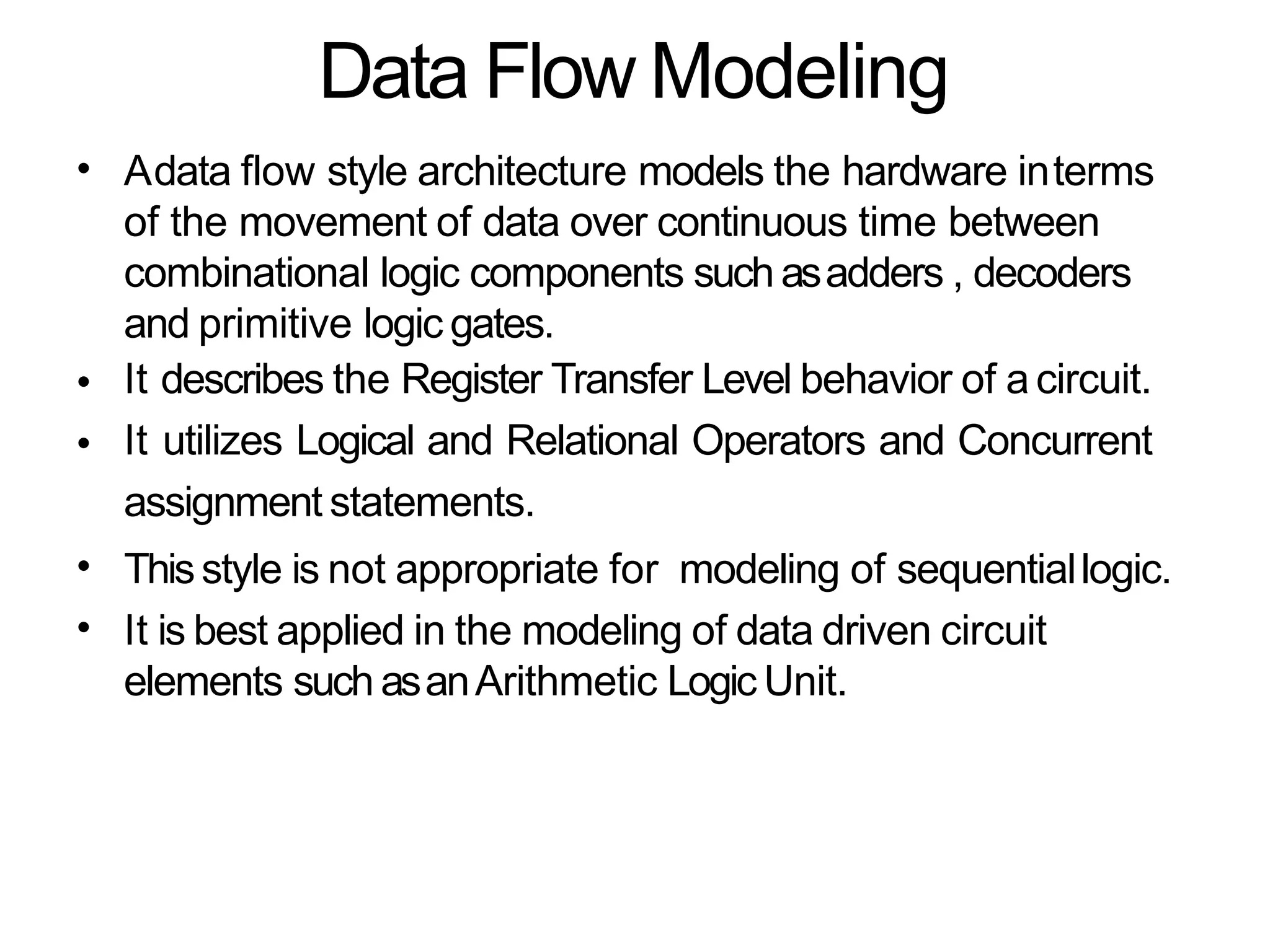
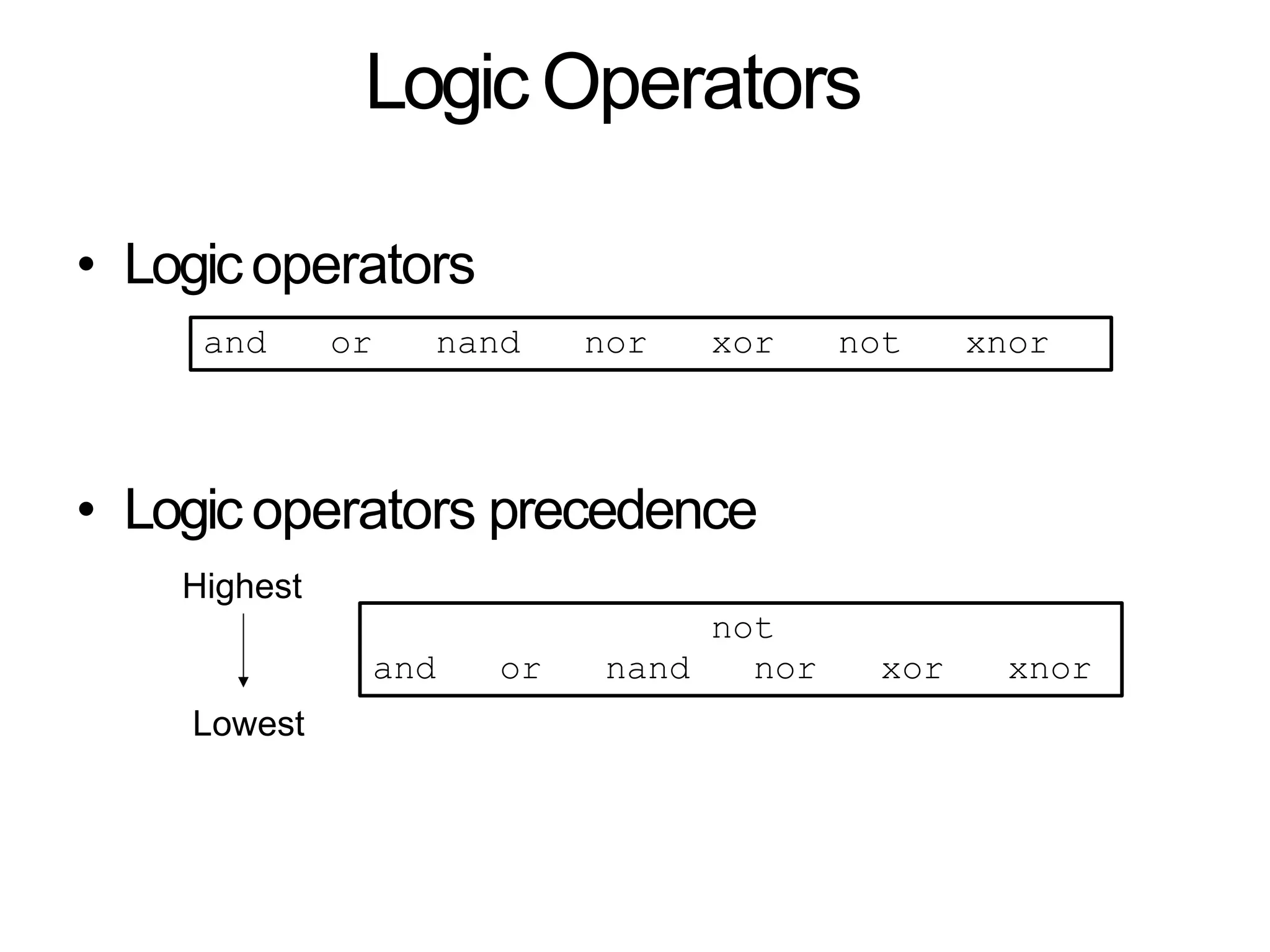
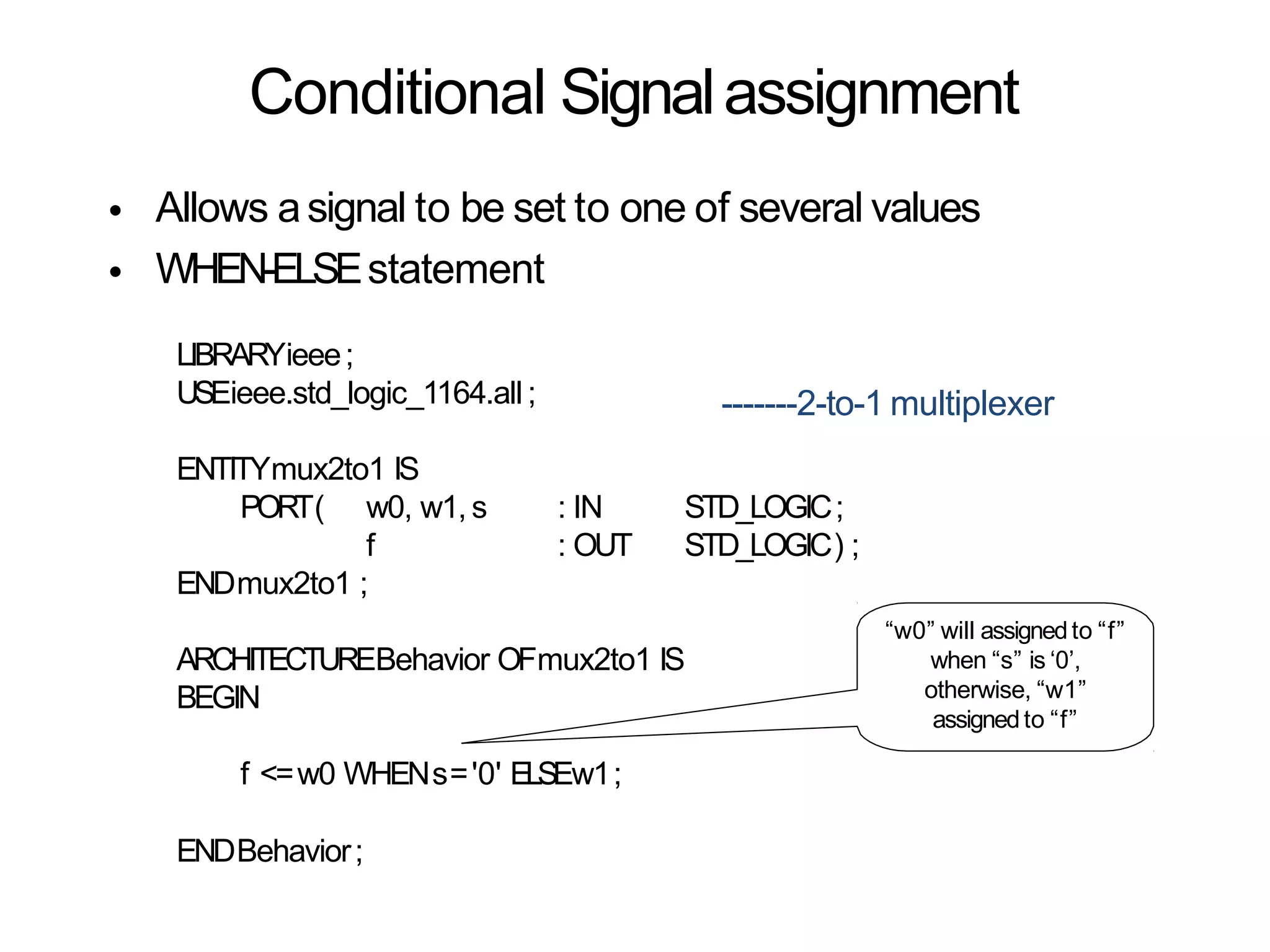
