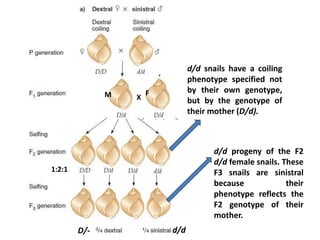
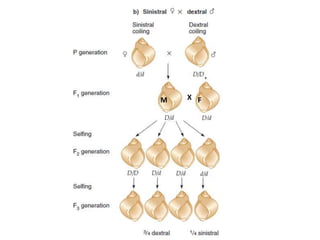
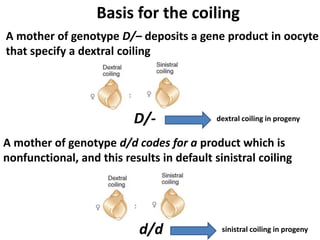
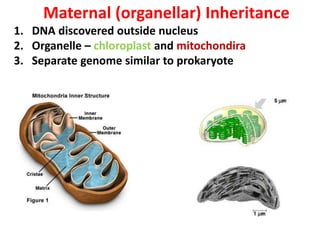
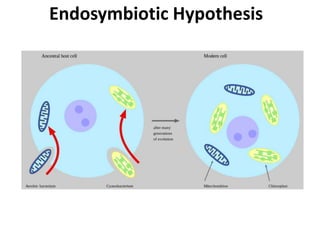
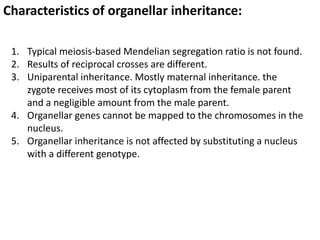
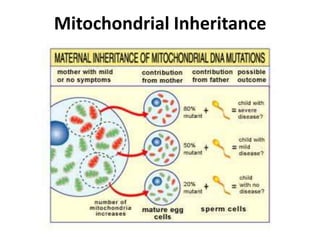
This document discusses three types of extranuclear inheritance: maternal effect, maternal (organelle) inheritance, and infectious inheritance. Maternal effect occurs when a phenotype is determined by the mother's nuclear genes rather than the offspring's own genes. Maternal (organelle) inheritance involves inheritance of mitochondria and chloroplasts, which have their own DNA and are passed exclusively from mother to offspring. Infectious inheritance occurs when a symbiotic microorganism is transmitted maternally in the cytoplasm and confers traits to offspring.