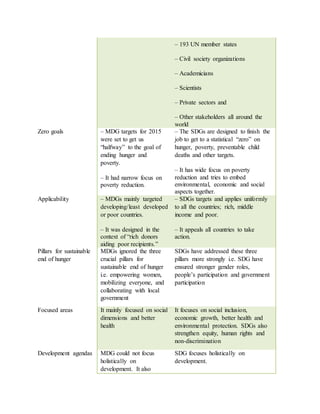
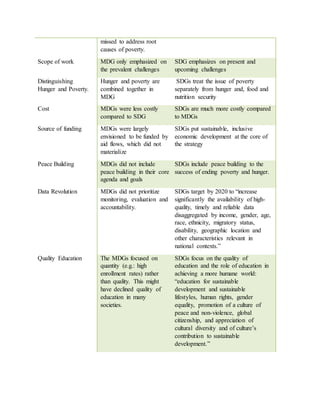
The document provides information on the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). It discusses the 8 goals of the MDGs from 2000-2015 related to poverty, education, gender equality, health, and environmental sustainability. It then outlines the 17 goals of the SDGs adopted in 2015 to build on the MDGs and address social, economic, and environmental issues globally in a more comprehensive manner through 2030. Key differences between the MDGs and SDGs include their scope, focus areas, targets, indicators, financing, and emphasis on quality of life and sustainability.