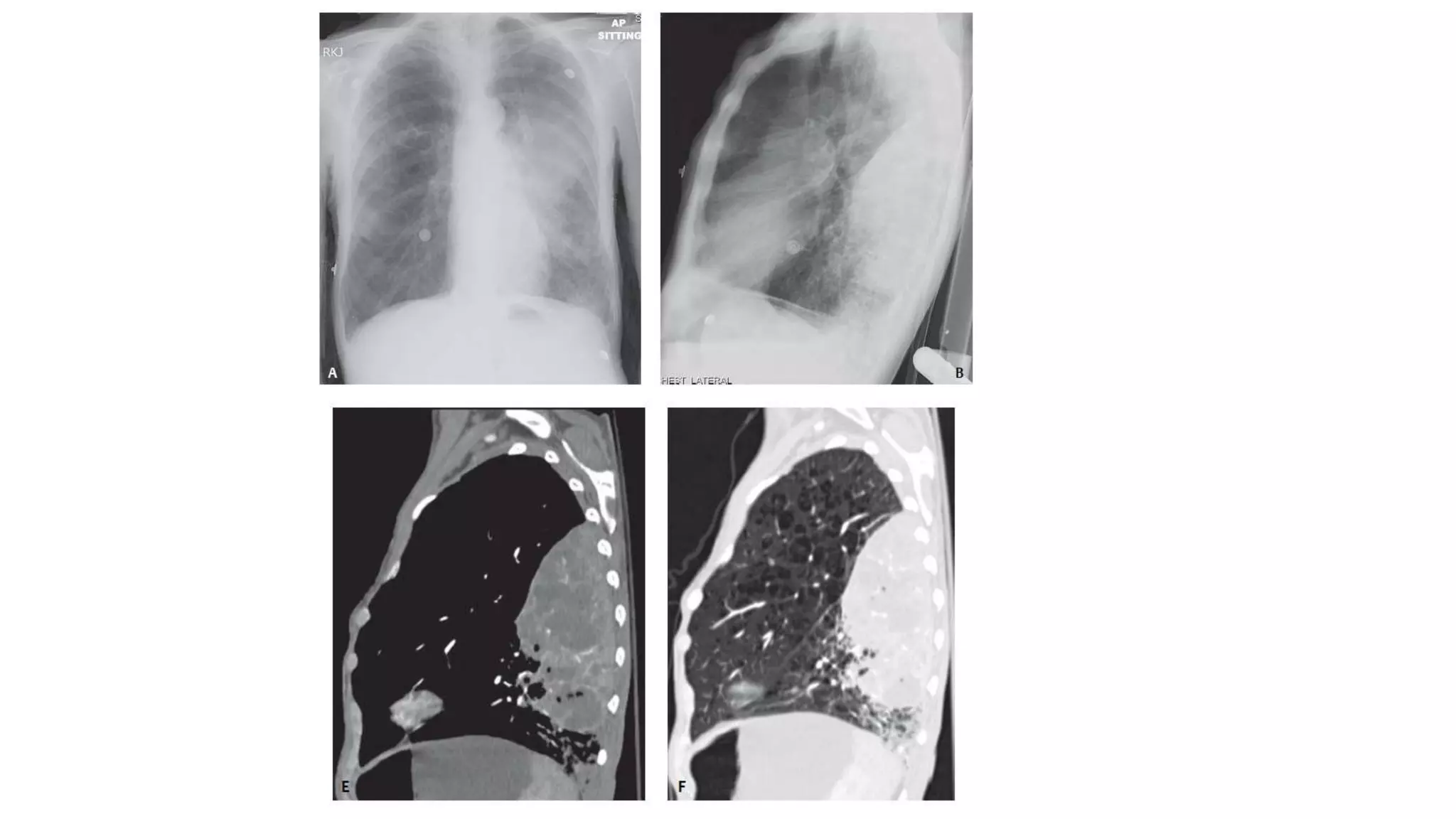
This document summarizes computed tomography findings for various chest diseases. It describes imaging appearances of different types of pneumonia including streptococcus, staphylococcus, haemophilus influenzae, klebsiella and pseudomonas. It also discusses tuberculosis and various lung cancers such as adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, small cell carcinoma and lymphoma. Key imaging features for differentiating benign from malignant lung nodules are provided. Imaging patterns for various infectious, inflammatory and neoplastic lung diseases are concisely described.