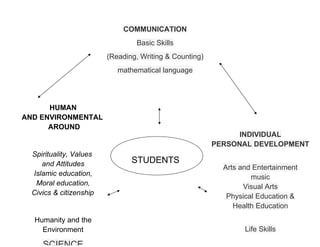
The document discusses the transformation of Malaysia's primary school curriculum. It aims to develop students' knowledge, skills, competencies and moral values to prepare them to be balanced individuals, global players, responsible citizens, and knowledge workers. The curriculum transformation involves changes to the curriculum's shape, organization, content, pedagogy, time allocation, and assessment methods. It focuses on critical thinking and creative innovation, and includes elements like creativity, entrepreneurship, and ICT skills. The transformation developed content standards and learning standards to ensure all students meet clear expectations and improve learning.