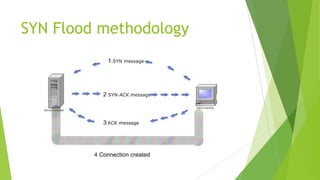
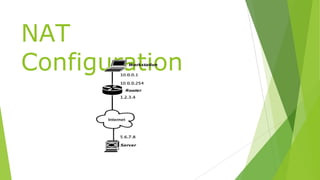
The document discusses denial of service (DoS) and distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks, detailing their methodologies and impacts. It explains common techniques used in DDoS attacks, such as SYN flood and IP spoofing, while also introducing mitigation strategies like access lists and network address translation (NAT). The document emphasizes the importance of understanding these attacks given the context of limited IPv4 addresses and the prevalence of botnets.