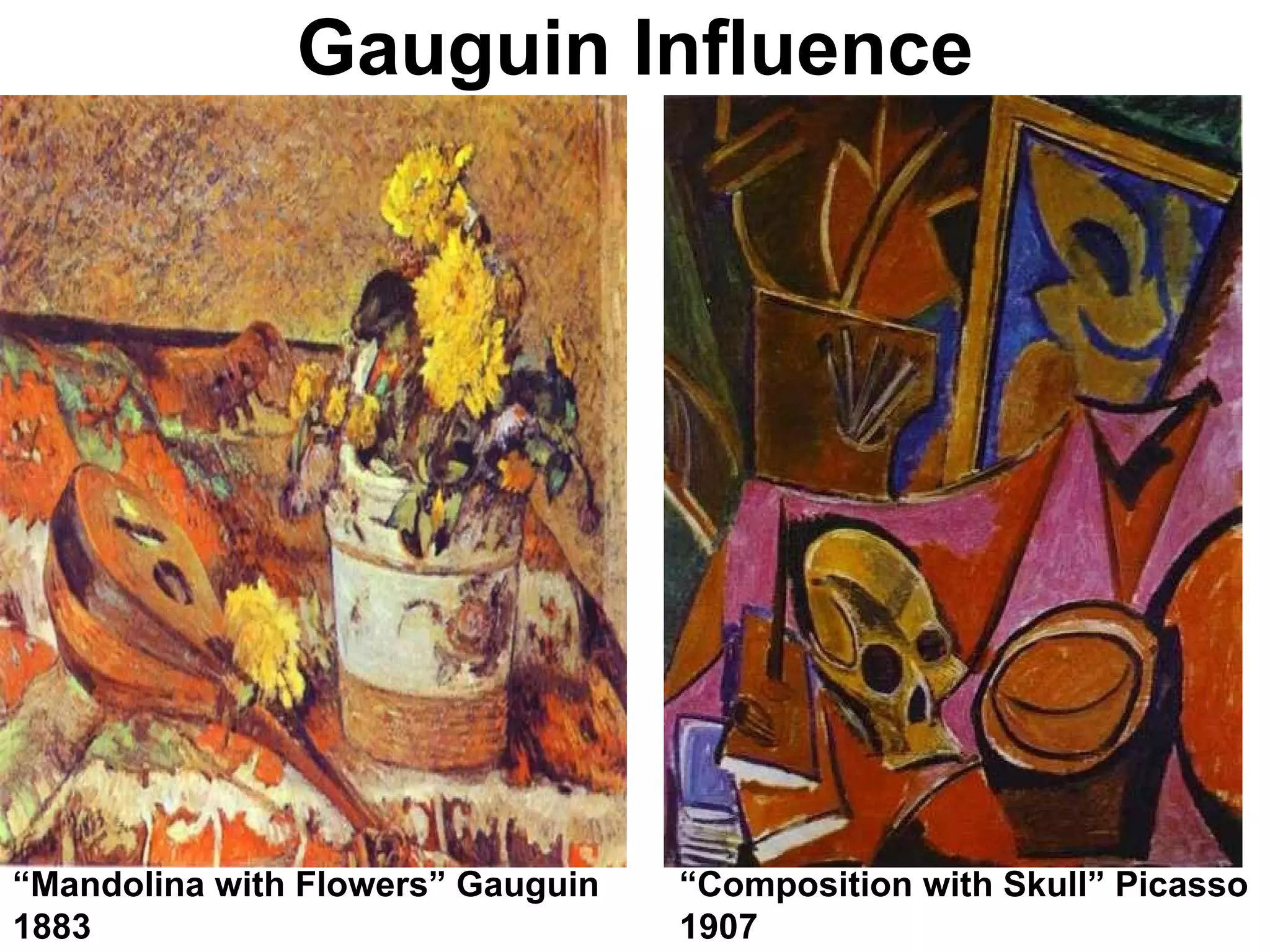
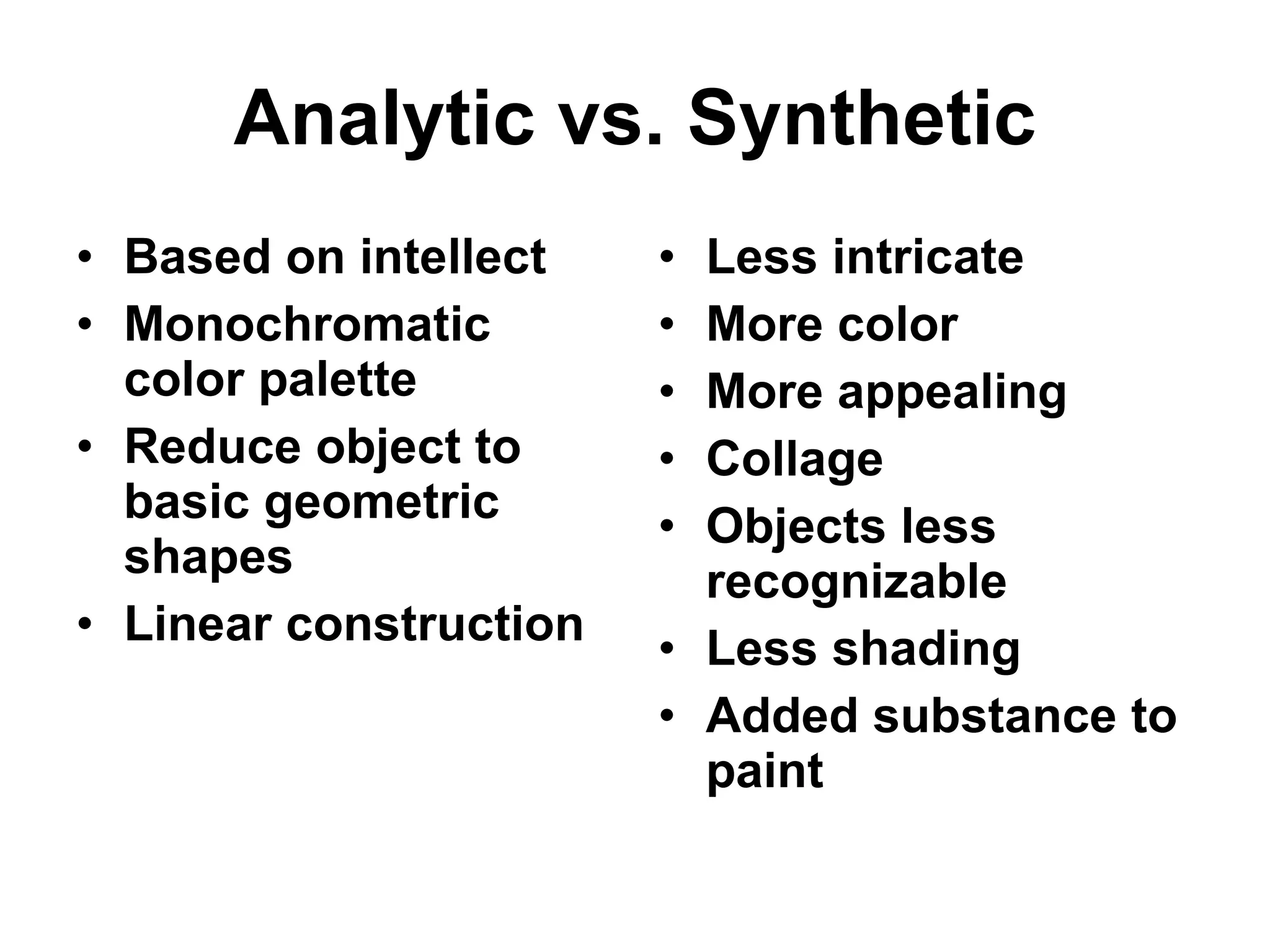
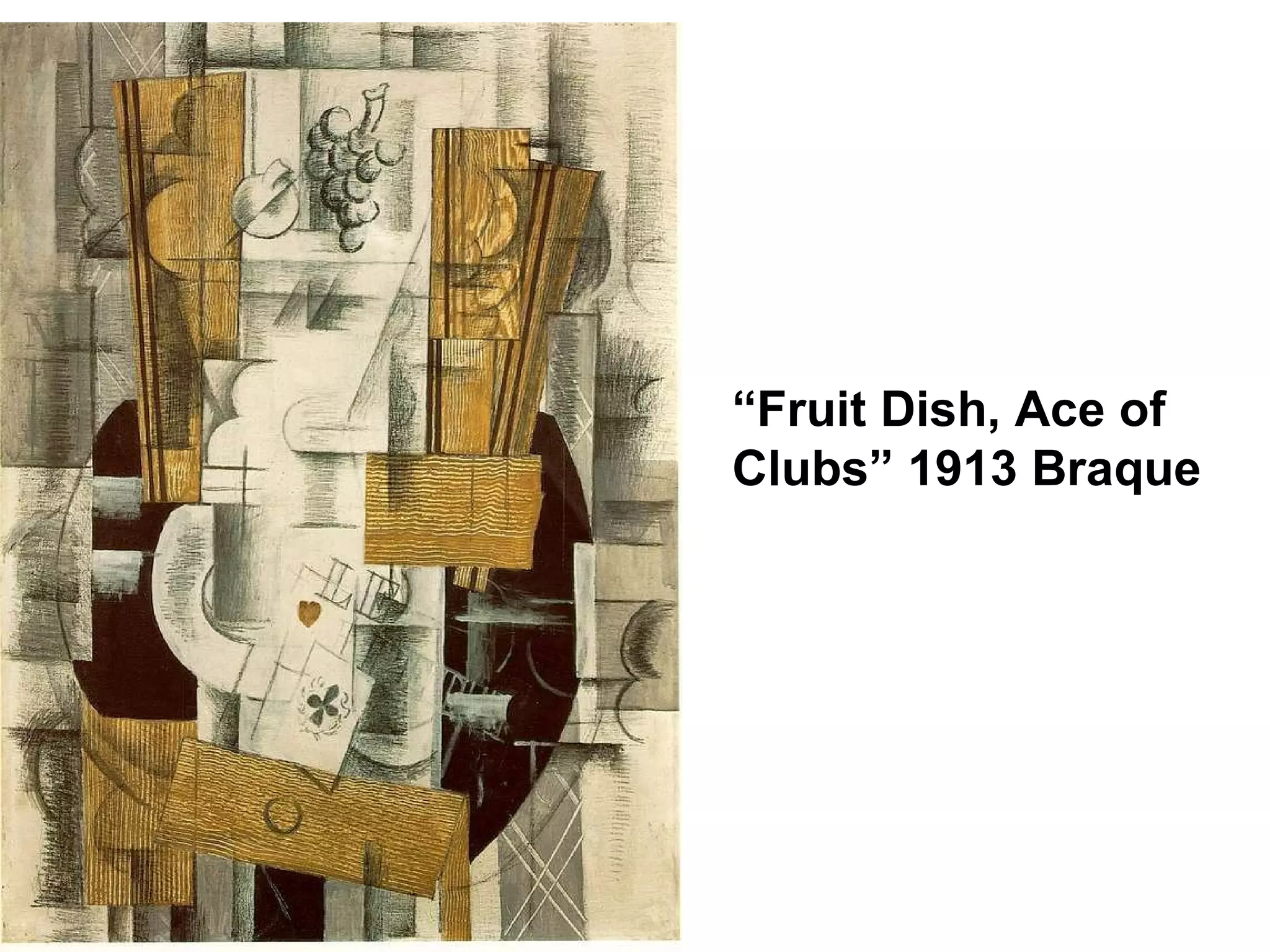
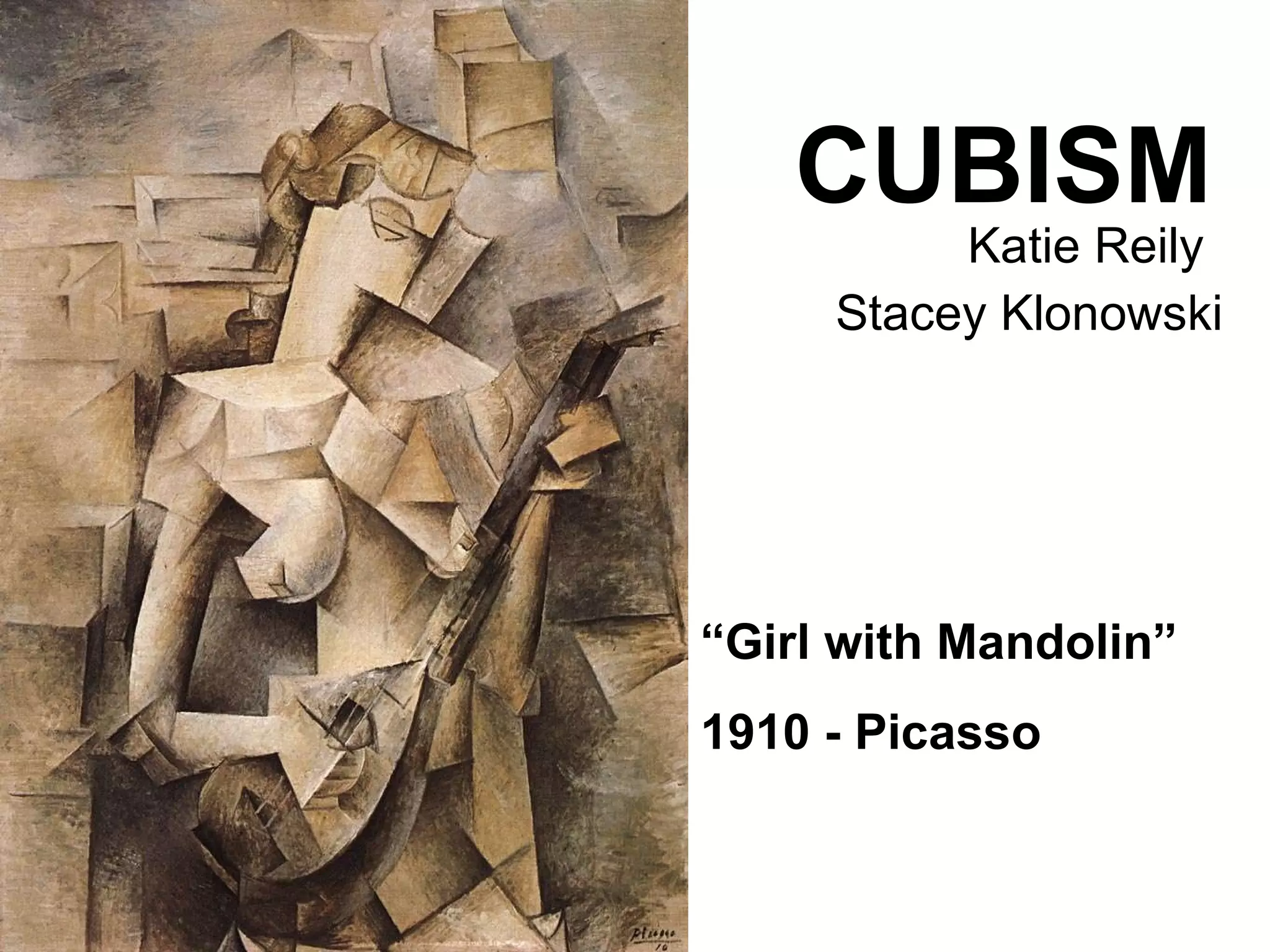