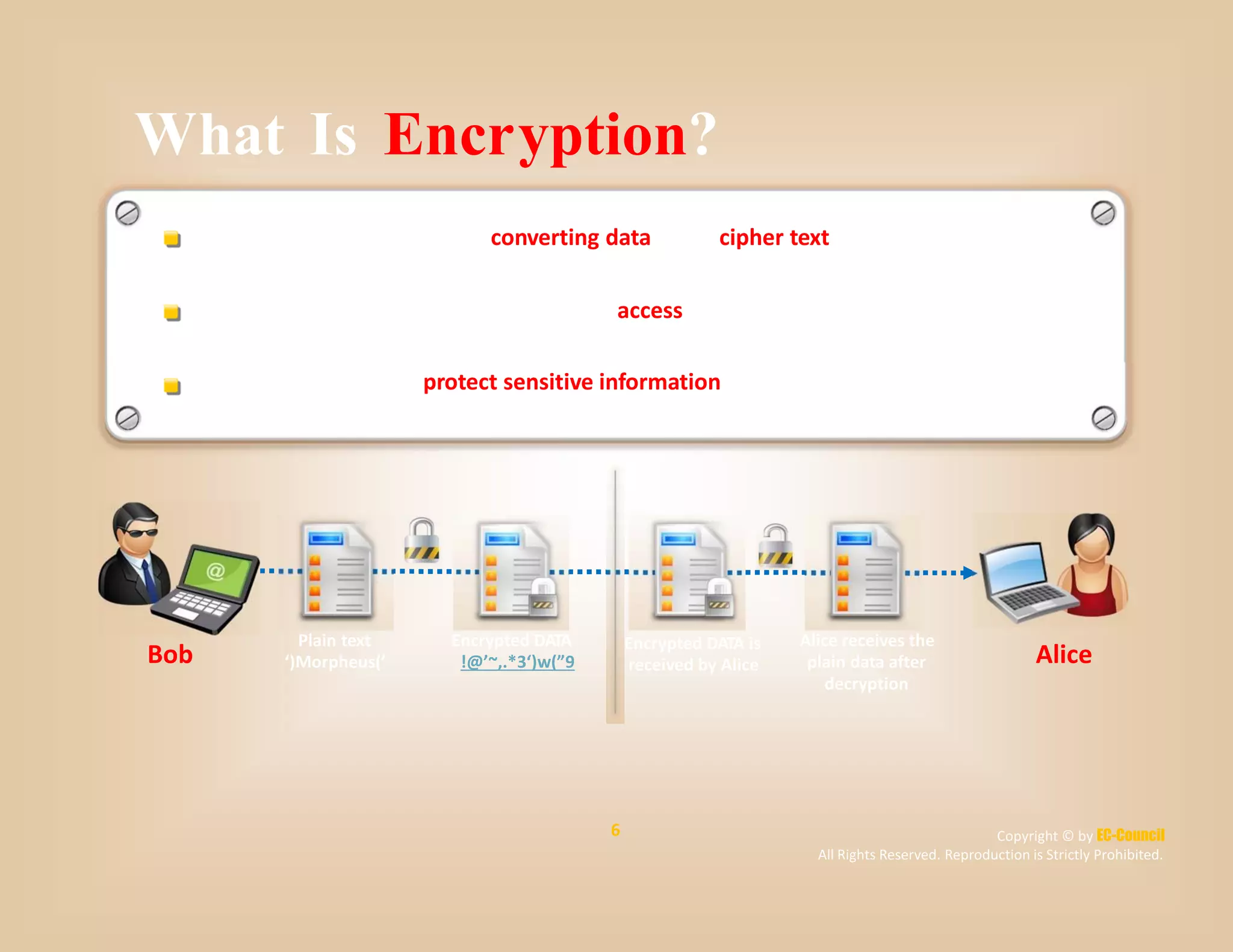
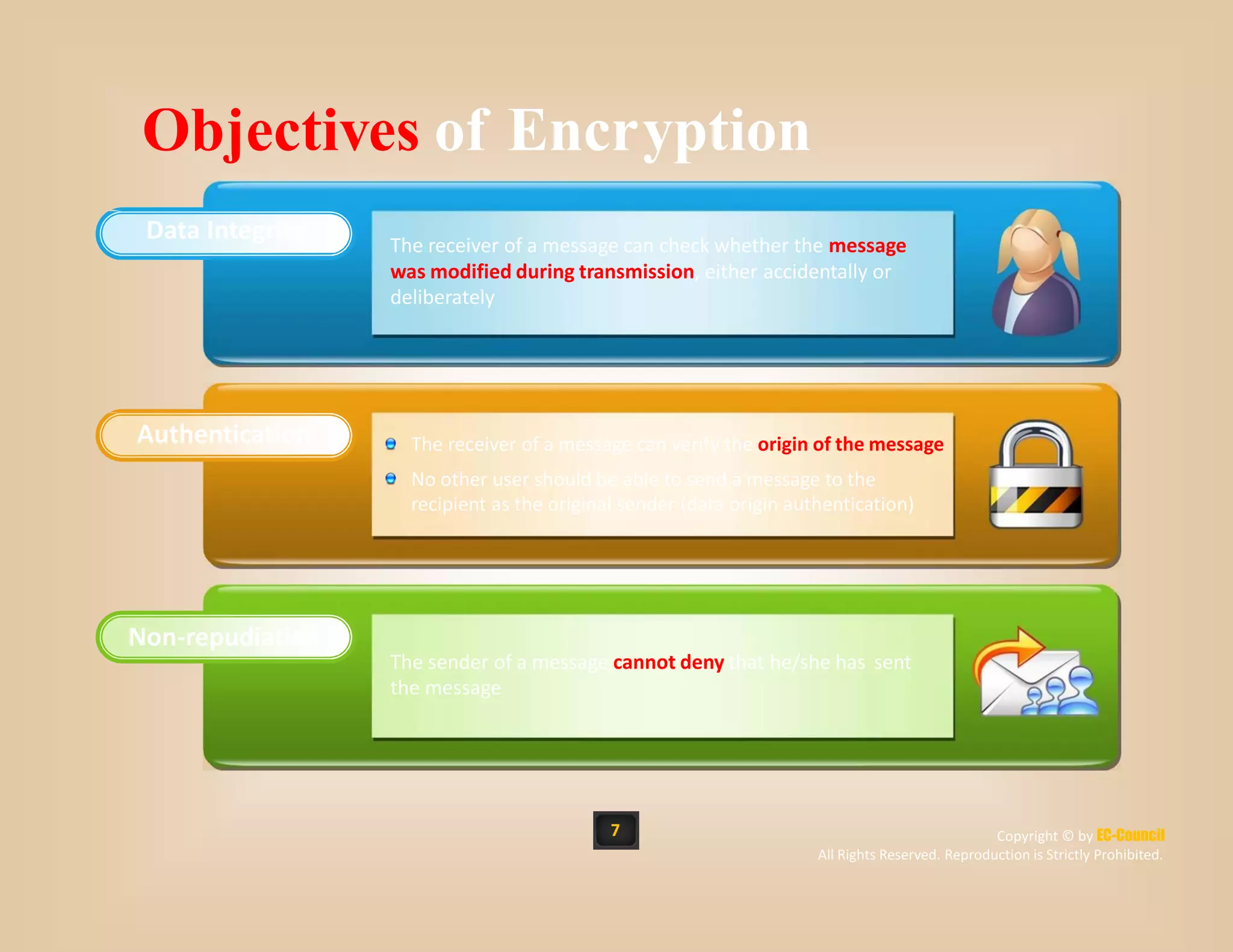
