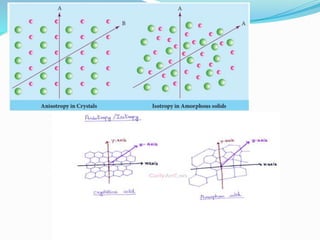
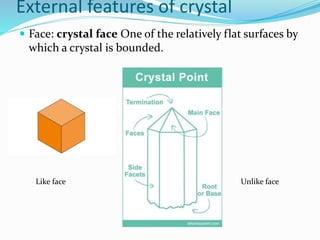
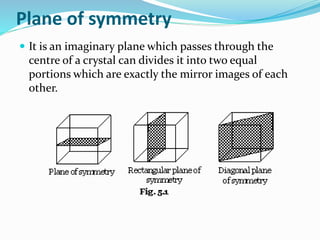
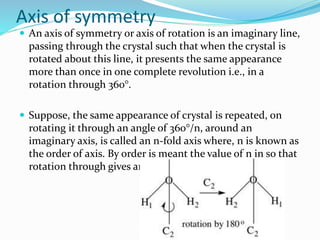
This document discusses the crystalline structure of materials and symmetry elements in crystals. It defines a crystal as a solid with atoms, molecules, or ions arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure called a lattice. Crystals can be isotropic, with uniform properties in all directions, or anisotropic, with properties that vary by orientation. The flat surfaces that bound a crystal are called faces. Crystals exhibit symmetry through repetitive patterns of atomic arrangement. There are three types of symmetry elements: planes of symmetry that divide the crystal into mirror images, axes of symmetry where rotation around the axis presents the same appearance multiple times, and centers of symmetry at the crystal's center point.