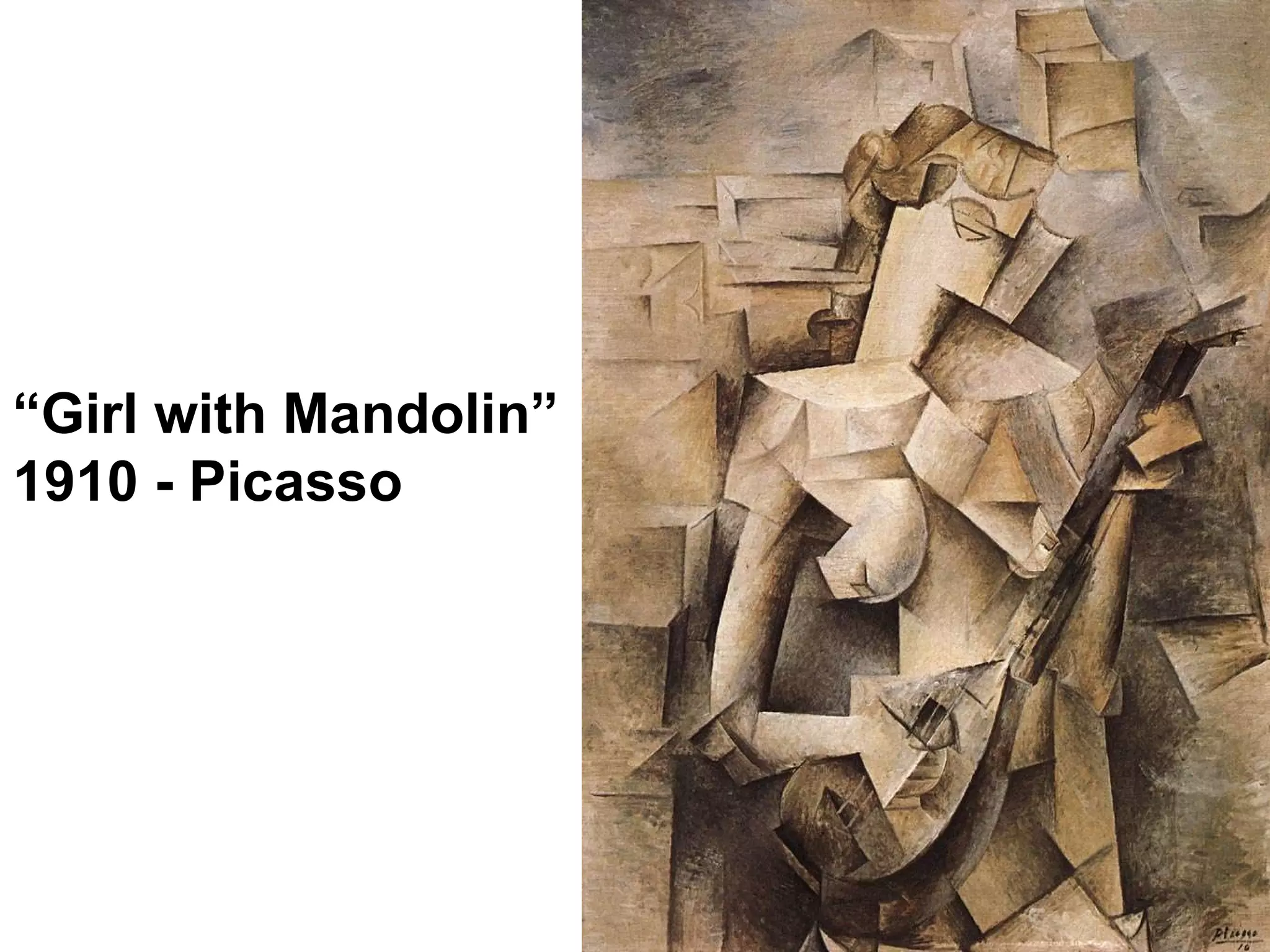Cubism was an early 20th century abstract art style developed by Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque that revolutionized European painting and sculpture. It involved depicting subjects from multiple viewpoints to represent the subject in a multidimensional way. The two main phases were Analytic Cubism, which used monochromatic colors and focused on reducing forms to geometric shapes, and Synthetic Cubism, which introduced collage and a wider use of color. Cubism influenced many later artistic movements and fundamentally changed how visual art was conceived.