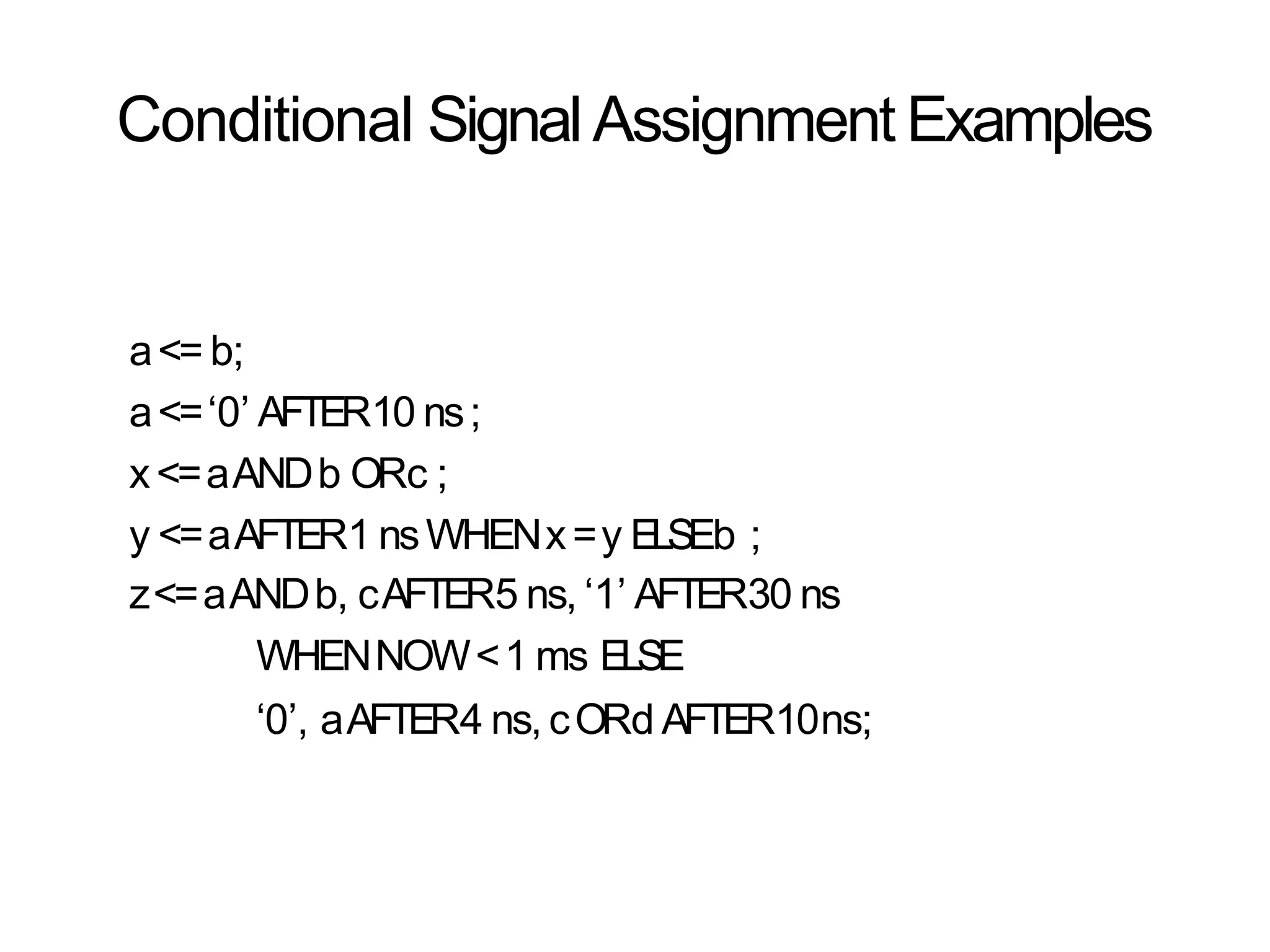
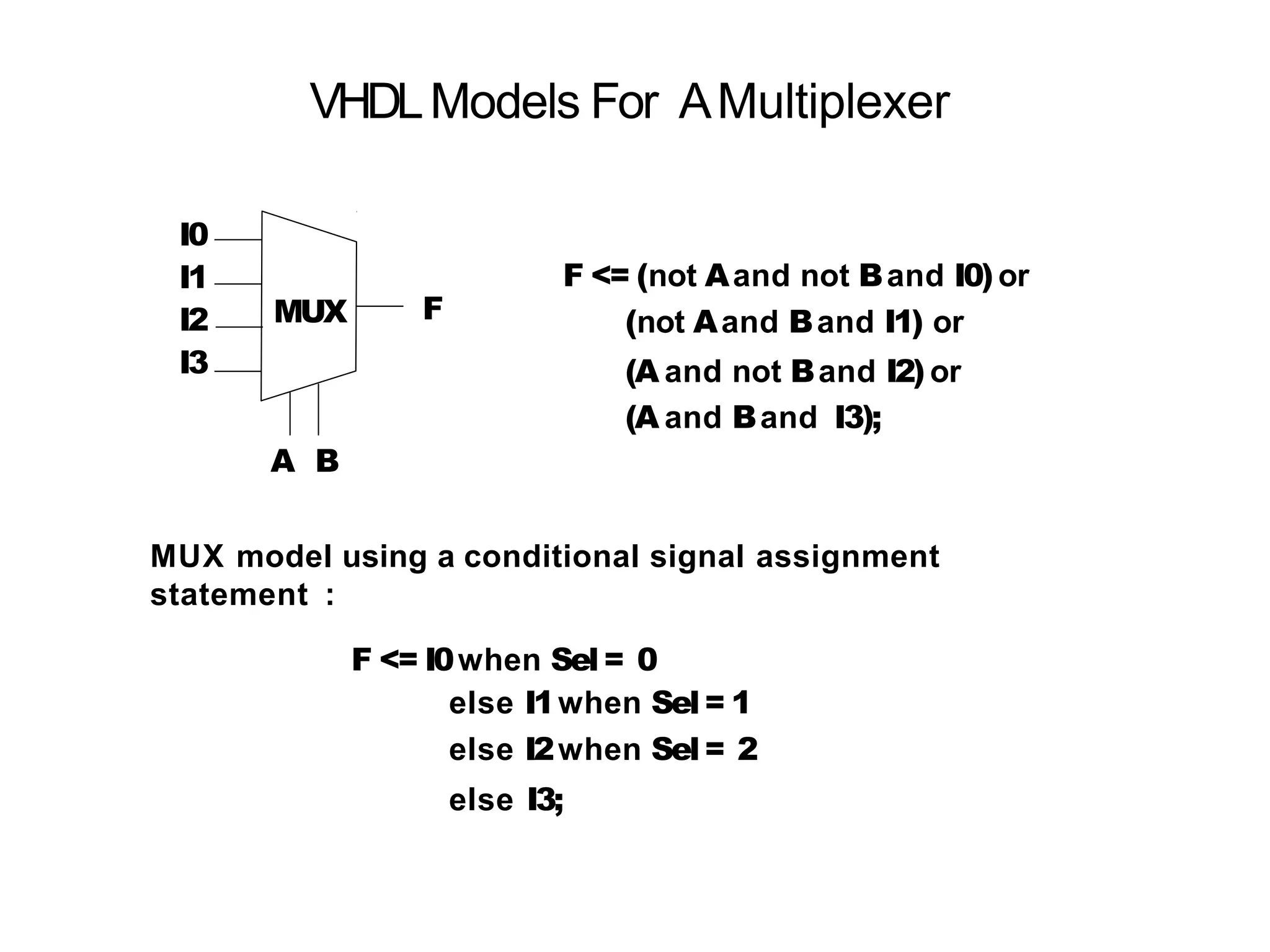
