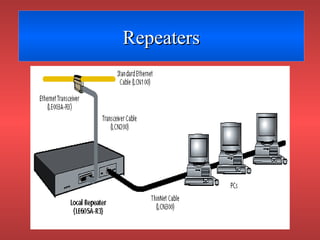
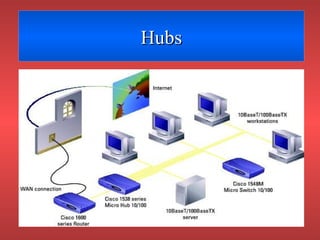
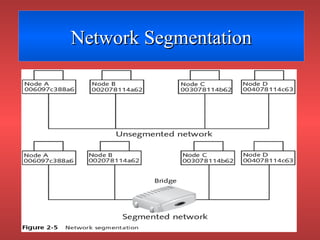
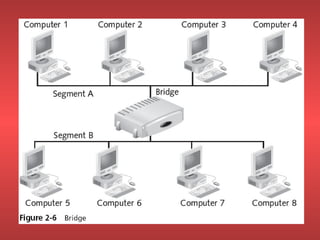
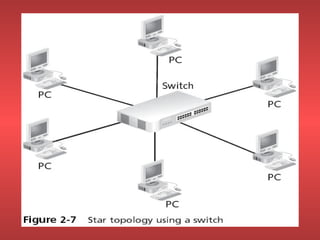
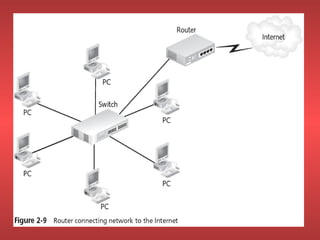
Network devices like repeaters, hubs, bridges, switches and routers are used to extend and segment networks. Repeaters regenerate signals to increase cable length while hubs connect cables without regeneration. Bridges segment networks at the data link layer using MAC addresses. Switches increase performance by opening virtual circuits between devices. Routers connect multiple networks at the network layer using IP addresses and dynamic routing.