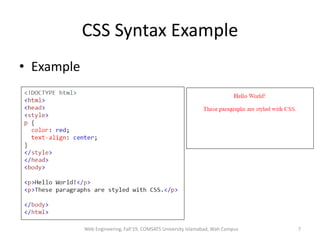
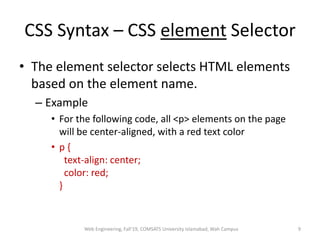
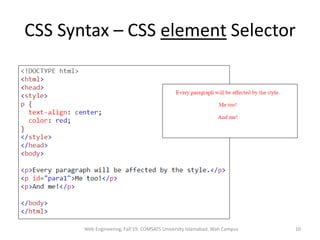
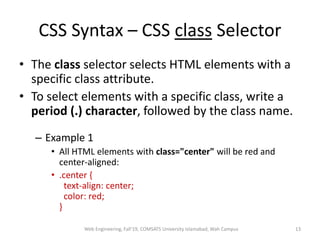
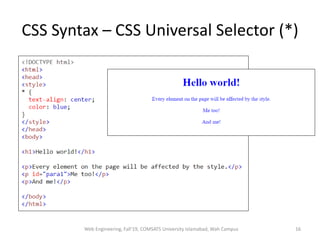
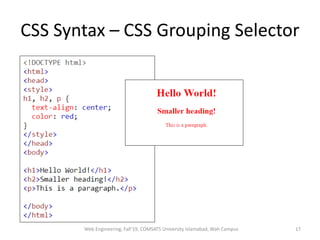
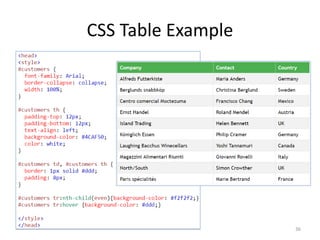
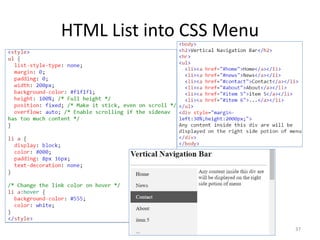
The document discusses Week 2 of a course on Cascading Style Sheets (CSS). It covers topics like what CSS is according to W3Schools, why CSS is used, CSS syntax including selectors, the CSS style tag, and adding CSS through internal, external, and inline styles. Examples are provided of different CSS selectors like the element, id, class, and grouping selectors. The document also discusses CSS comments, HTML tags like <article> and <div>, pseudo-classes, tables, and converting HTML lists into menus with CSS.