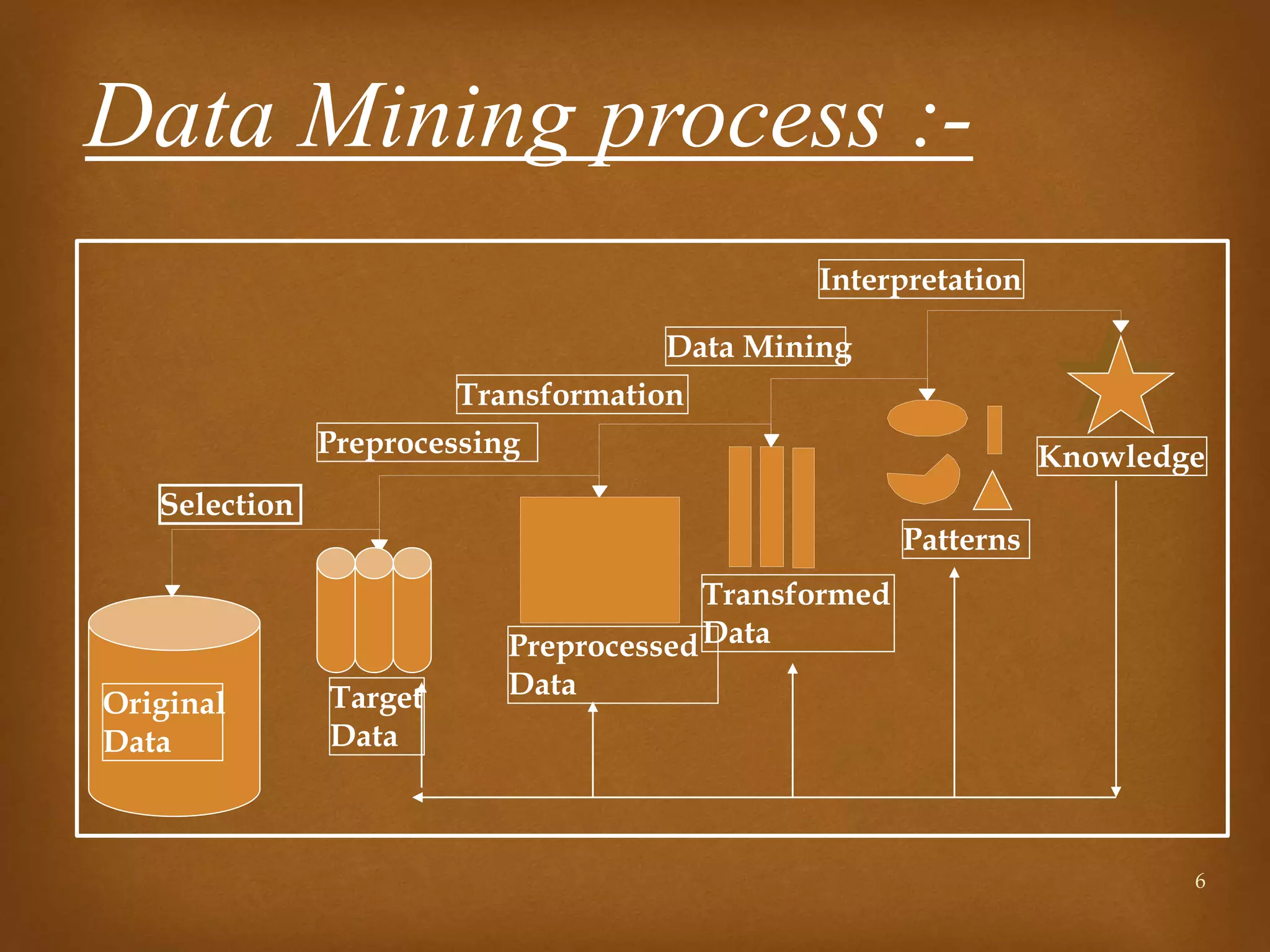
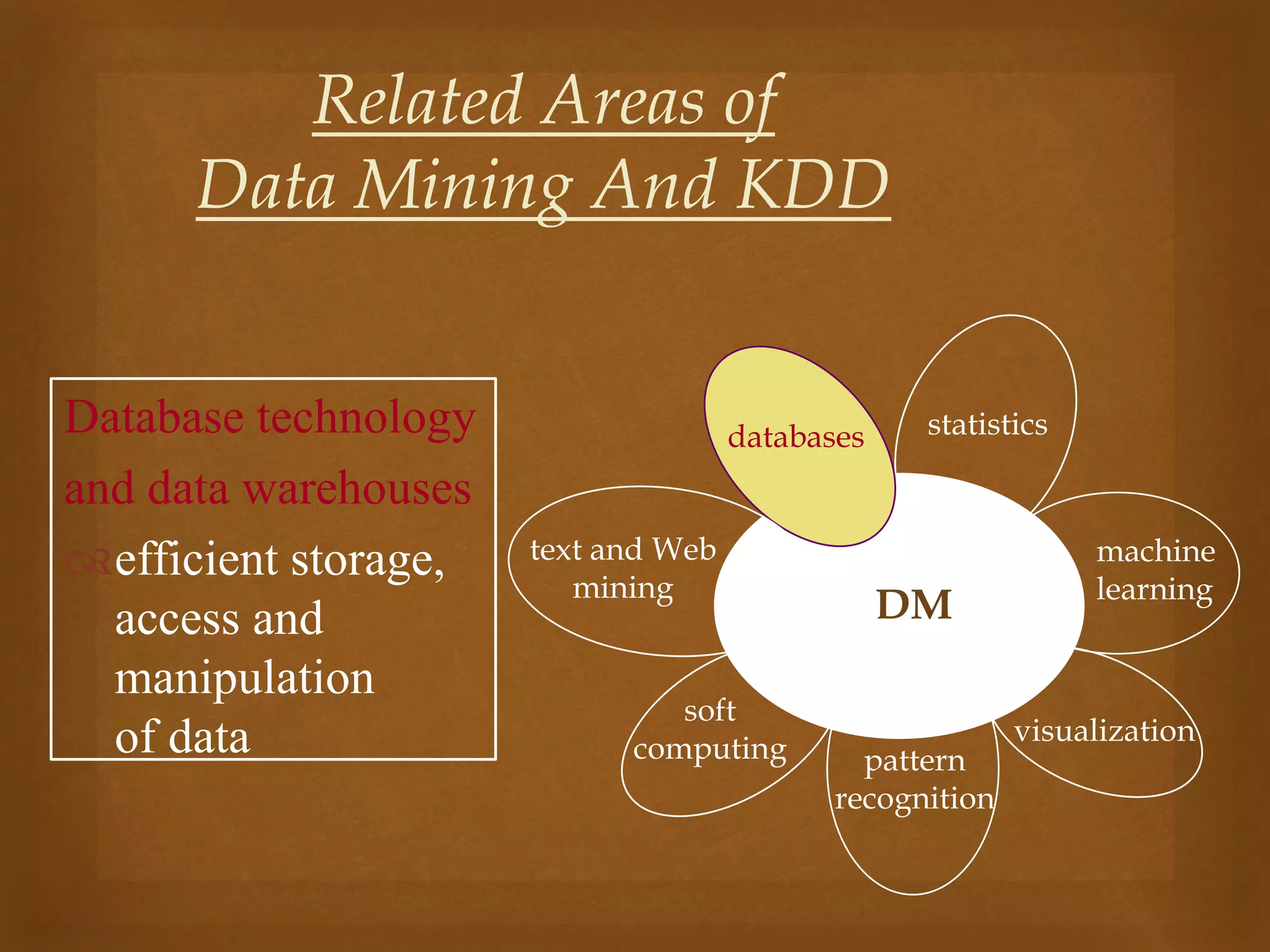
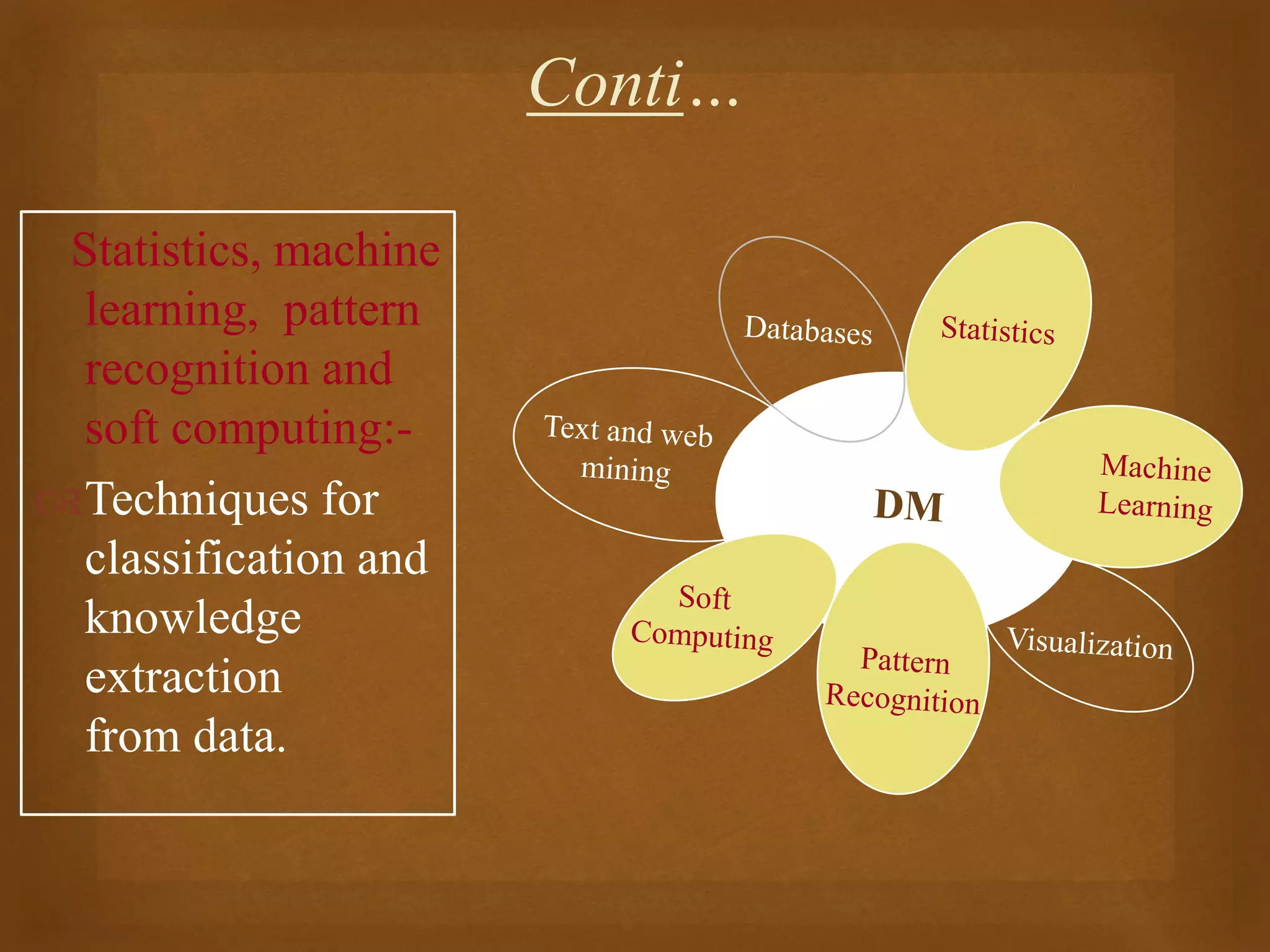
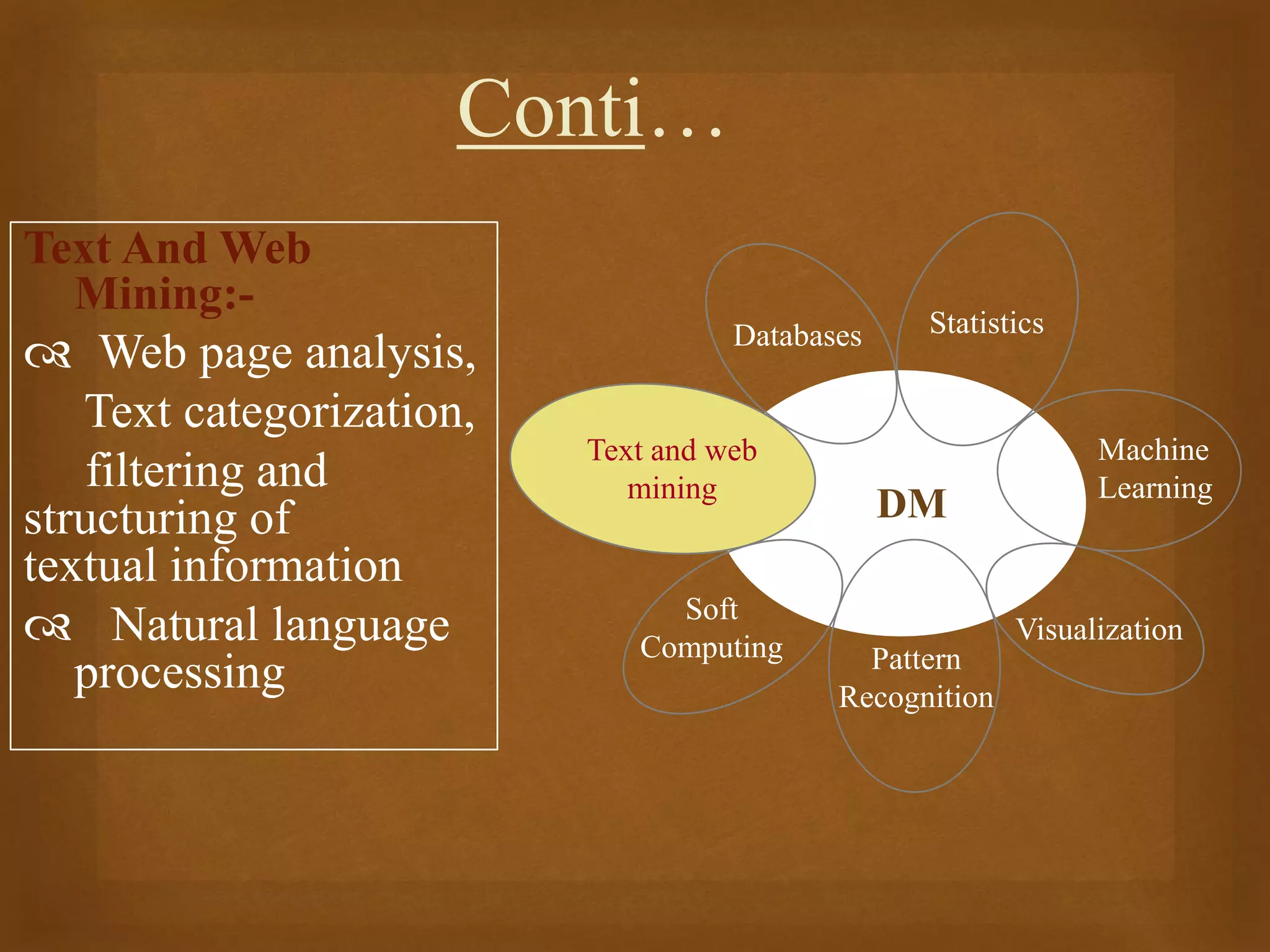
Data mining is the process of discovering patterns in large data sets and is a core part of the knowledge discovery process. It involves preprocessing, transforming, and mining data to extract useful patterns. Main data mining tasks include classification, association rule mining, clustering, sequential pattern mining, and deviation detection. The goal is to extract valid, novel, useful, and understandable patterns that can be interpreted into knowledge through an iterative and interactive process.