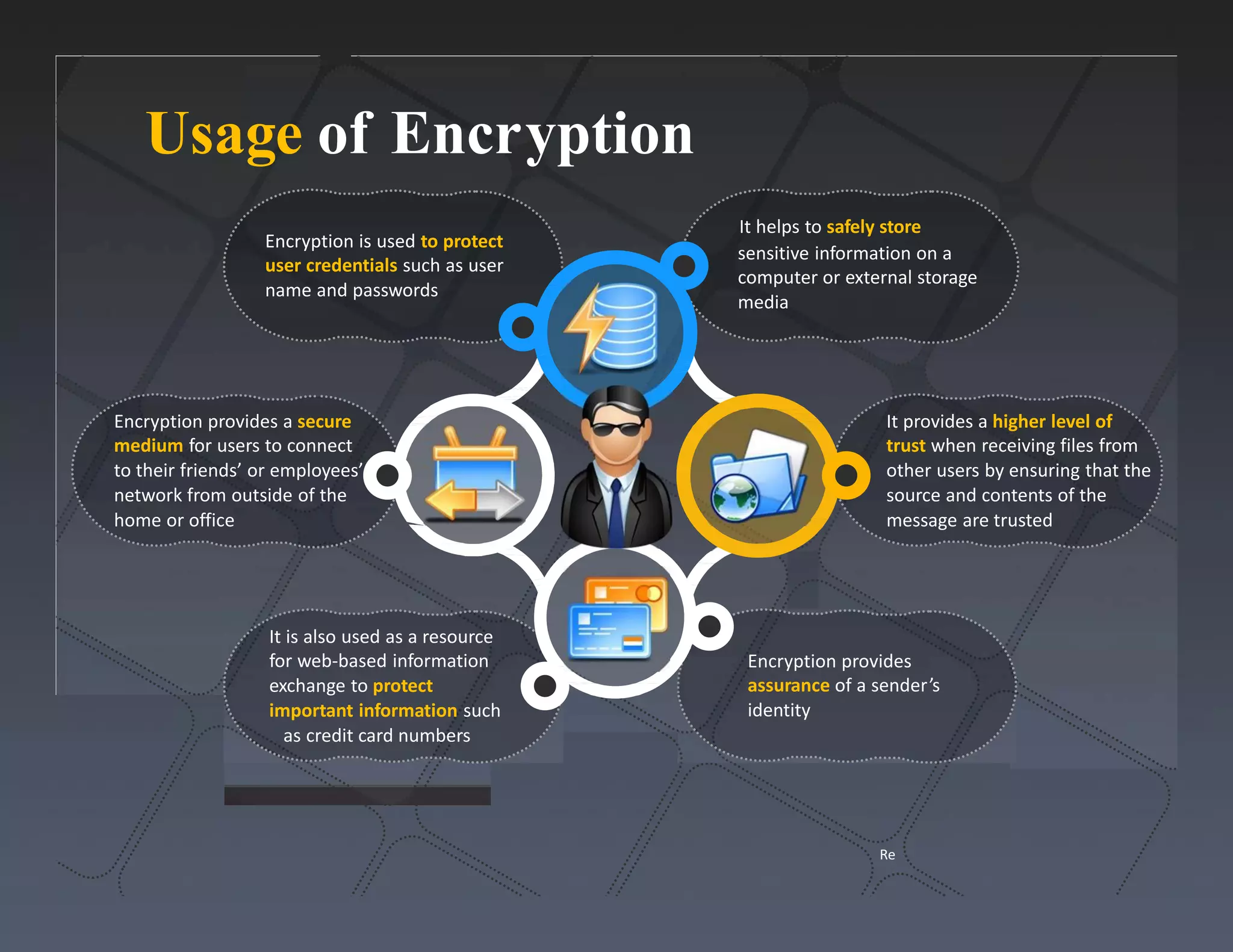
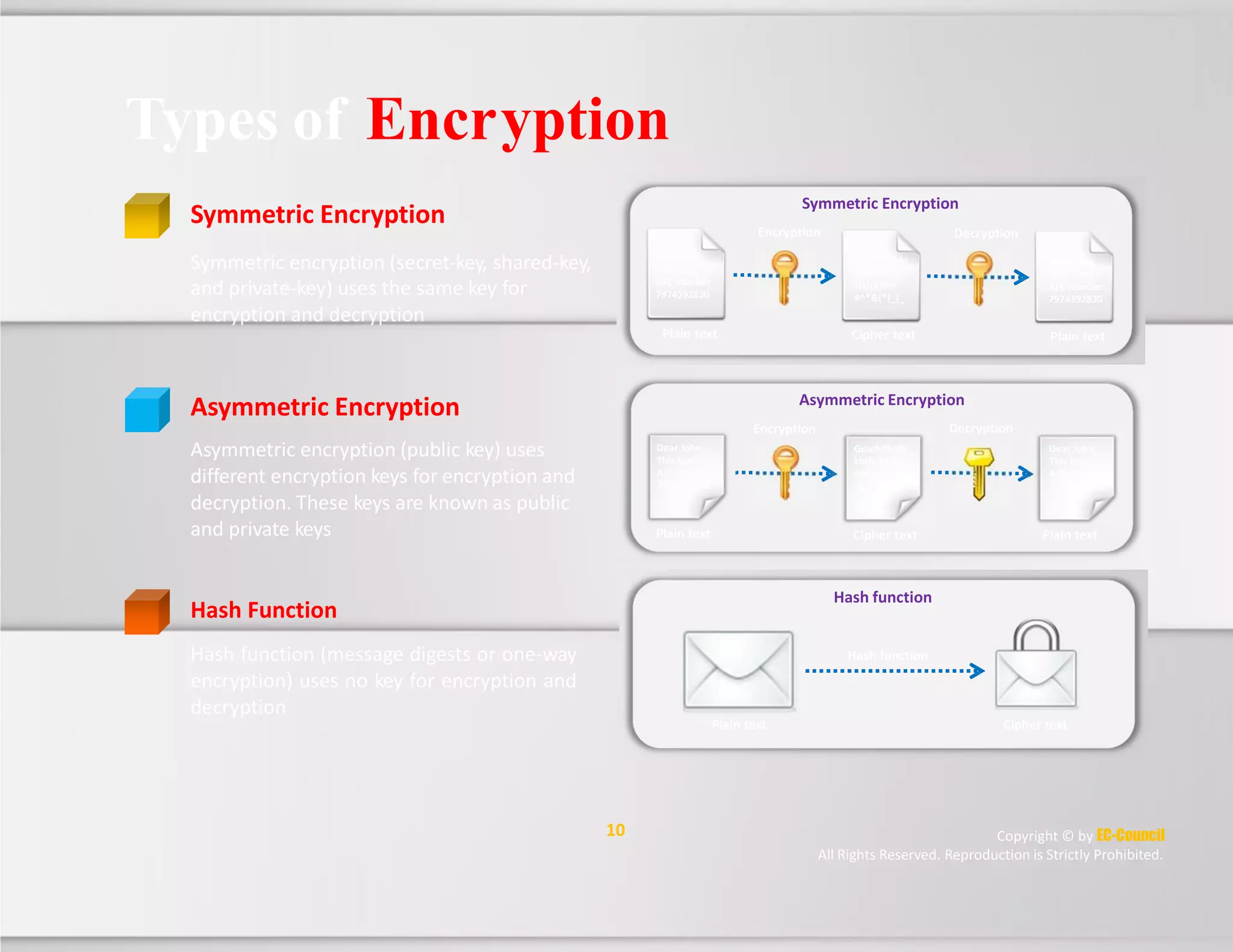
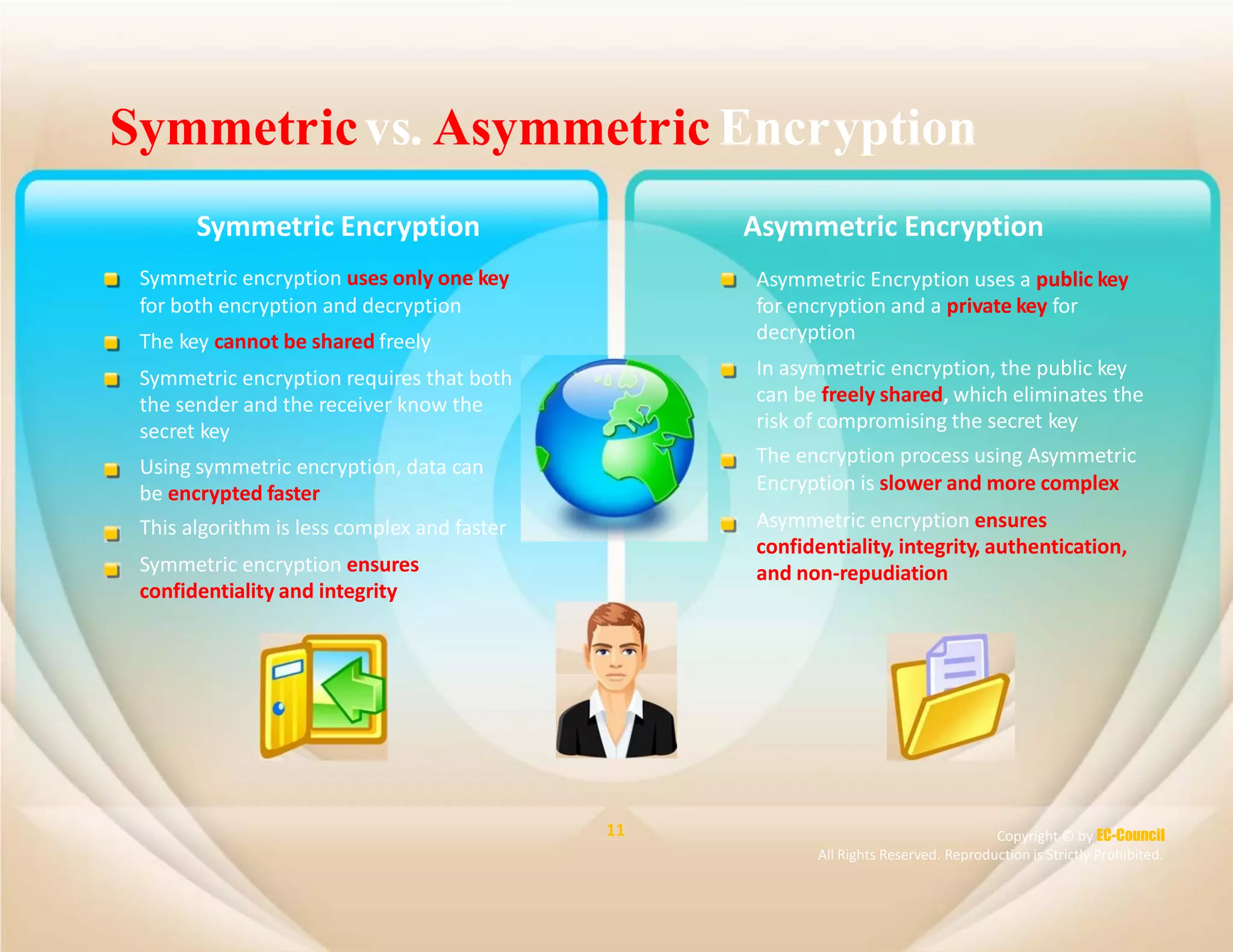
