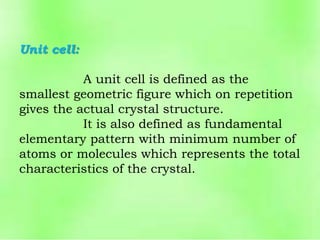
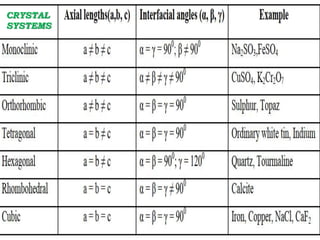
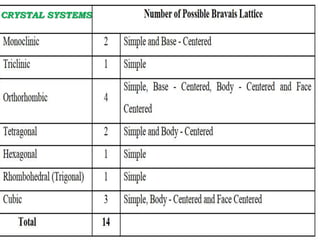
This document discusses the classification and structure of crystalline solids. It begins by introducing the differences between solids, liquids, and gases, and how the properties of solids depend on their structure at the atomic level. Solids are then classified as either crystalline or amorphous based on whether the atoms are arranged in a systematic pattern or irregularly. Crystalline solids can be single crystals or polycrystals. Crystallography studies the structures, properties, and symmetries of crystals. Crystals have a repeating lattice structure defined by lattice points, lines, and planes. This lattice structure combined with a basis of atoms forms the overall crystal structure. Crystals are further classified into seven crystal systems and fourteen Bravais latt