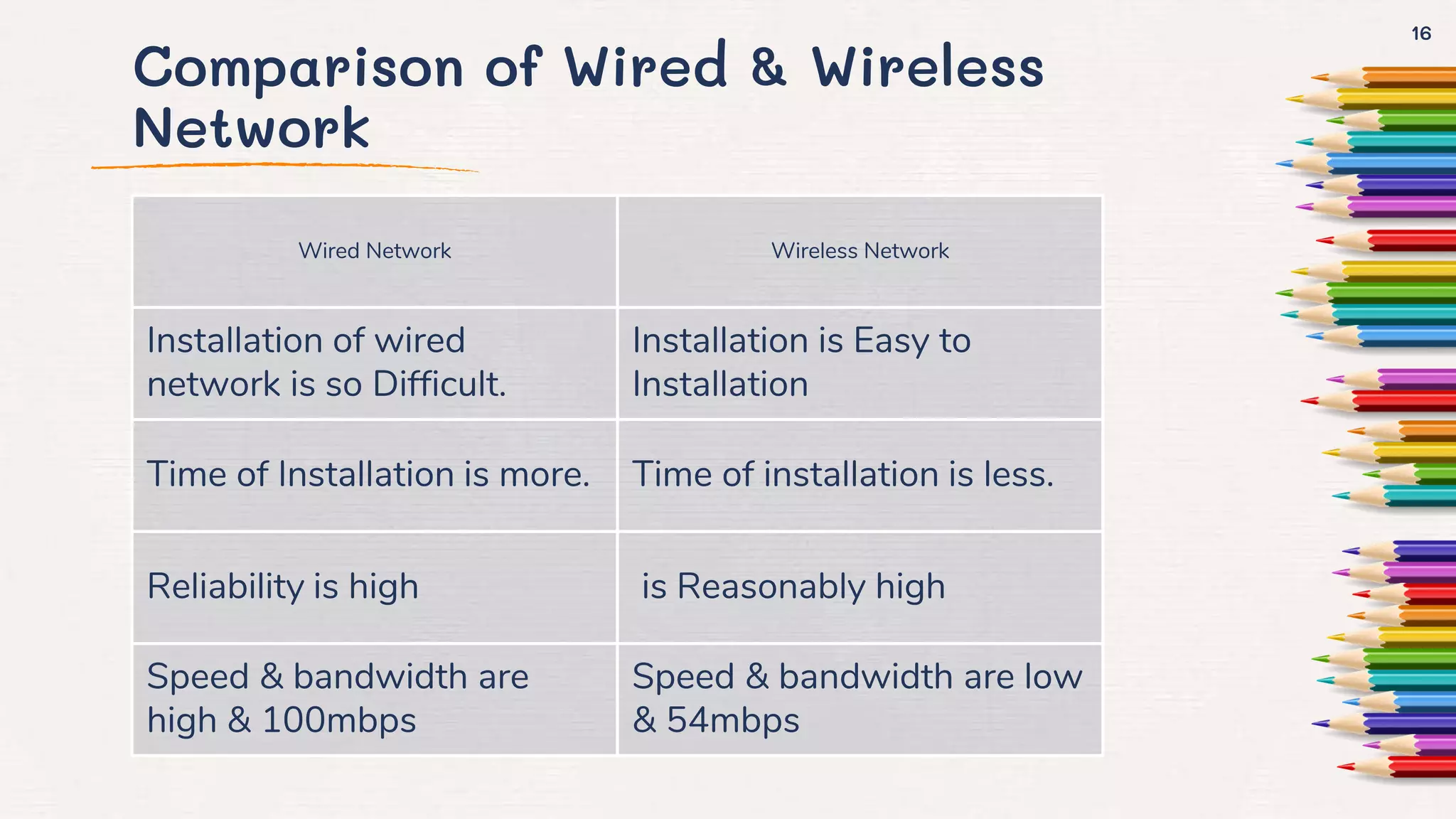
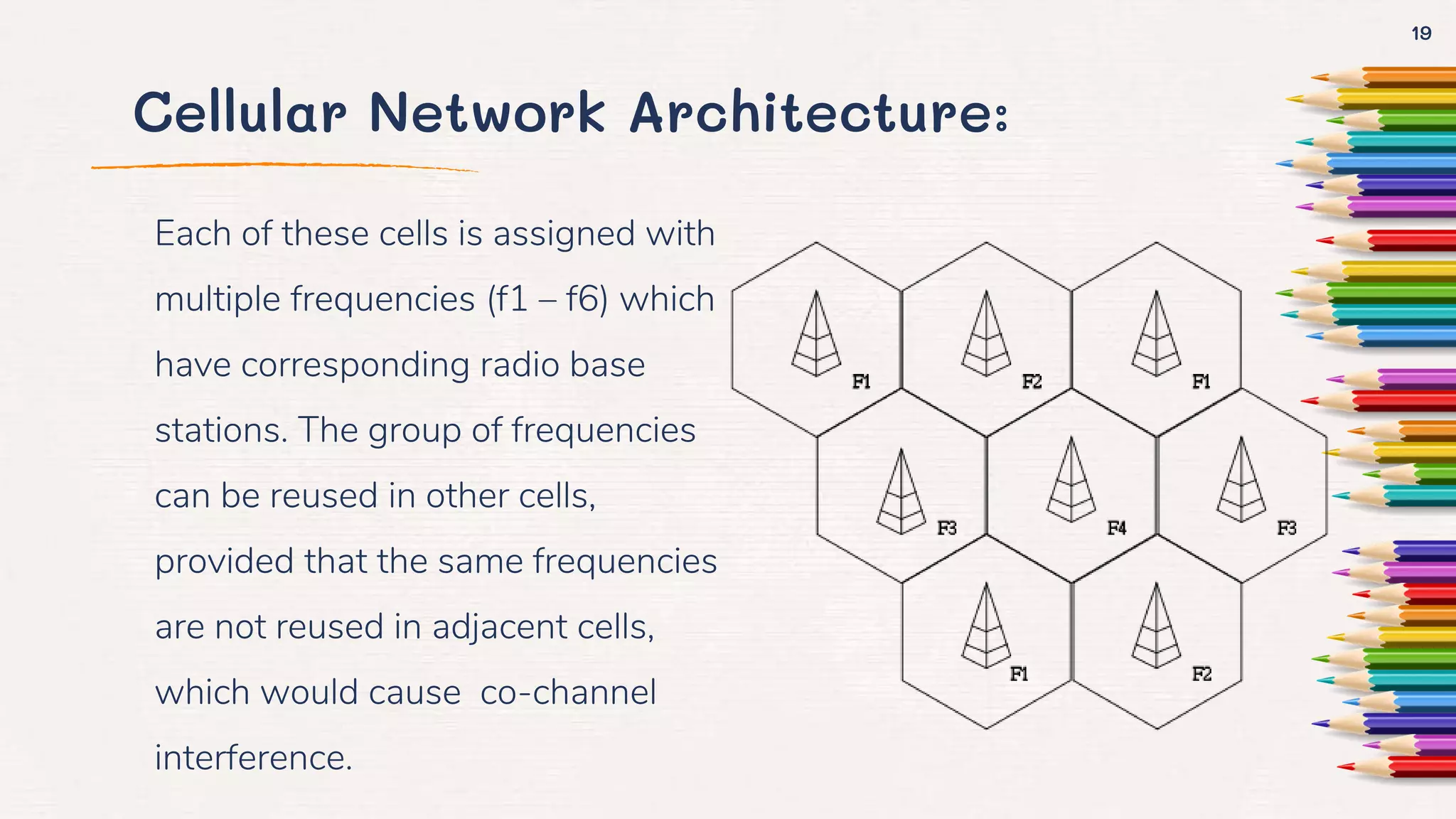
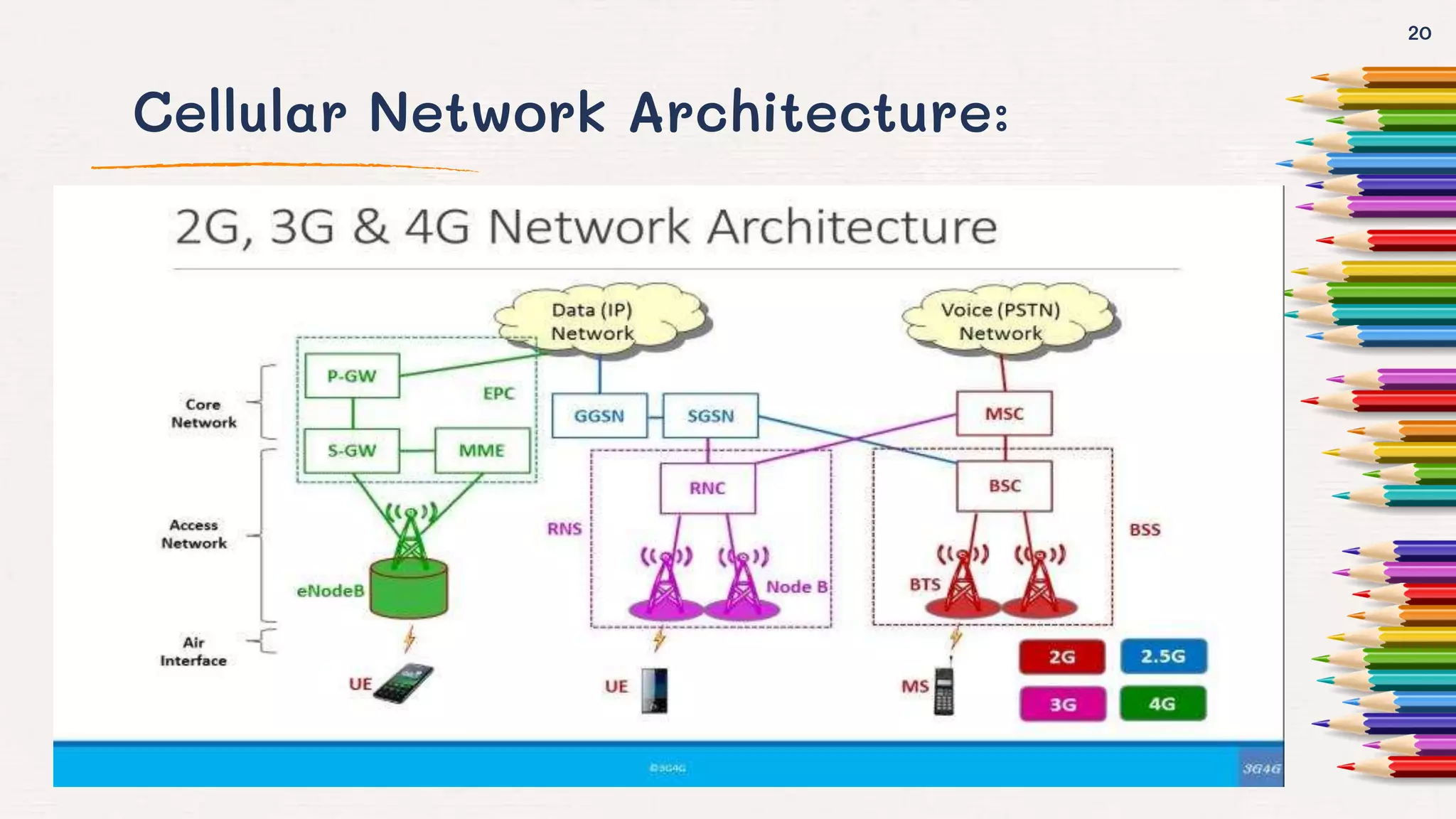
The document provides an overview of wireless networks, including their definition, needs, and types, such as WLANs, WPANs, and WMANs. It discusses the advantages and disadvantages of wireless networks, their comparison with wired networks, and the architecture of cellular networks. Additionally, it highlights various applications of wireless technology and concludes with remarks on future networking technologies.