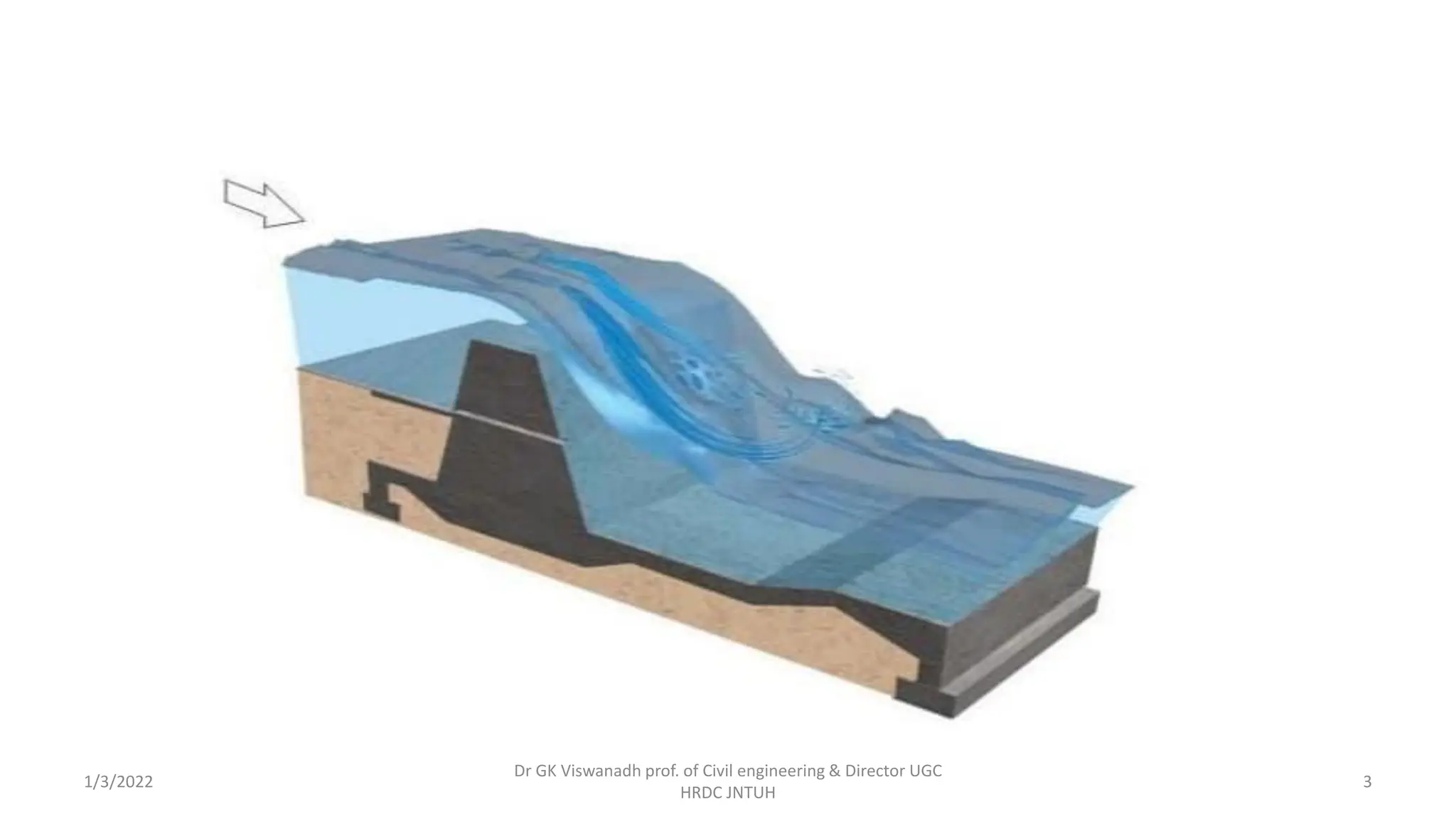
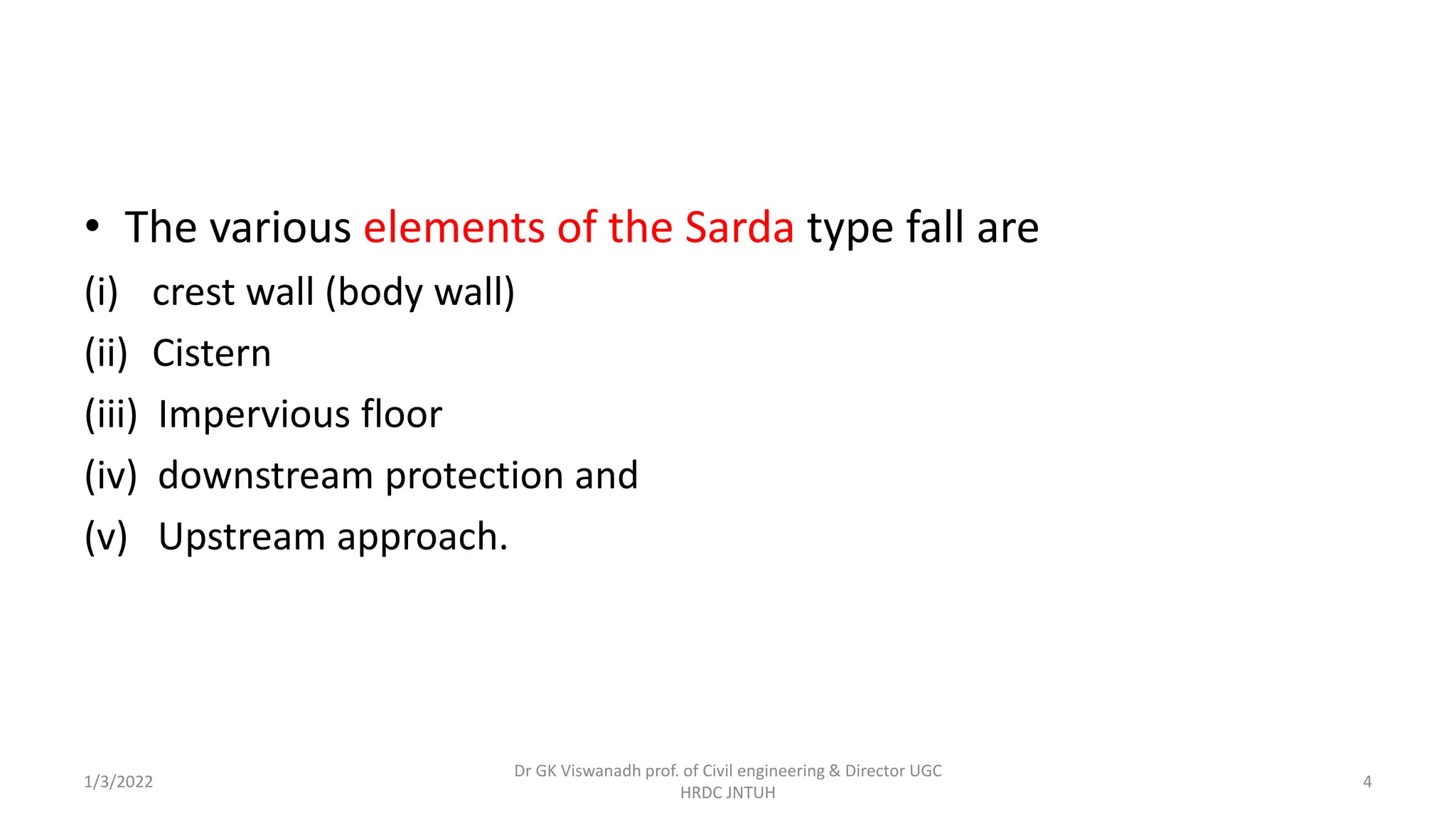
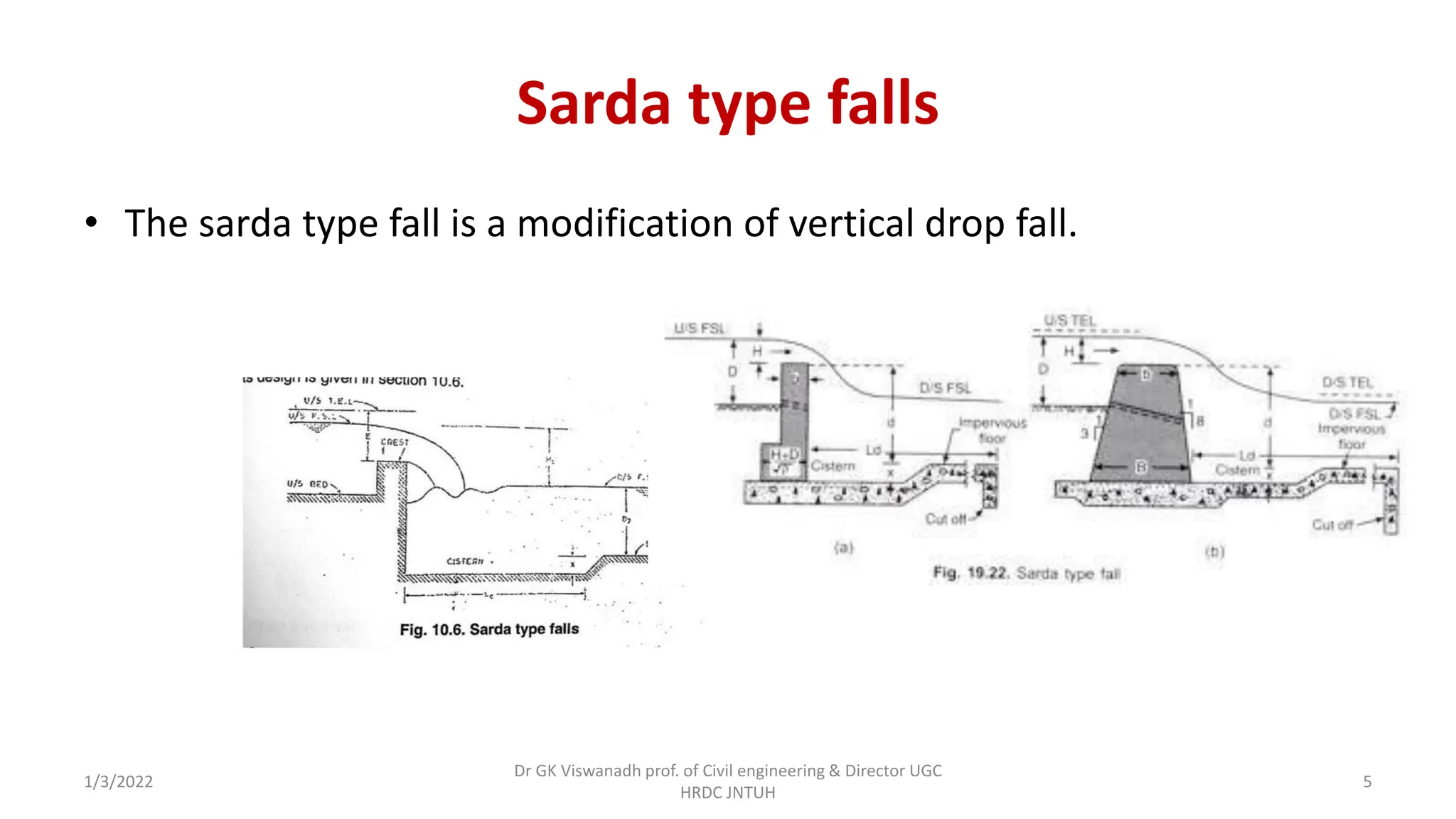
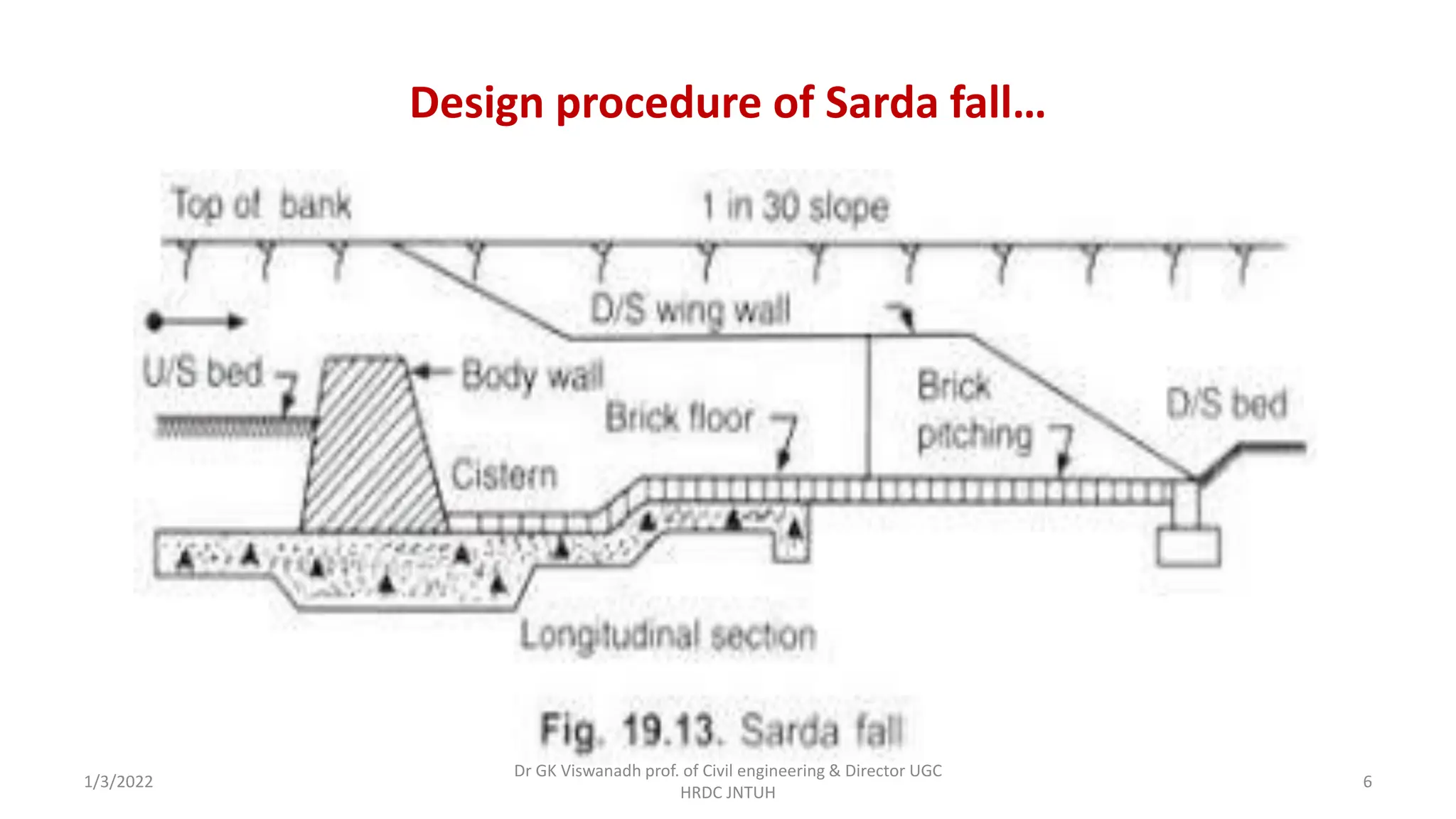
