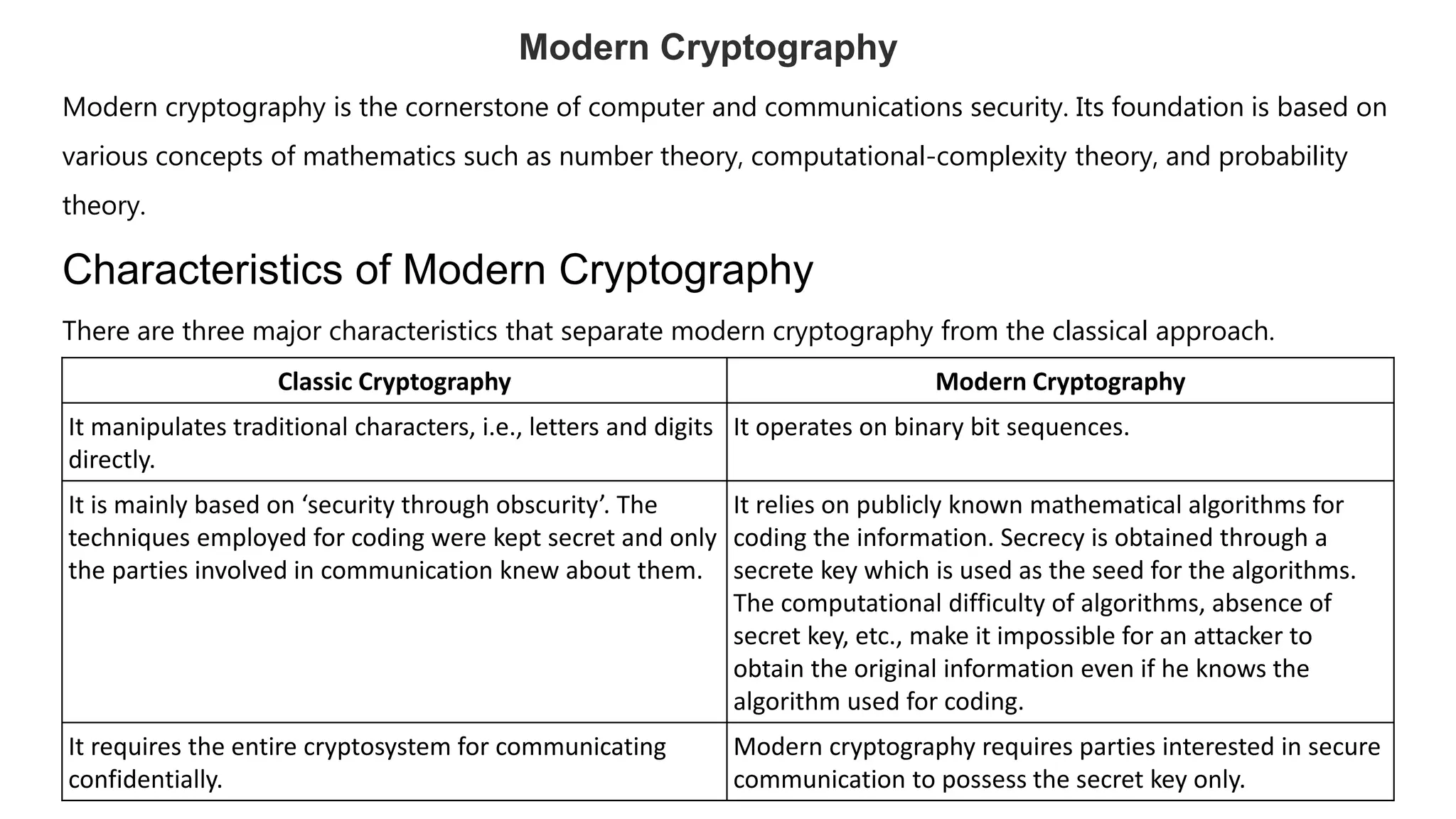