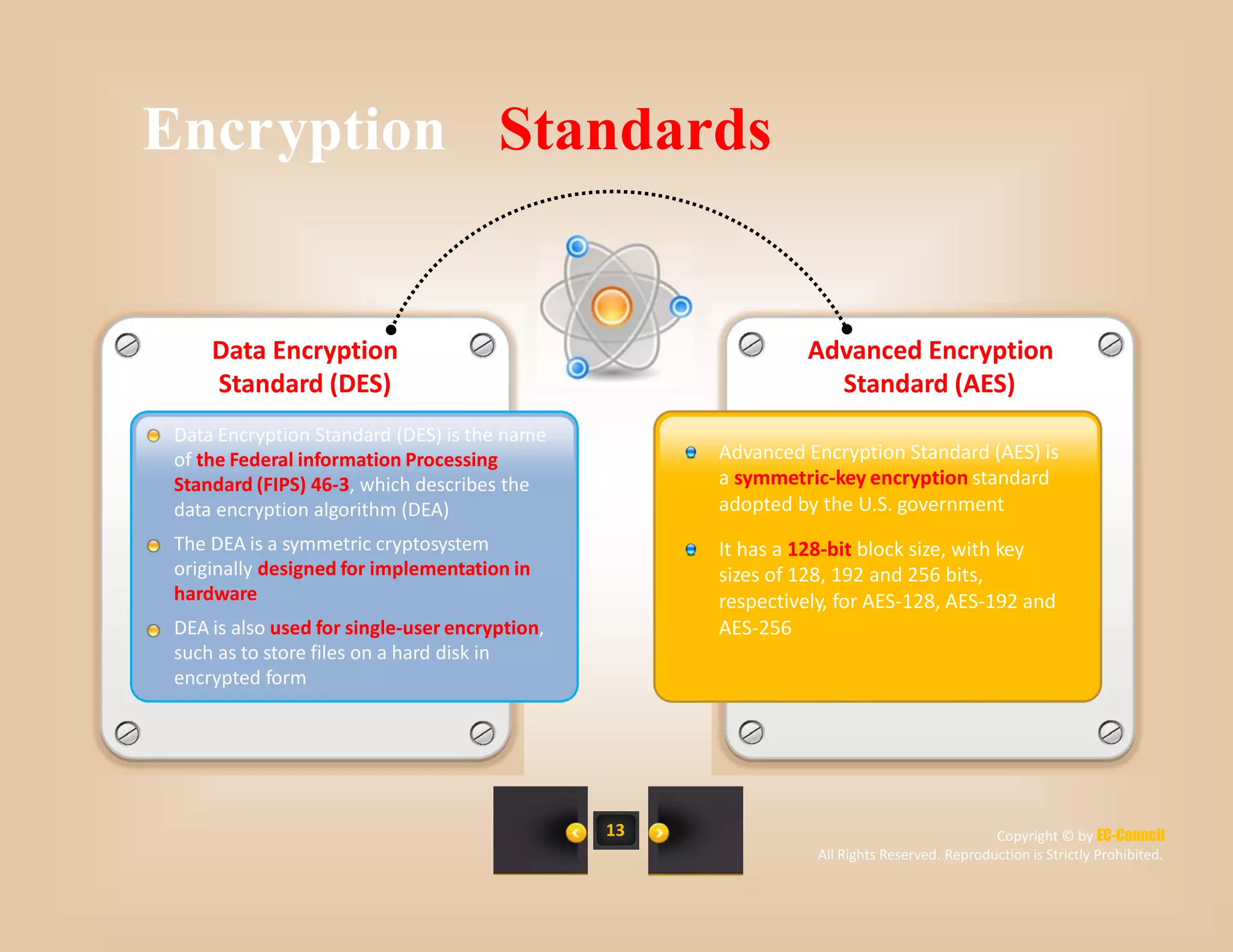
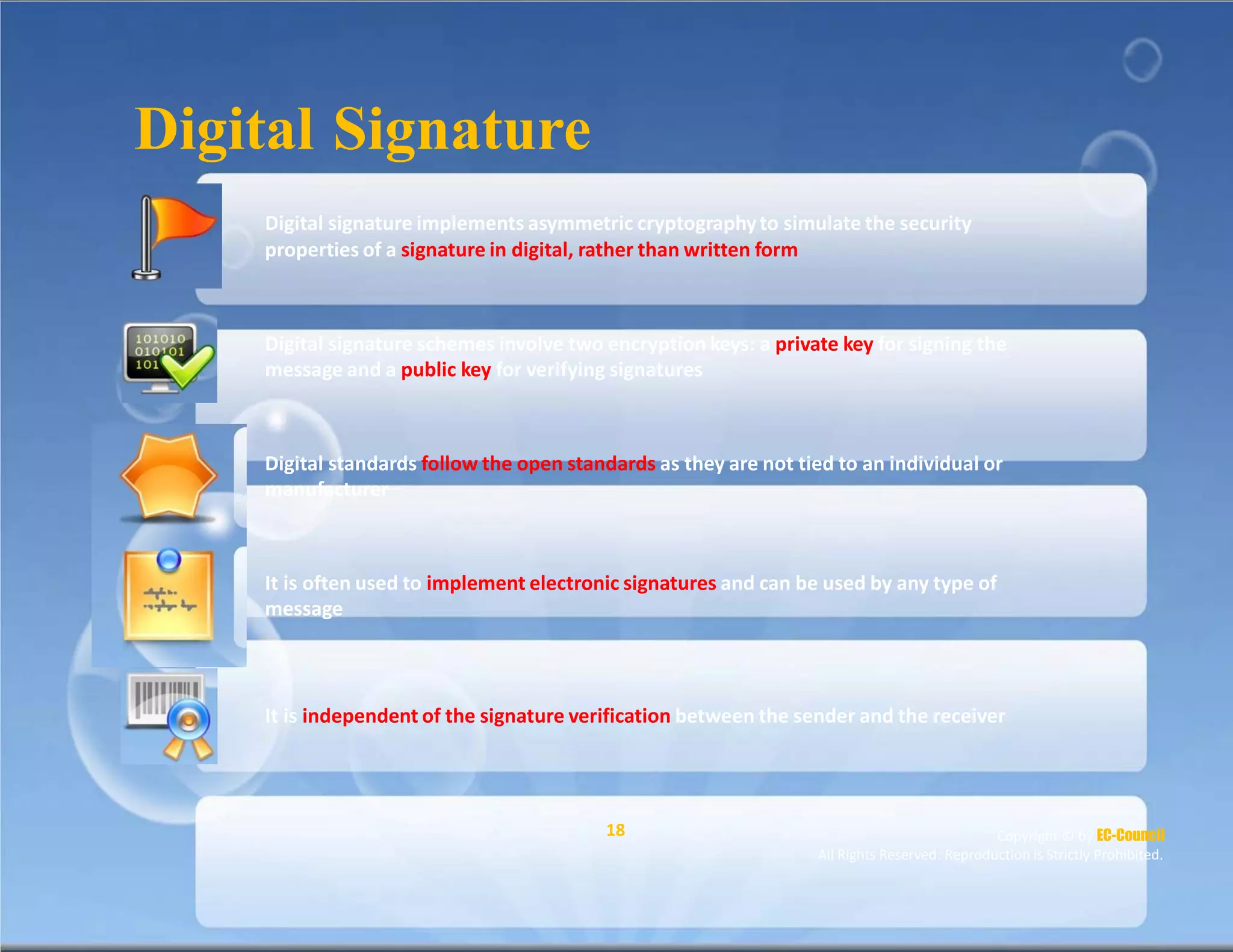