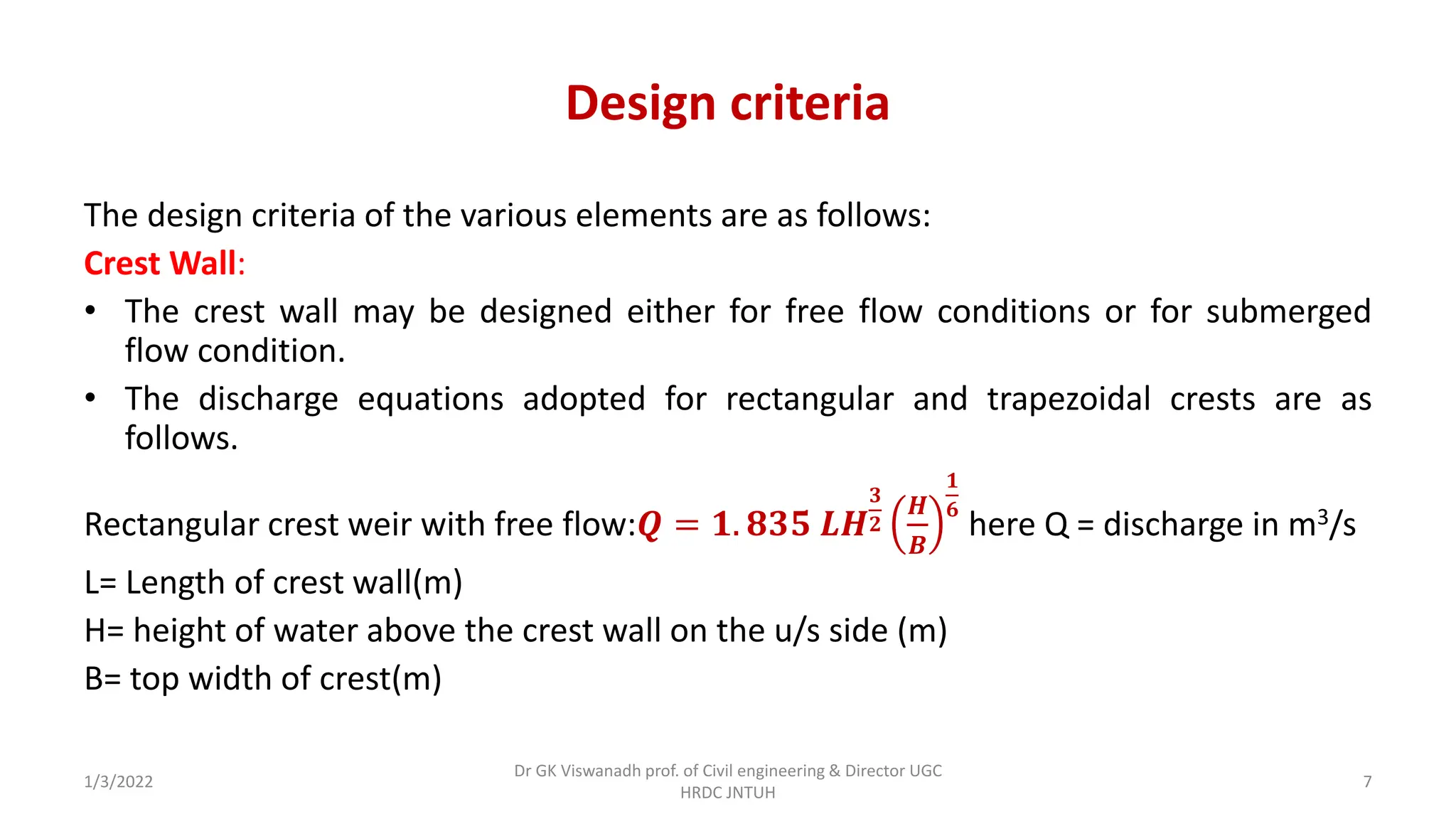
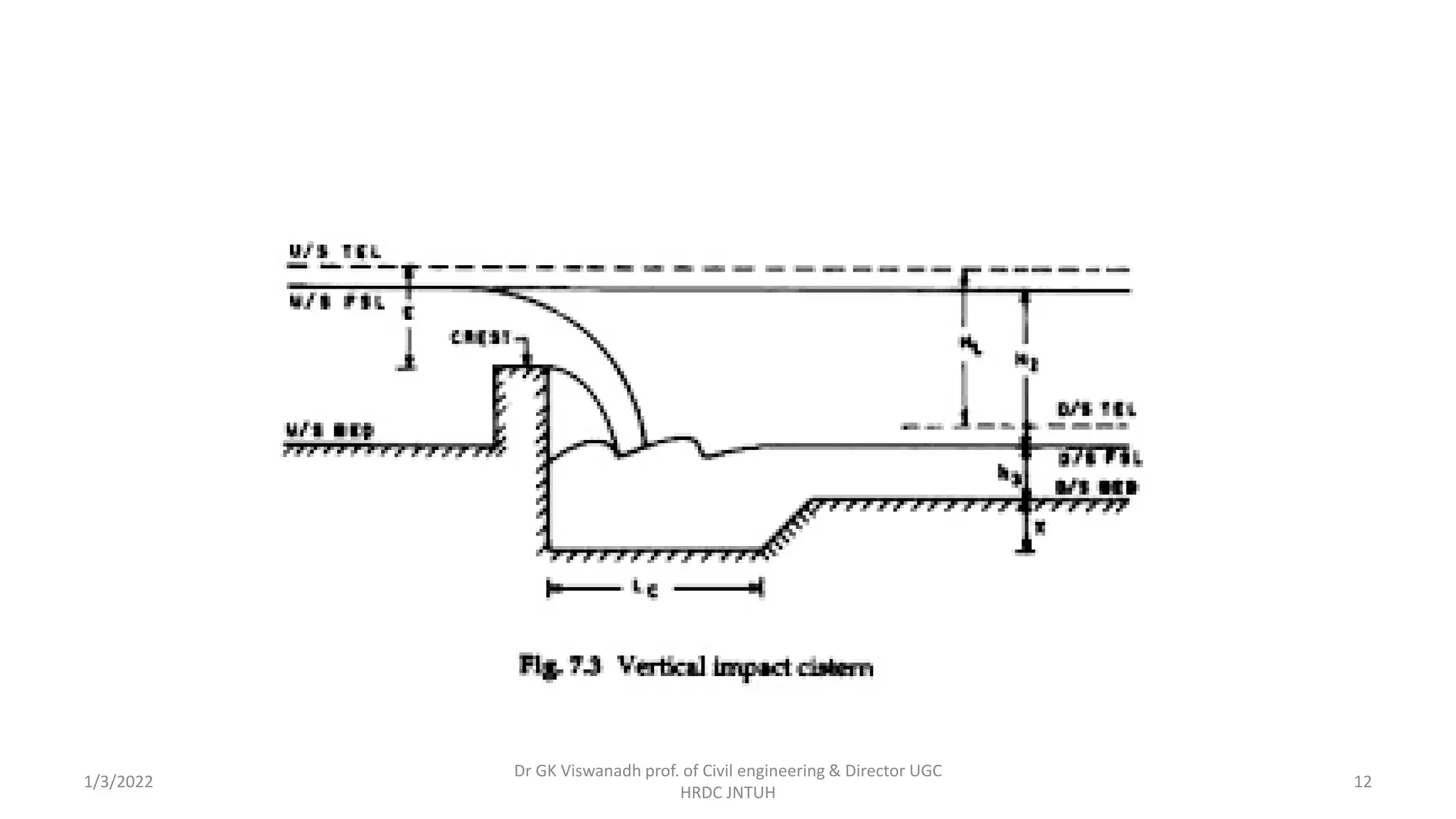
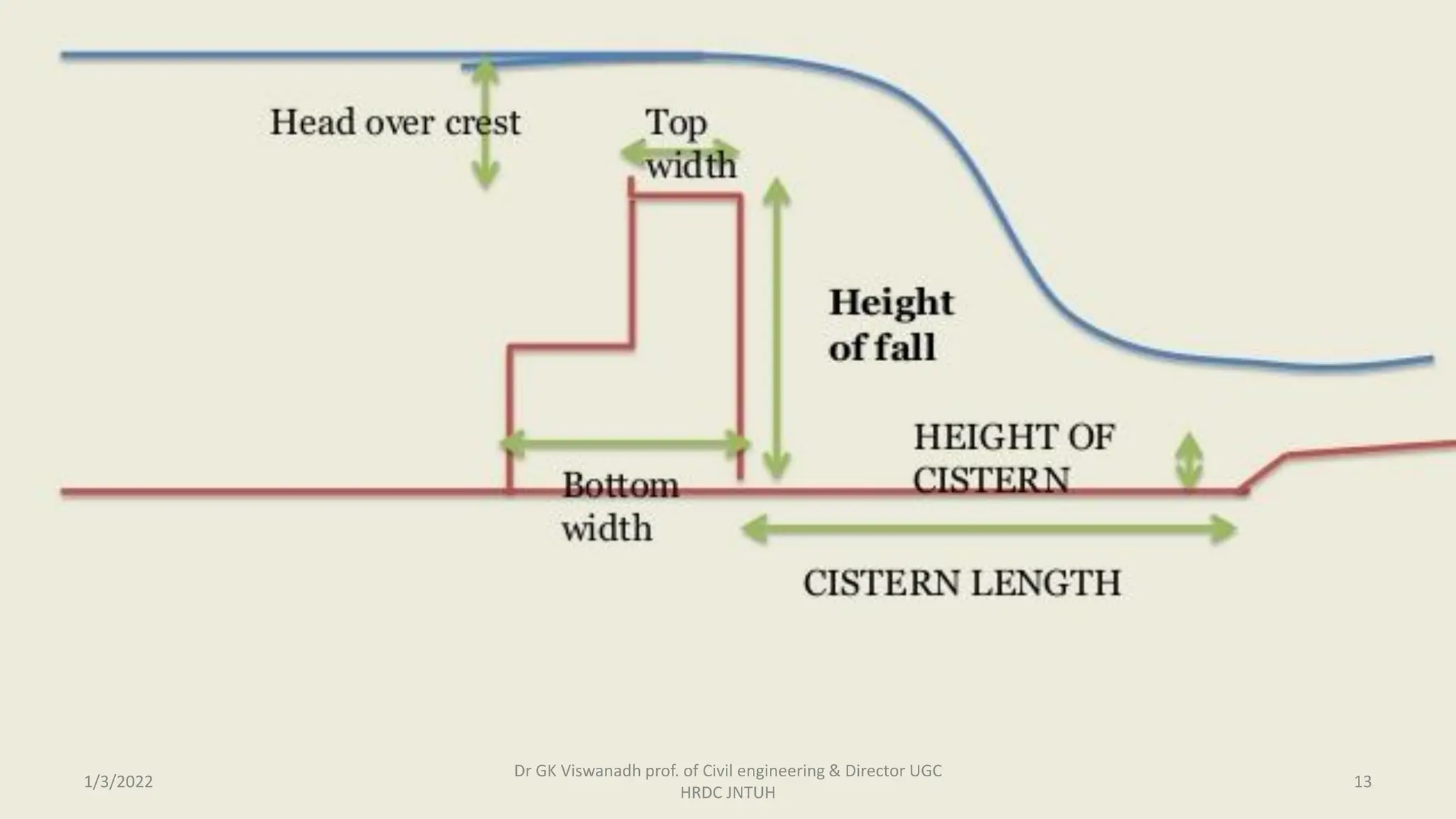
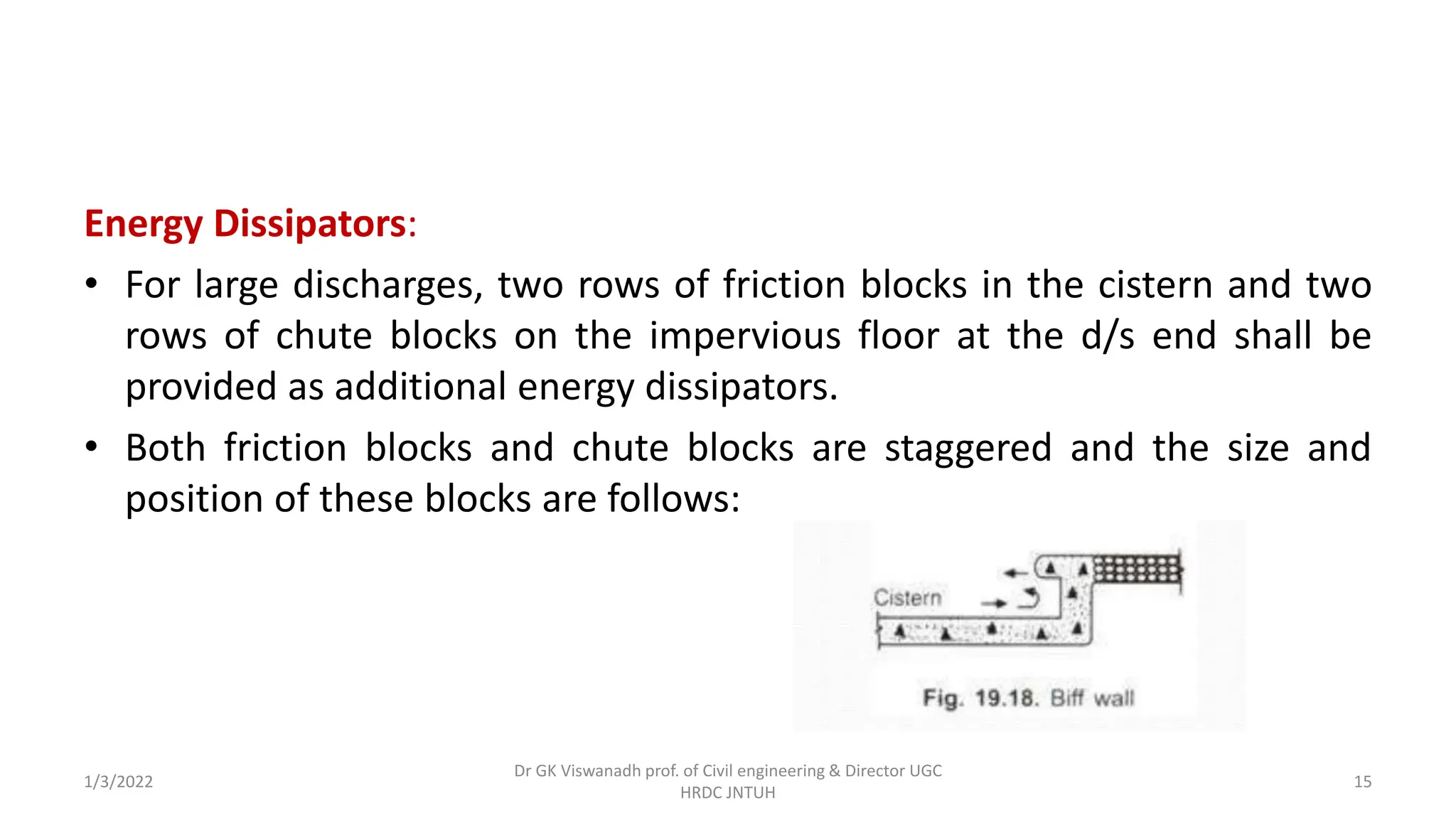
