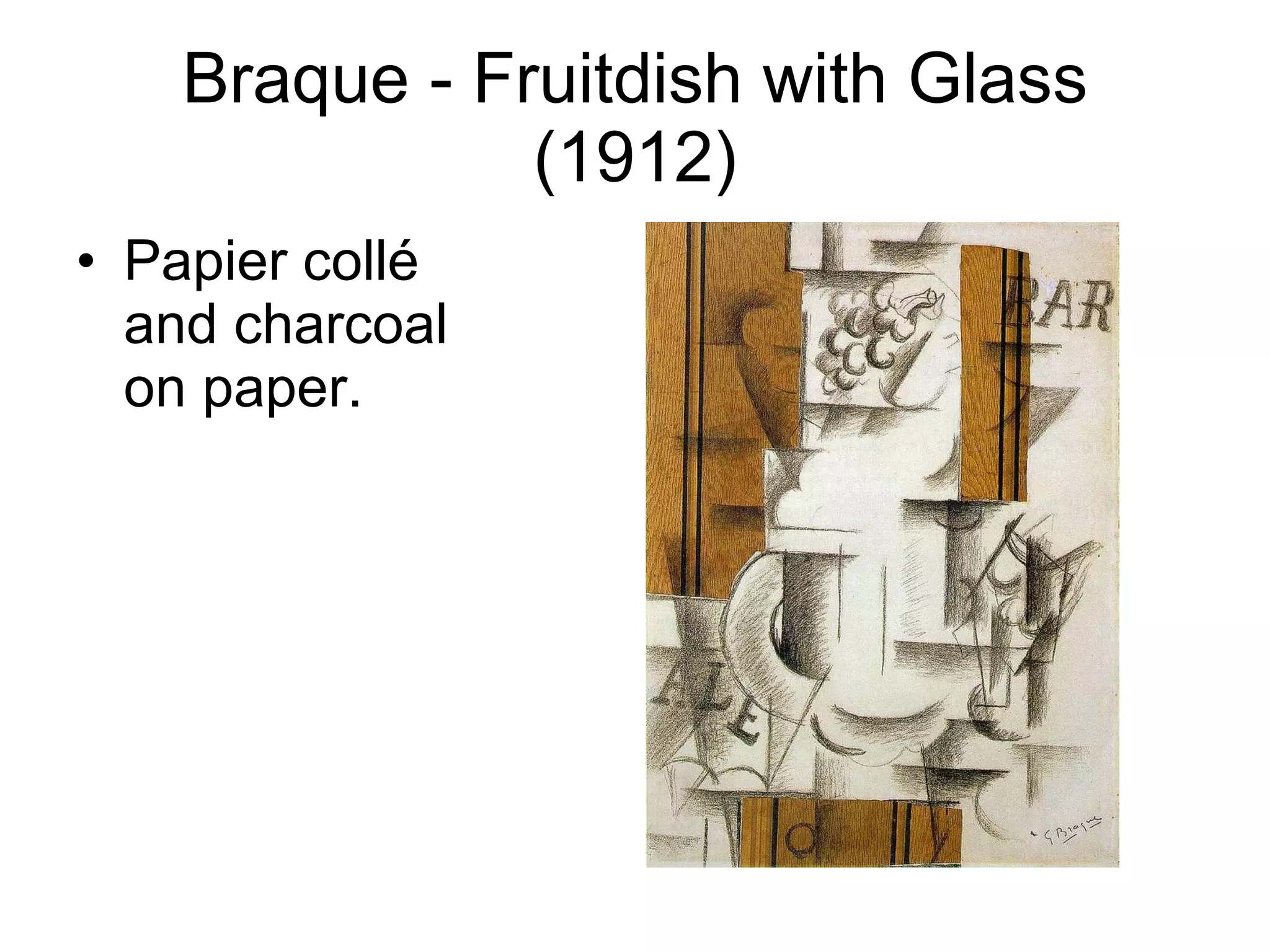
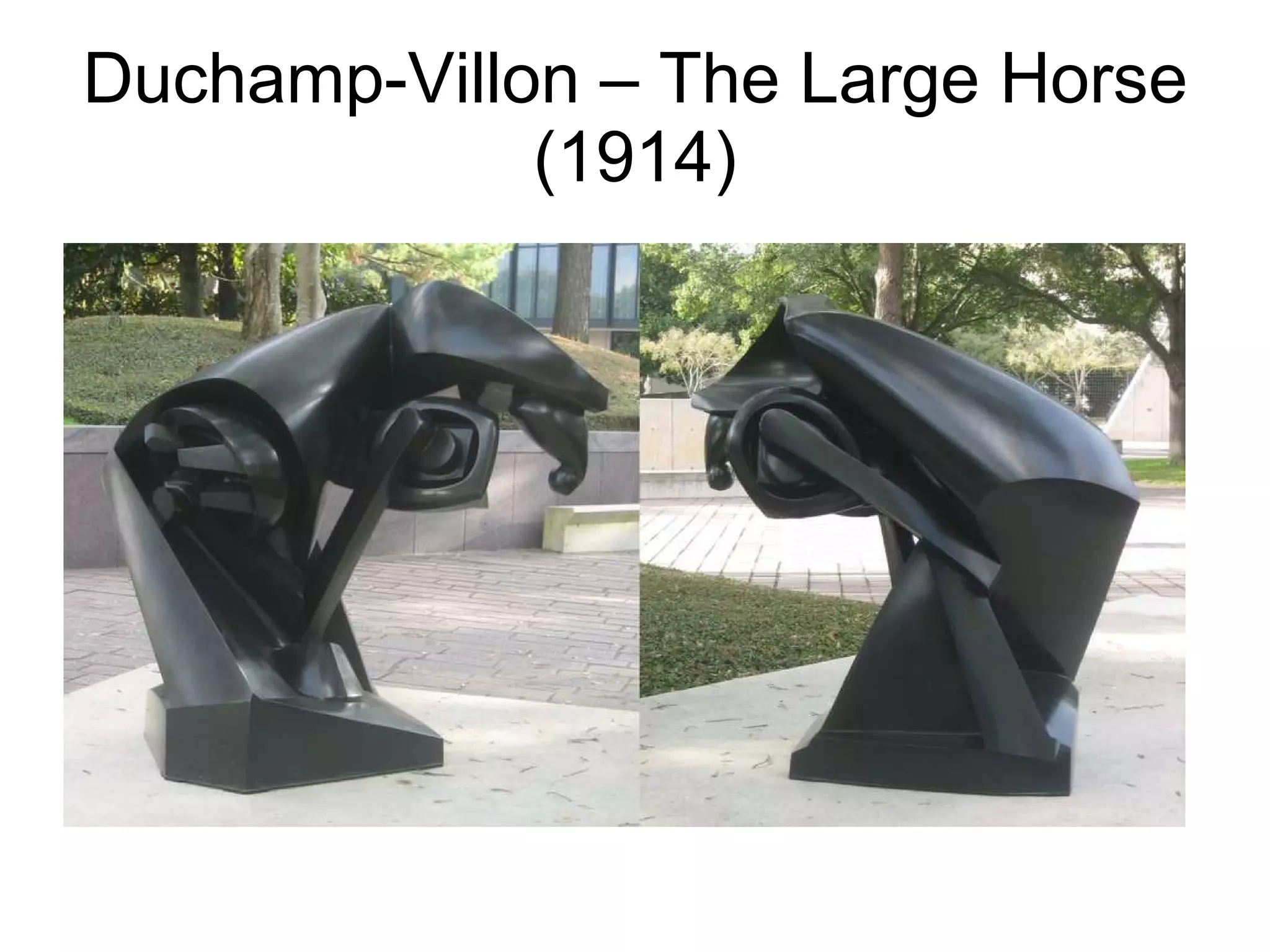
Cubism was a highly influential early 20th century avant-garde art movement that revolutionized European painting and sculpture. [1] Cubist artists such as Picasso, Braque, Gris and others depicted subjects from multiple viewpoints rather than a single perspective, breaking up objects into geometric facets and reassembling them in an abstracted form. [2] This new approach was inspired by African tribal art, Cezanne's flattening of forms, and scientific theories of the time challenging the traditional concept of absolute space and time. [3] Cubism had a profound impact on the development of art in the early 20th century, paving the way for further abstraction and revolutionizing how the visual world was