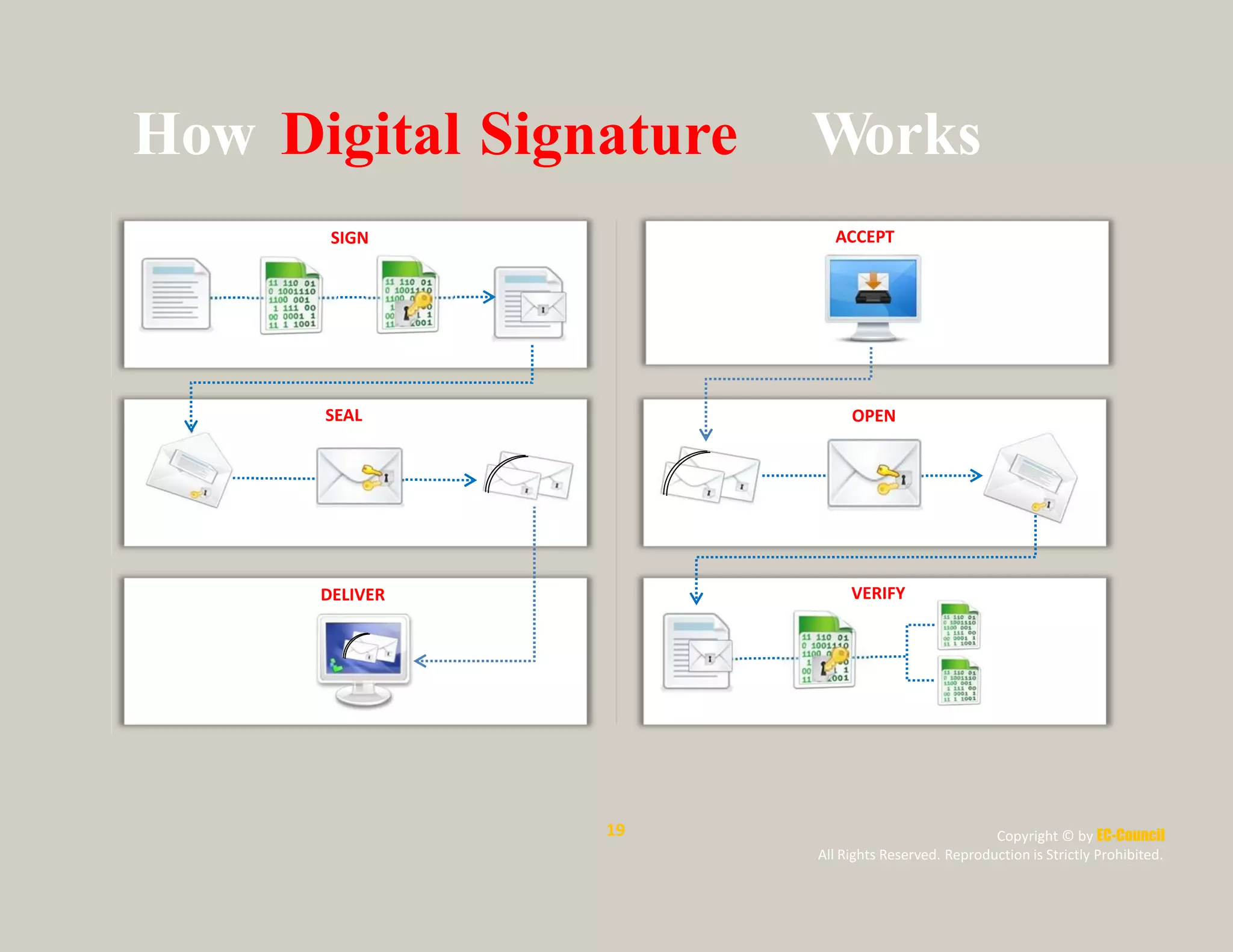
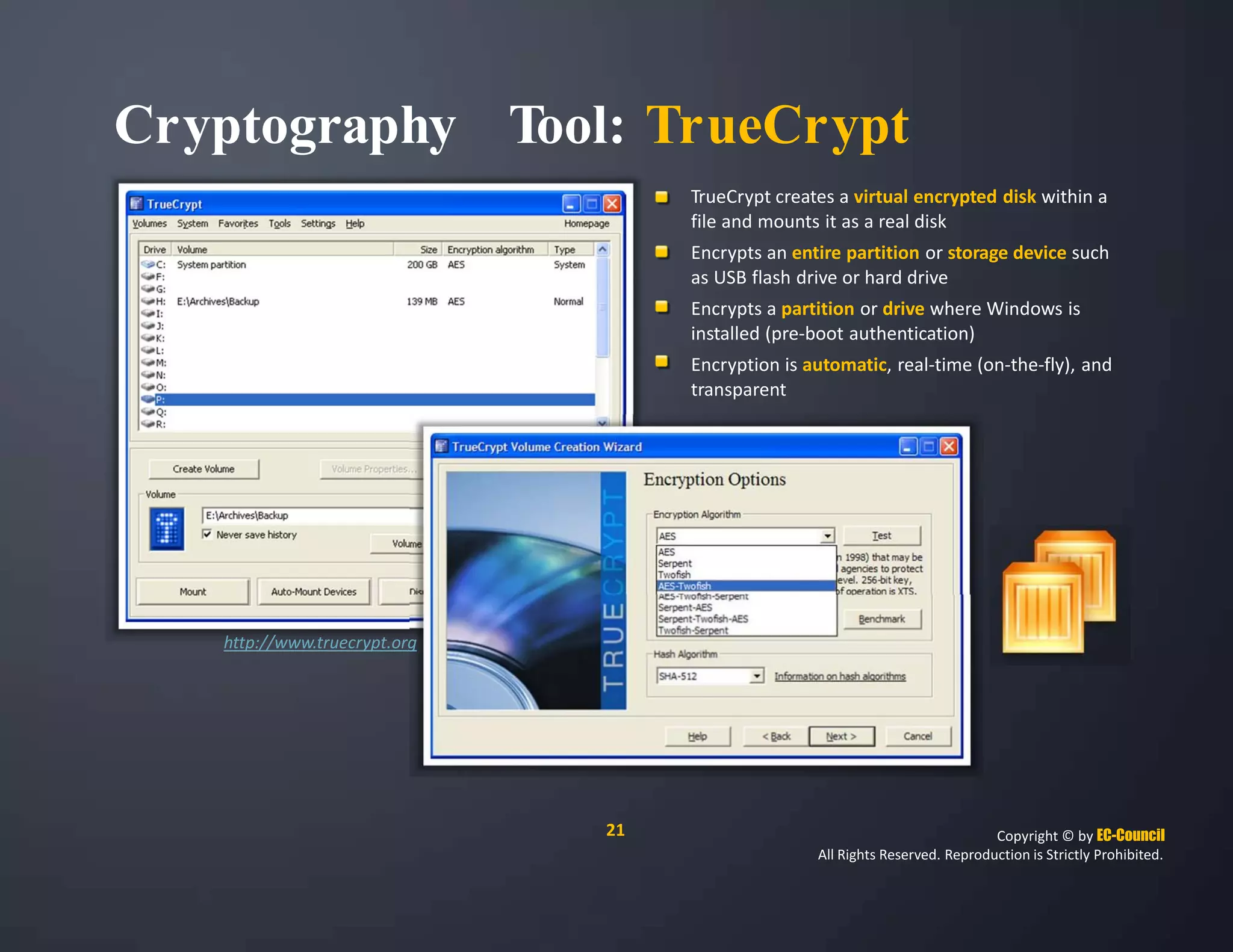
The document discusses a survey of IT security specialists that found 40% believe they could hold their employer's network hostage by withholding encryption keys after leaving the company. A third were confident they could bring a company to a halt with little effort using their knowledge of encryption keys and certificates. The CEO of Venafi, which conducted the survey, said companies must effectively manage encryption keys to avoid breaches.