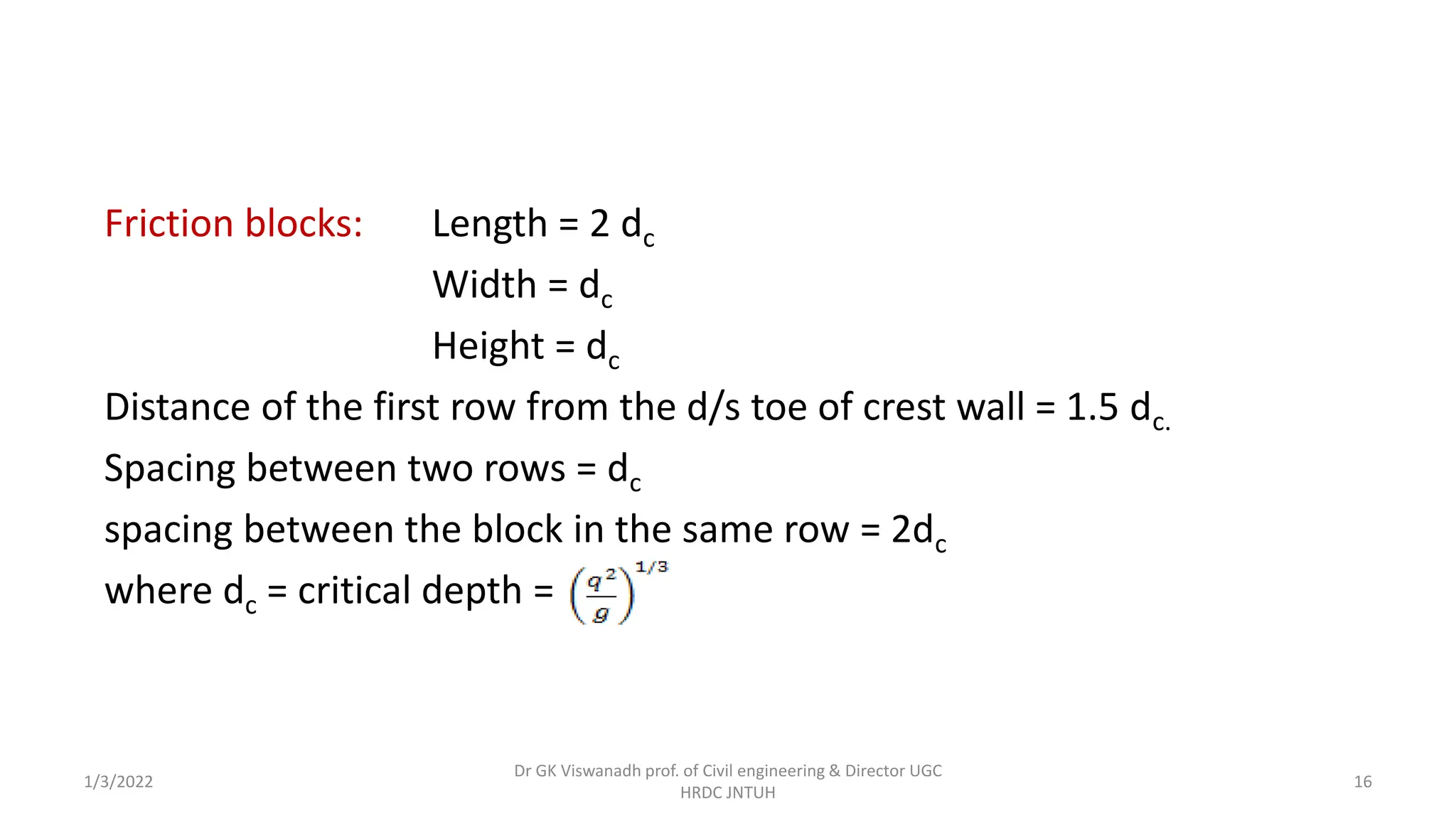
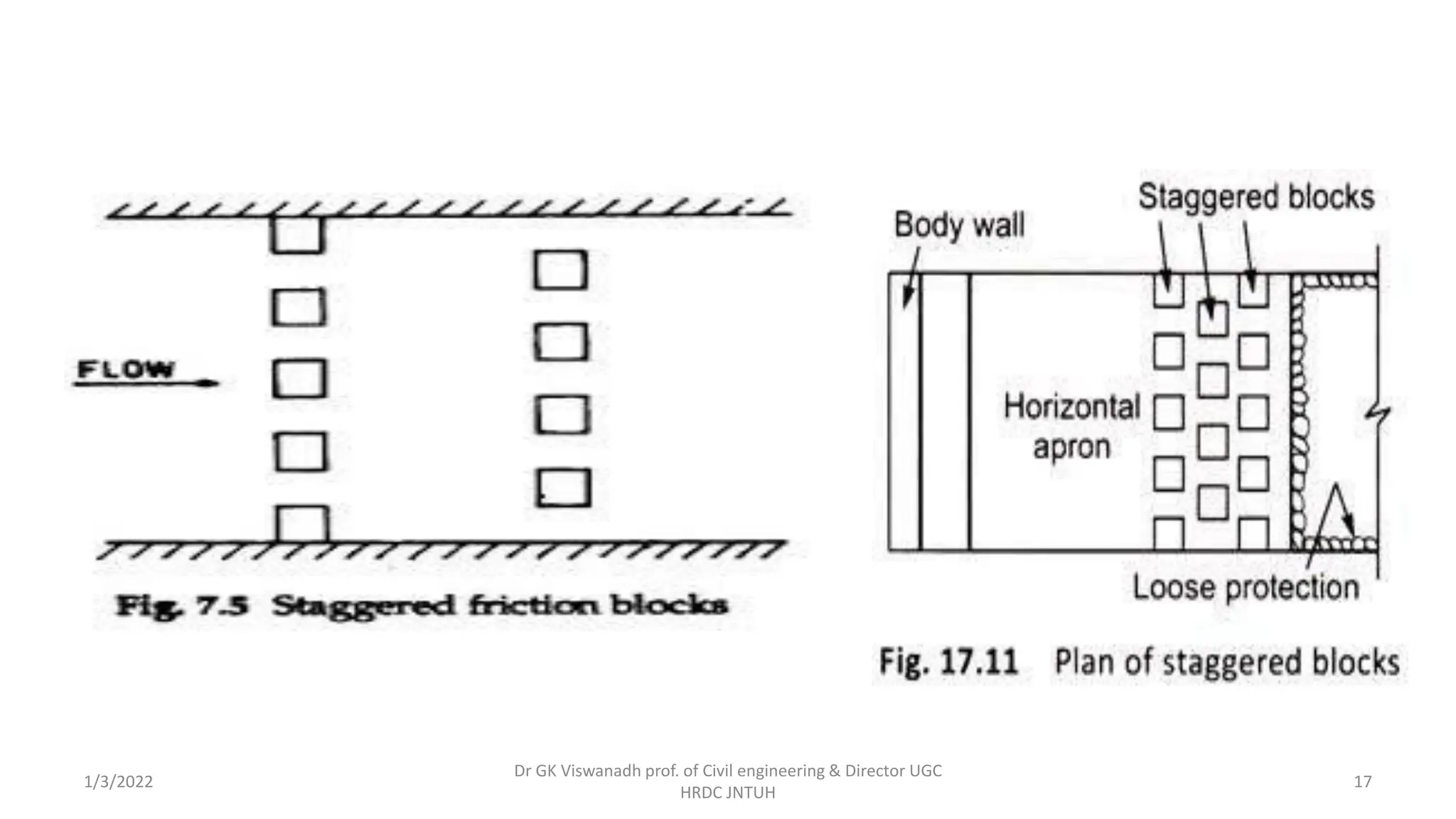
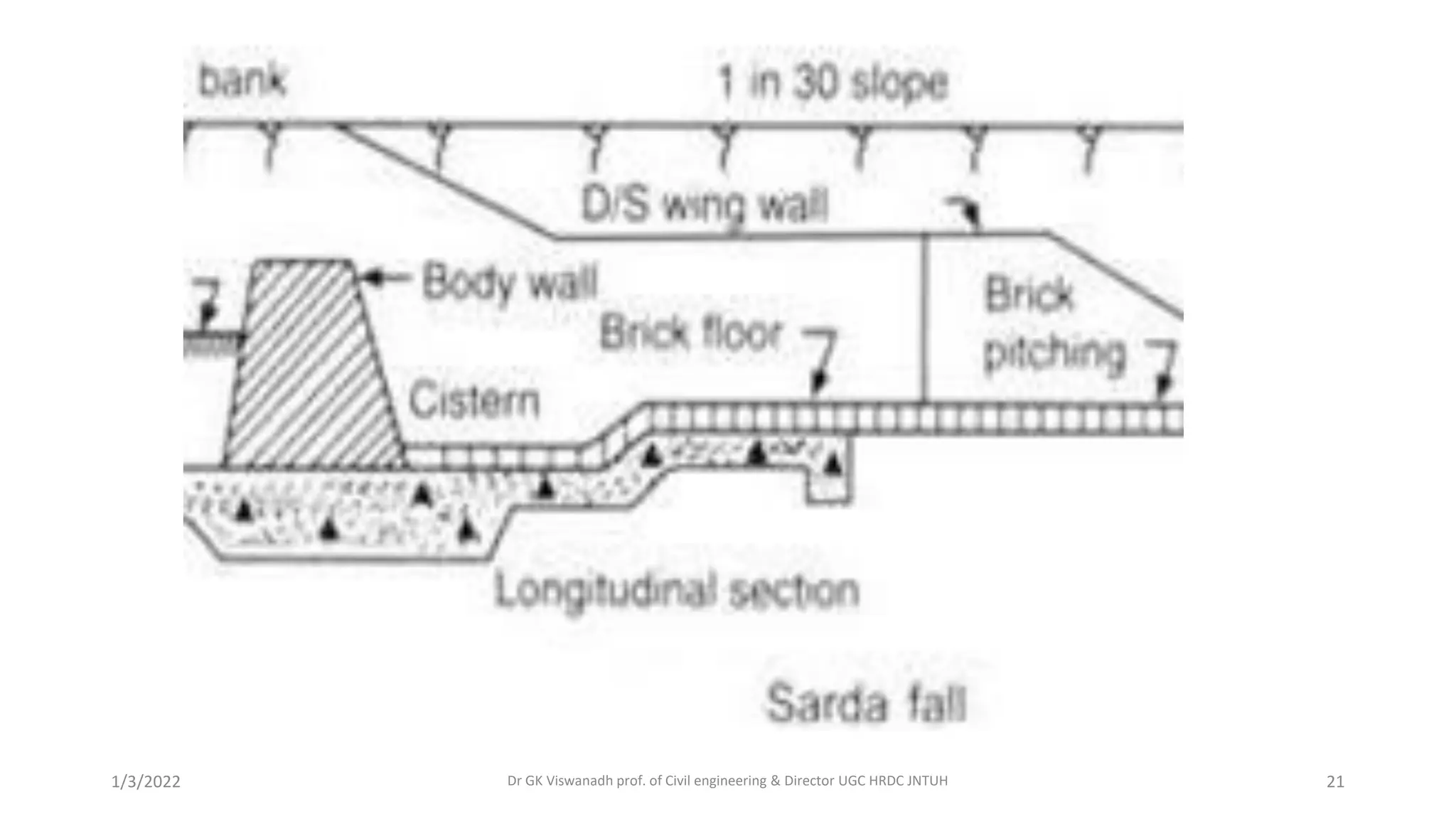
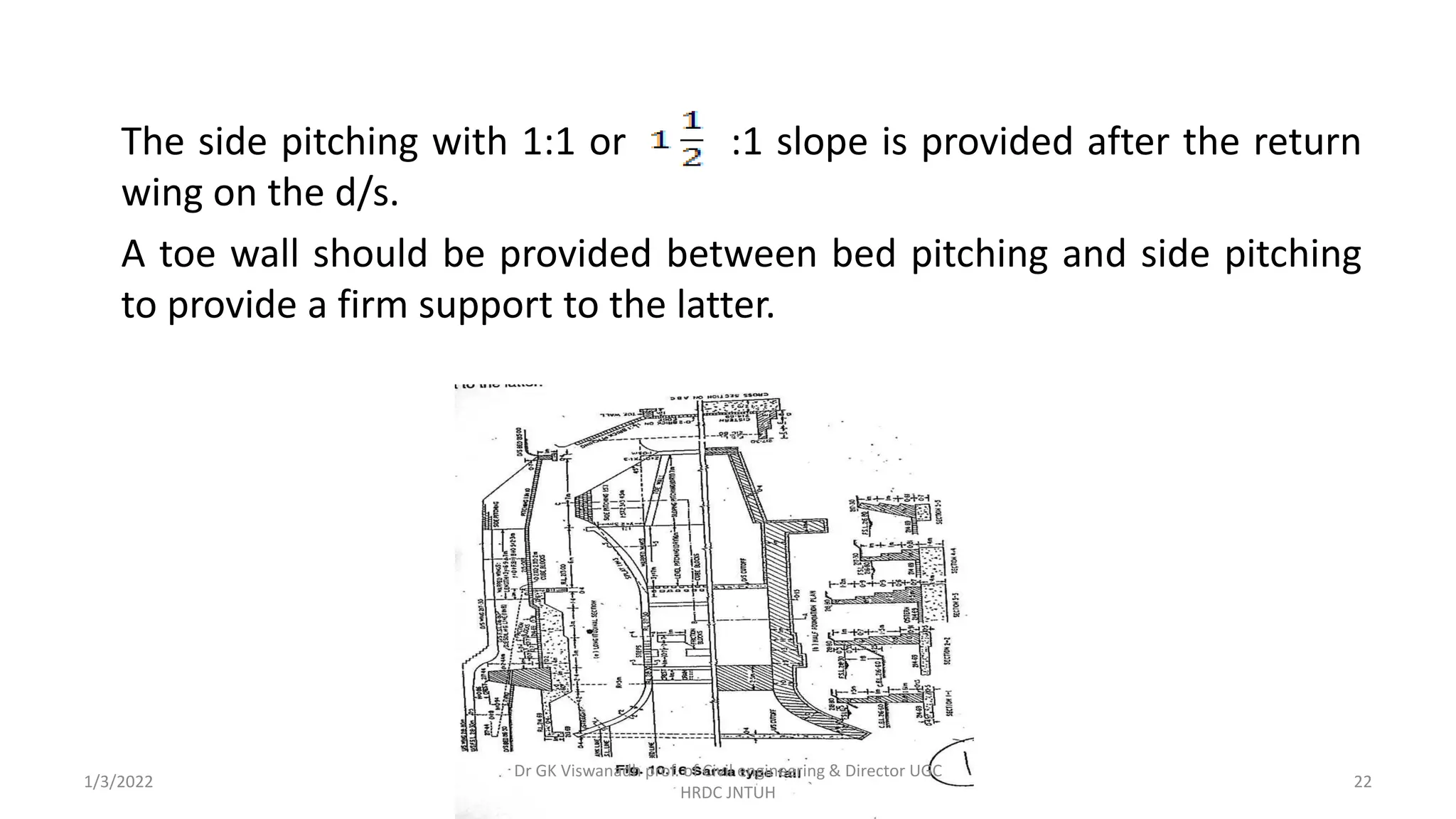