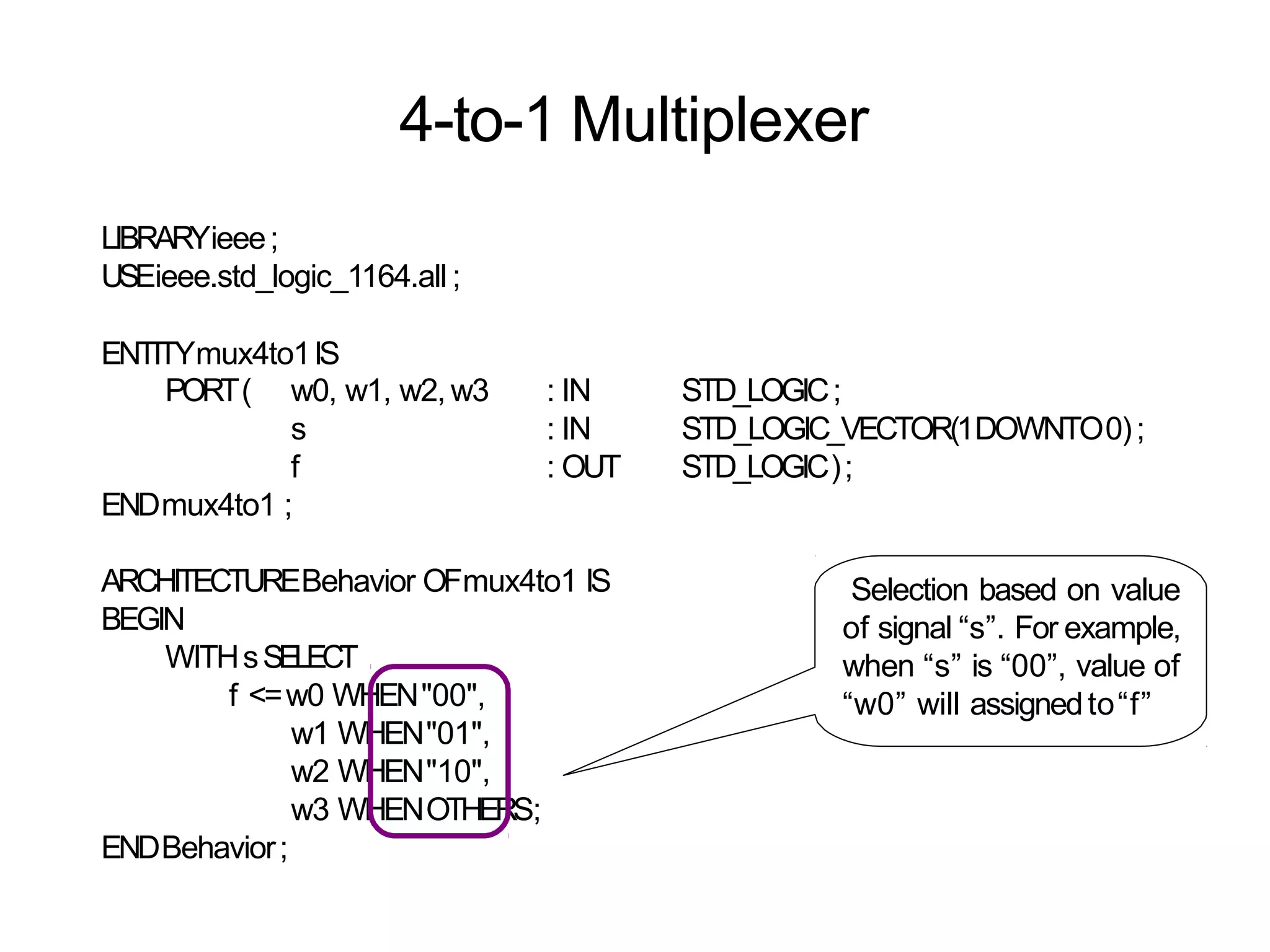
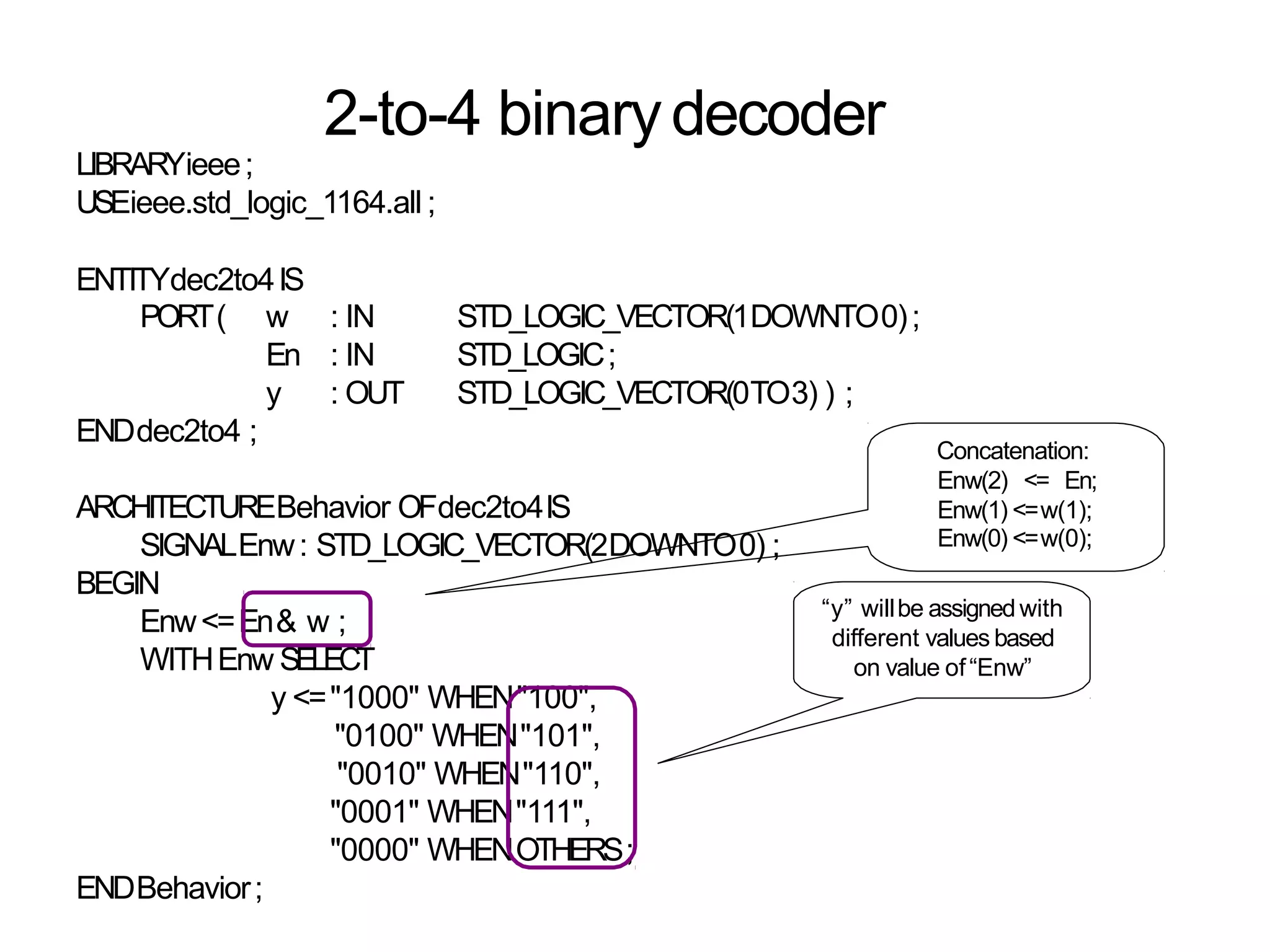
Data flow modeling describes hardware using the movement of data between combinational logic components over time. It models circuits at the register transfer level using logical and relational operators and concurrent signal assignments. This style is best for modeling data-driven circuits like arithmetic logic units. Examples shown include half adders, full adders, decoders, multiplexers, and an 8-bit adder modeled using data flow and concurrent assignments.