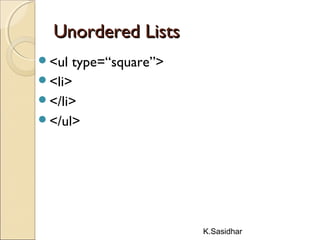
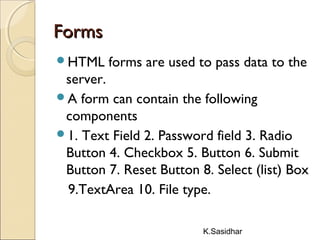
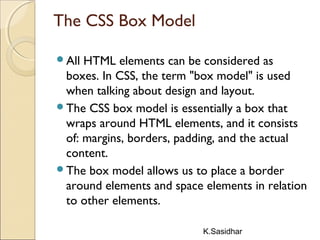
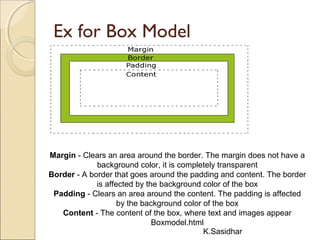
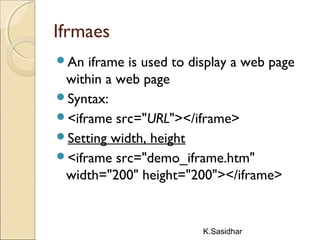
This document provides an overview of web technologies including definitions of key terms like the web, world wide web, hypertext, hyperlinks, browsing, and web browsers. It describes different types of browsers and explains concepts like websites, web servers, and HTTP. The document also summarizes common web technologies like HTML, CSS, forms, images, frames, tables and entities. It provides examples and explanations of how to use various HTML tags to structure documents and embed content.