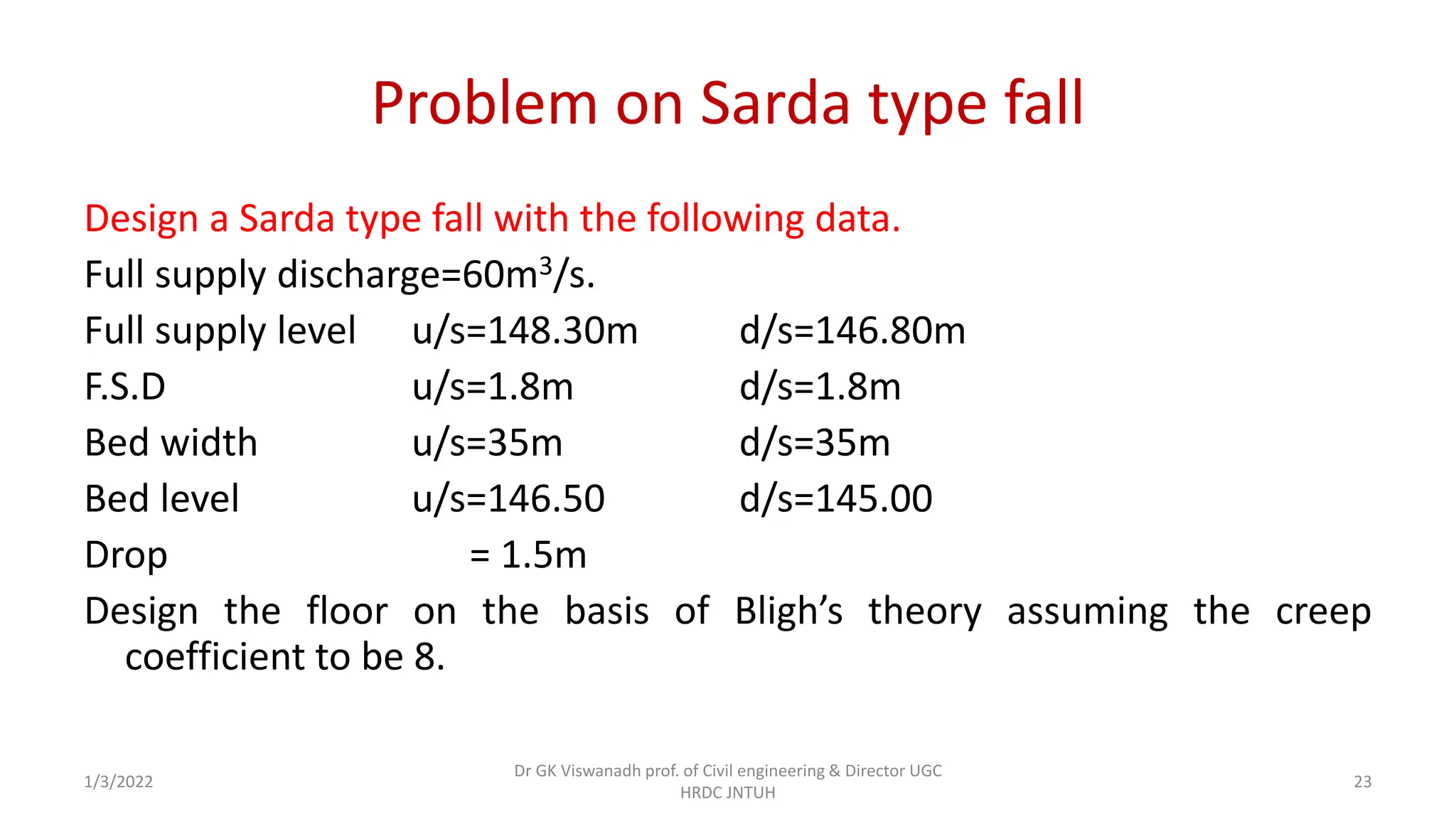
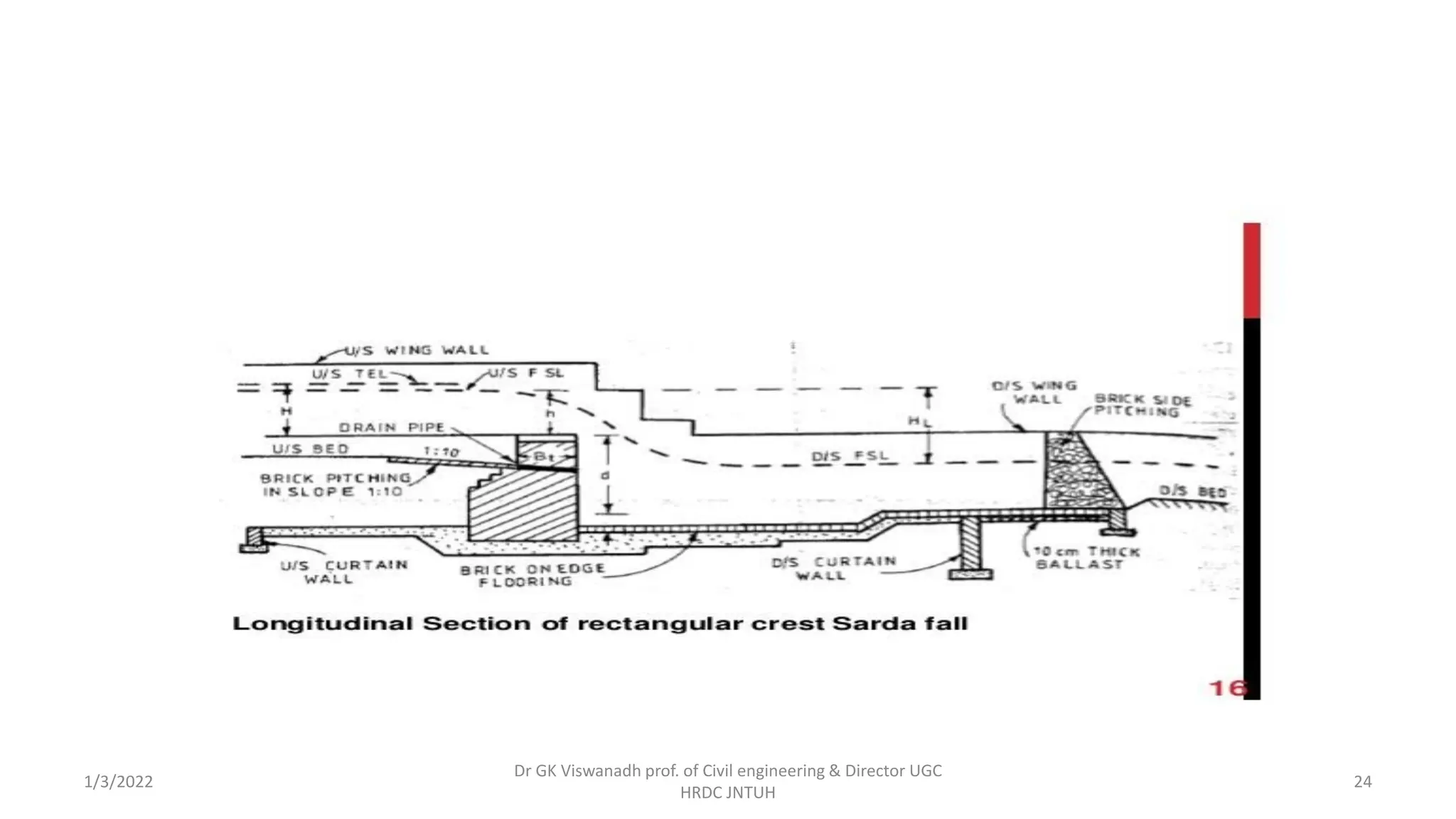
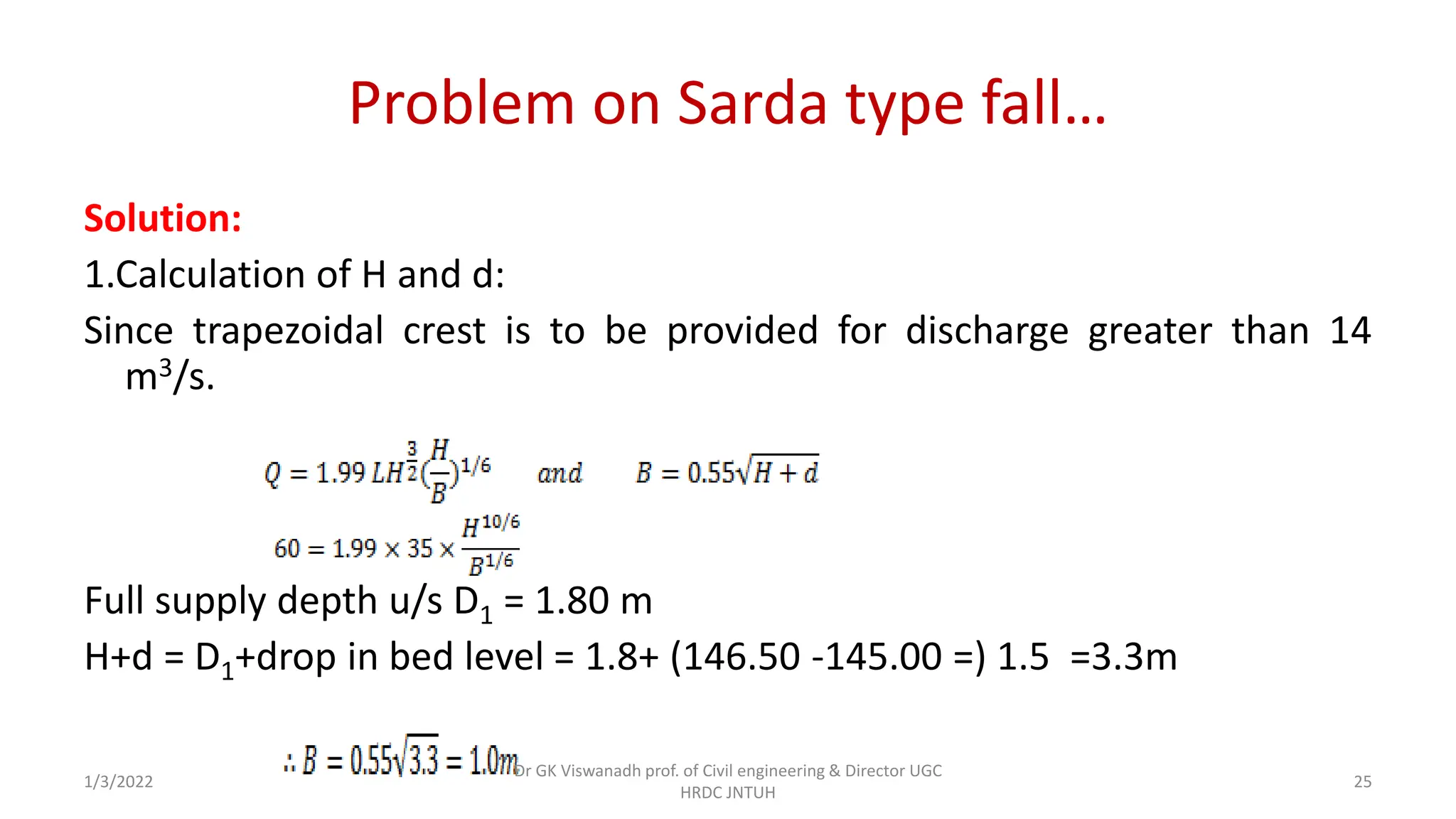
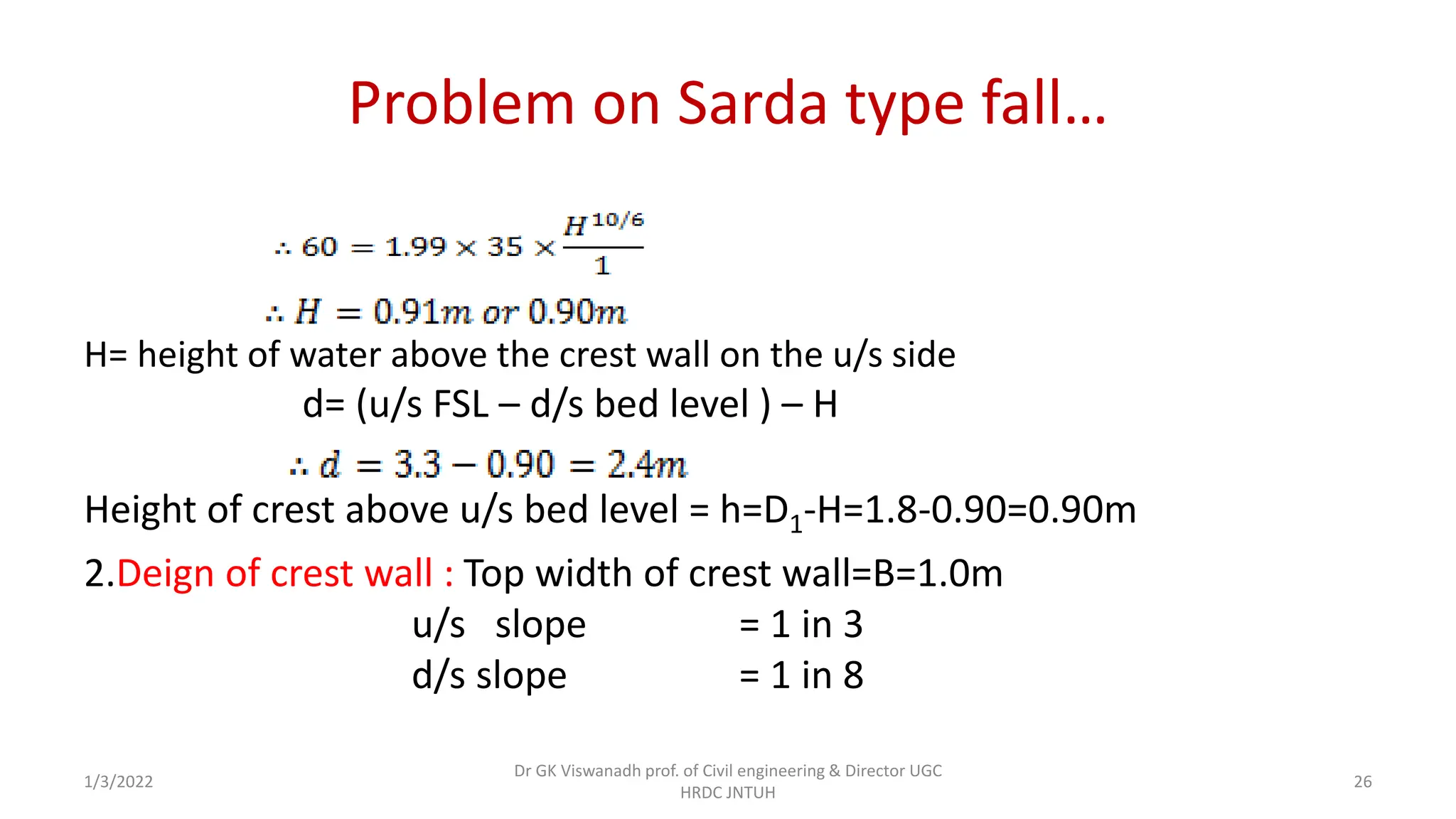
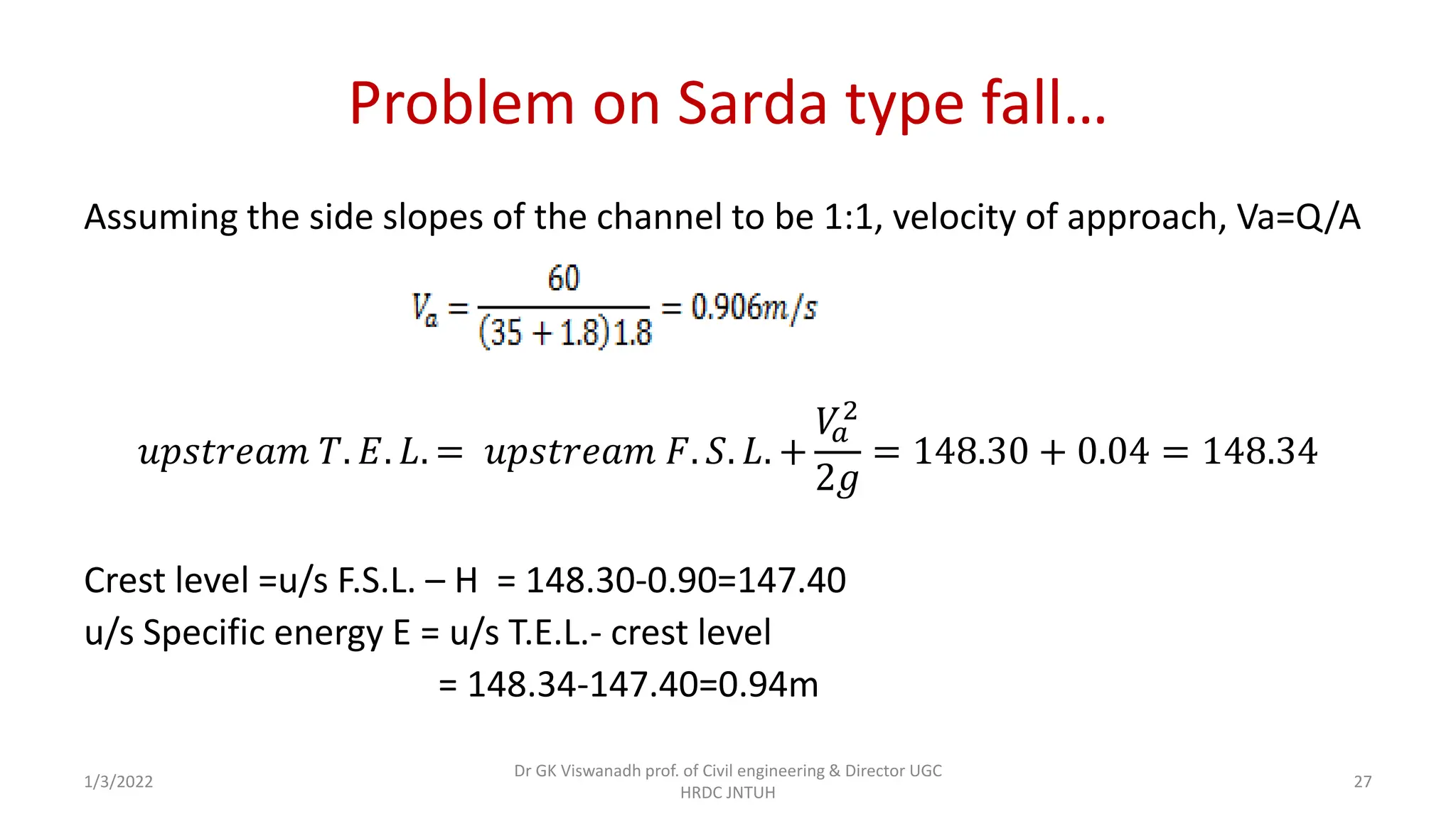
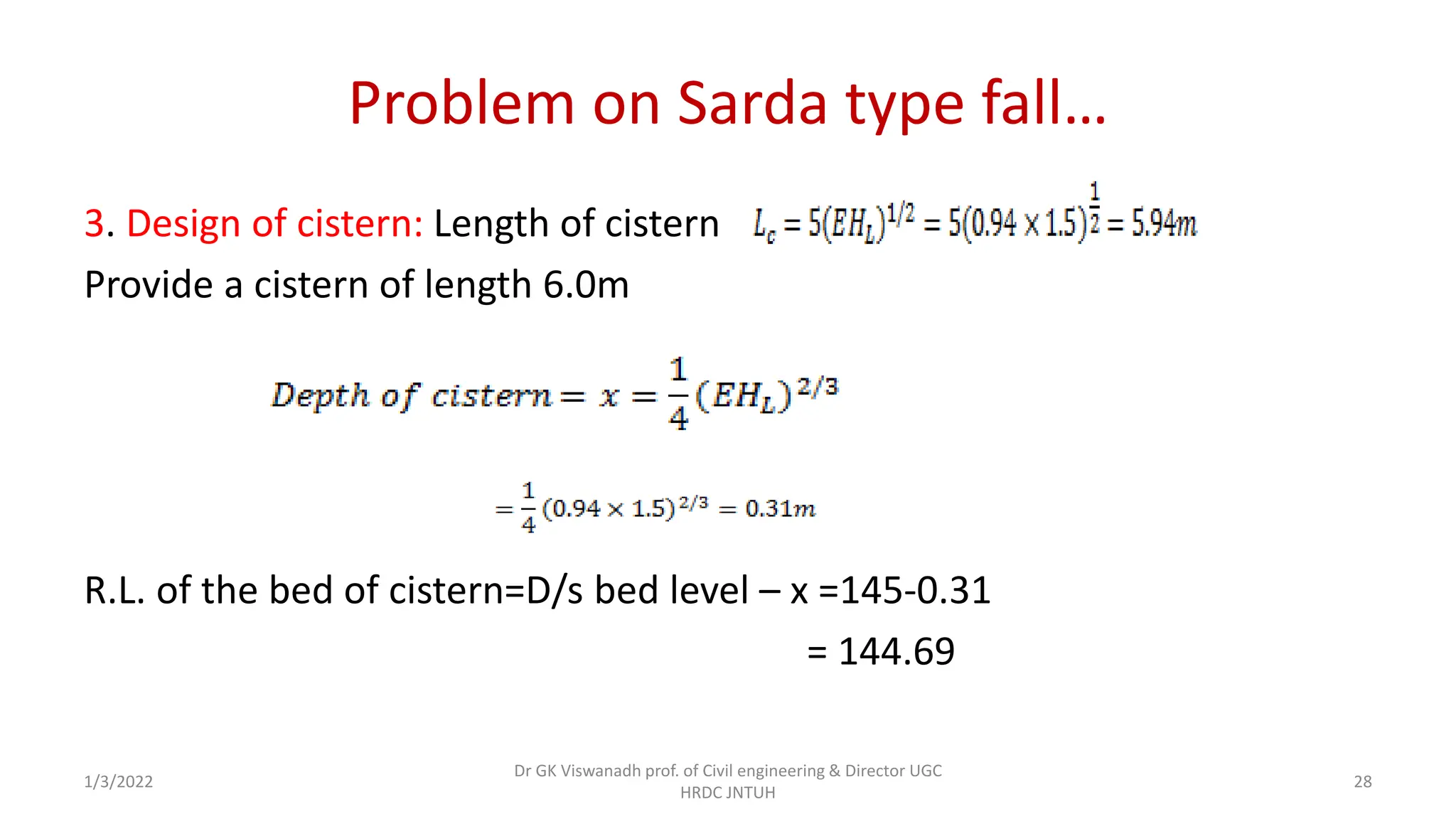
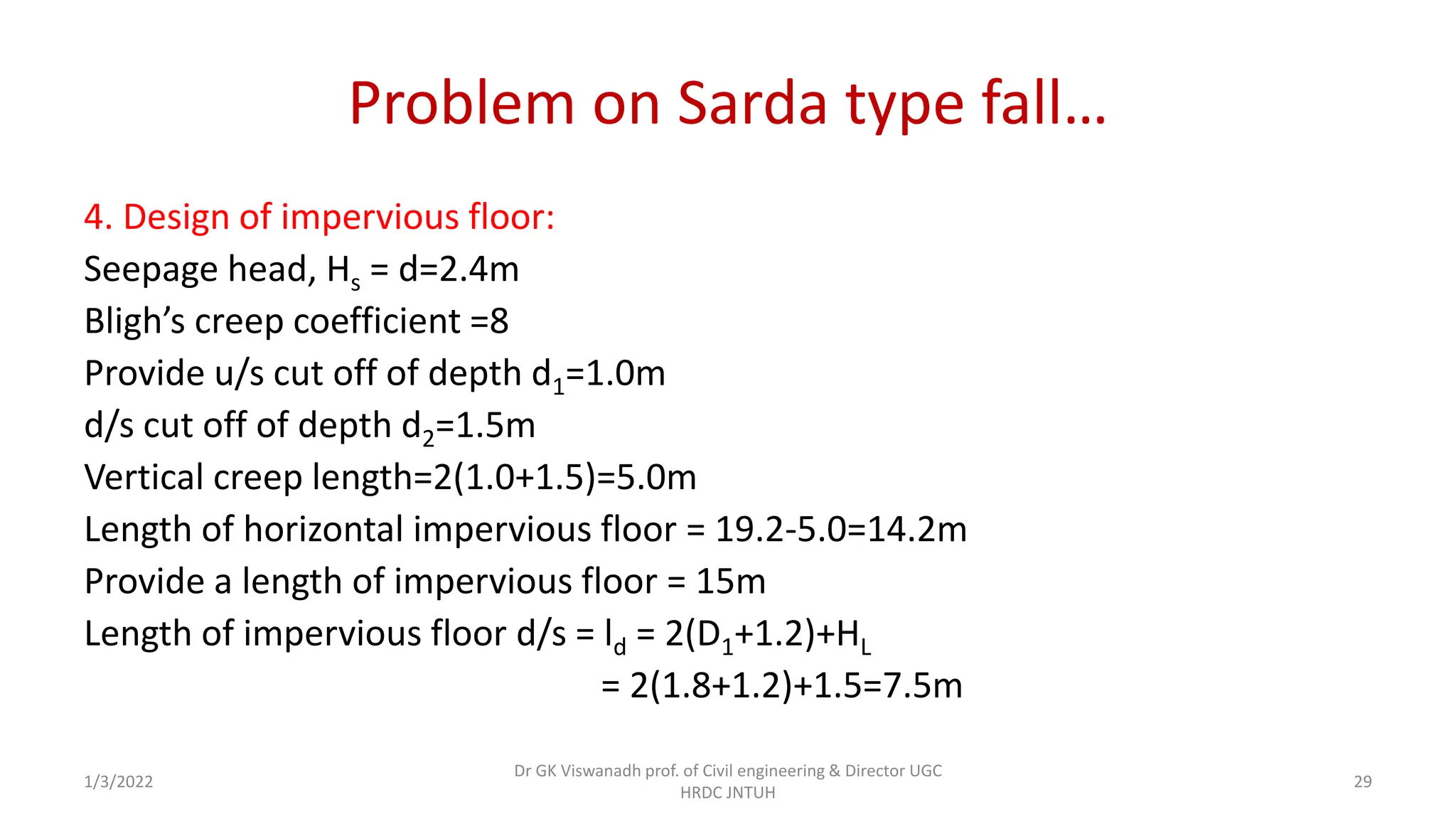
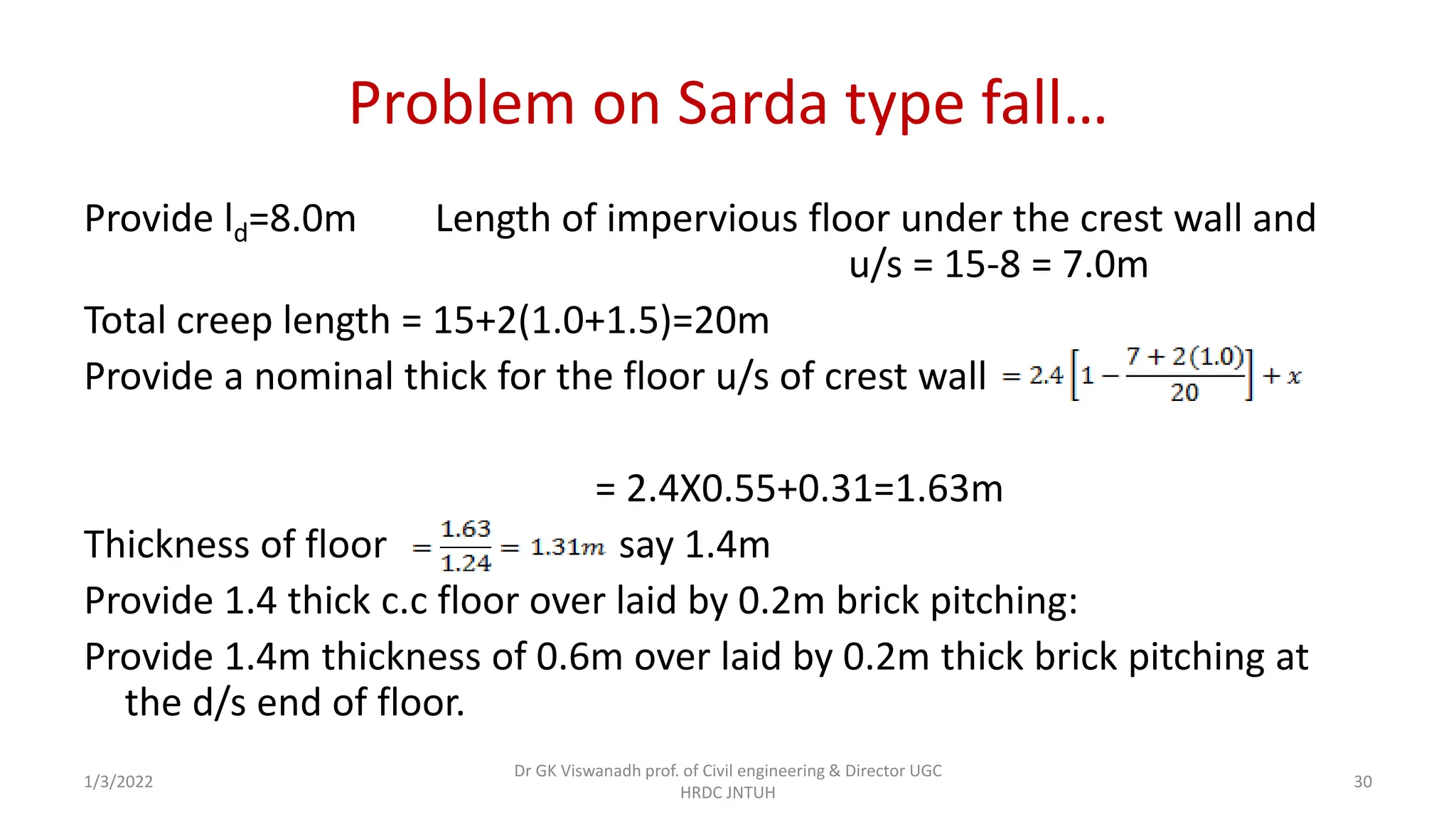
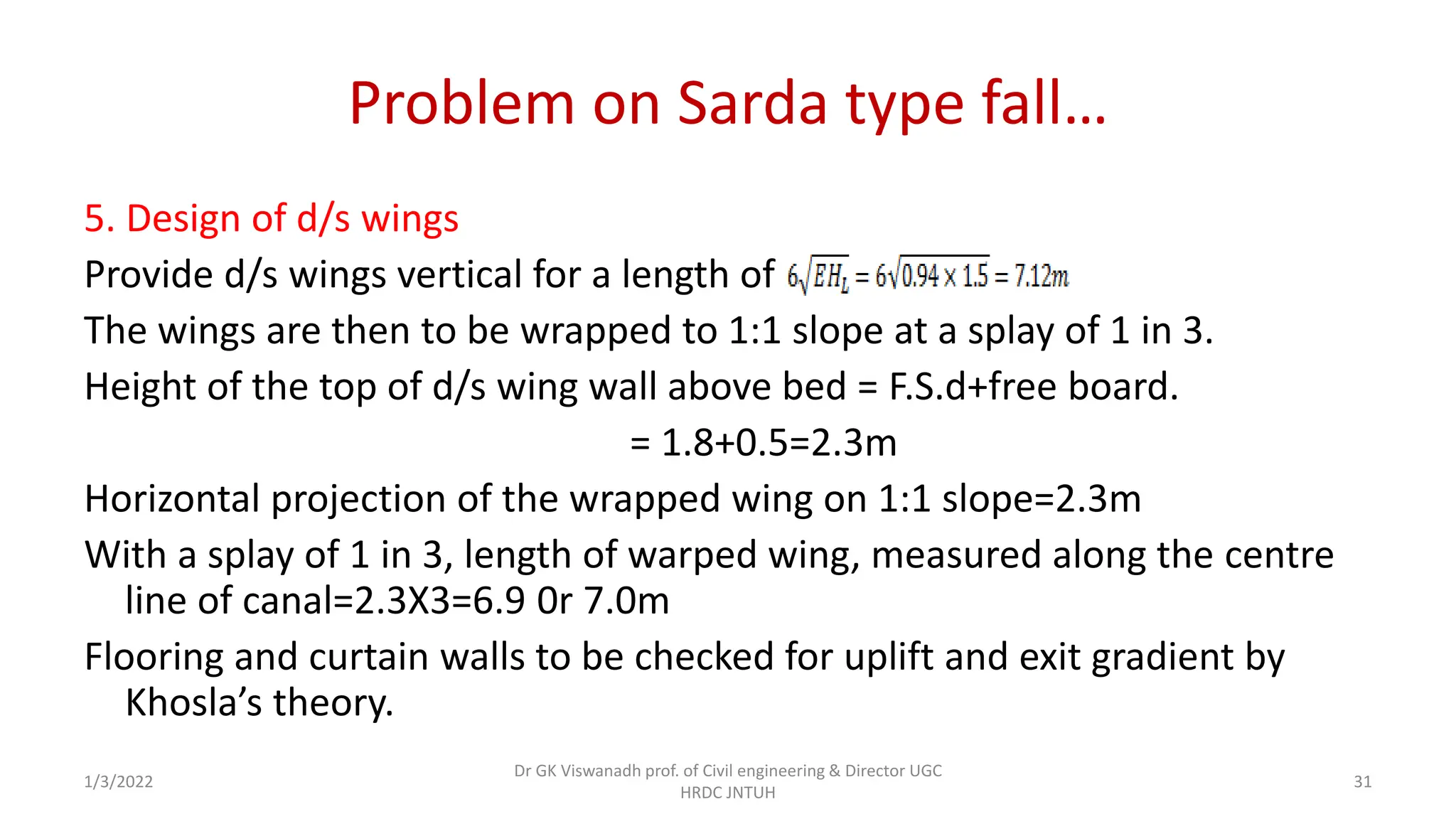
The document describes the design of a Sarda type fall. Key elements include a trapezoidal crest wall, cistern, impervious floor designed using Bligh's theory, downstream wings and protection works. An example problem is included where a Sarda fall is designed for a given canal reach with a discharge of 60 cumecs and drop of 1.5m. The crest wall, cistern, impervious floor length of 15m, downstream wings and protections works are designed and friction blocks are used as energy dissipators.