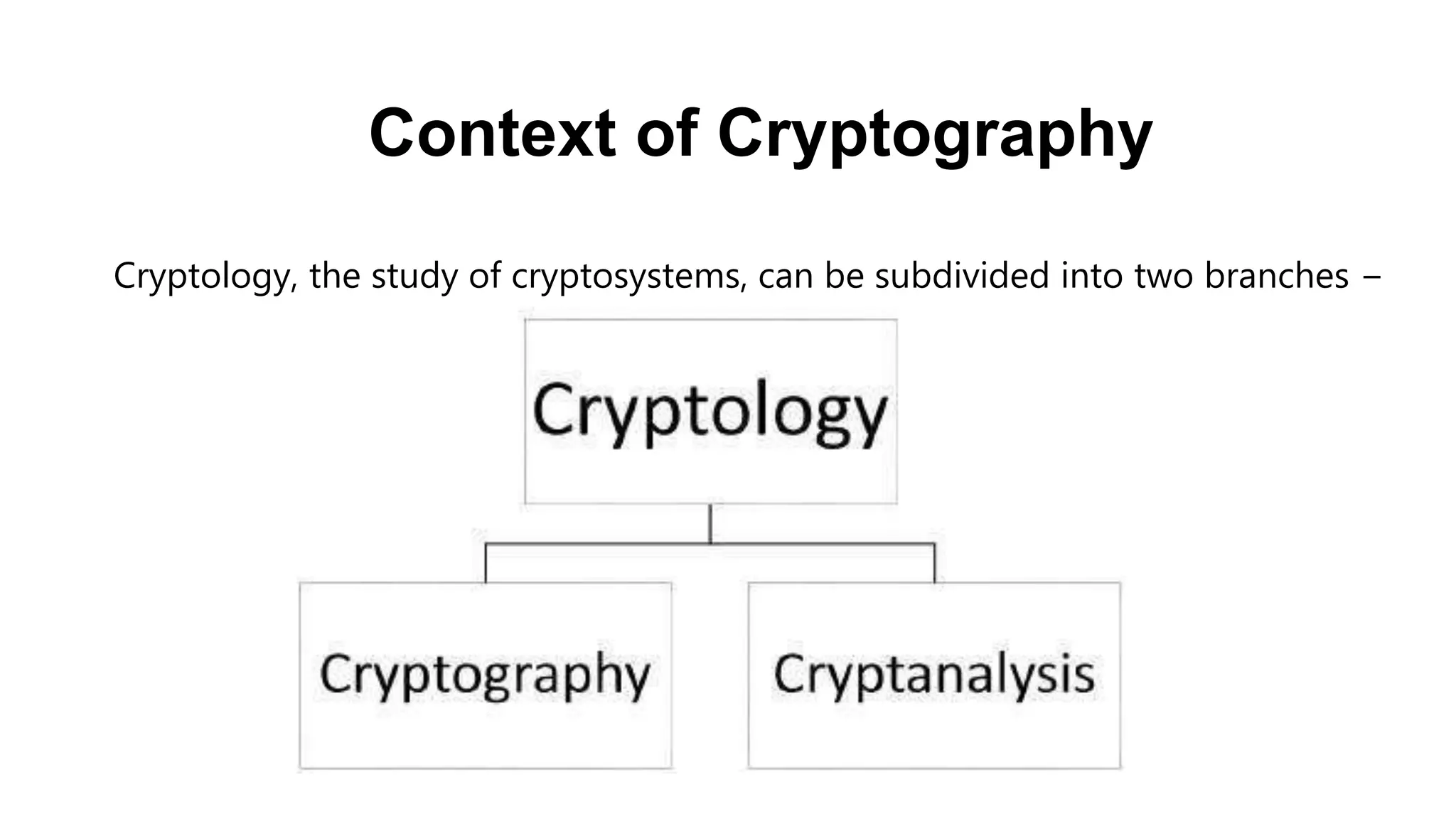
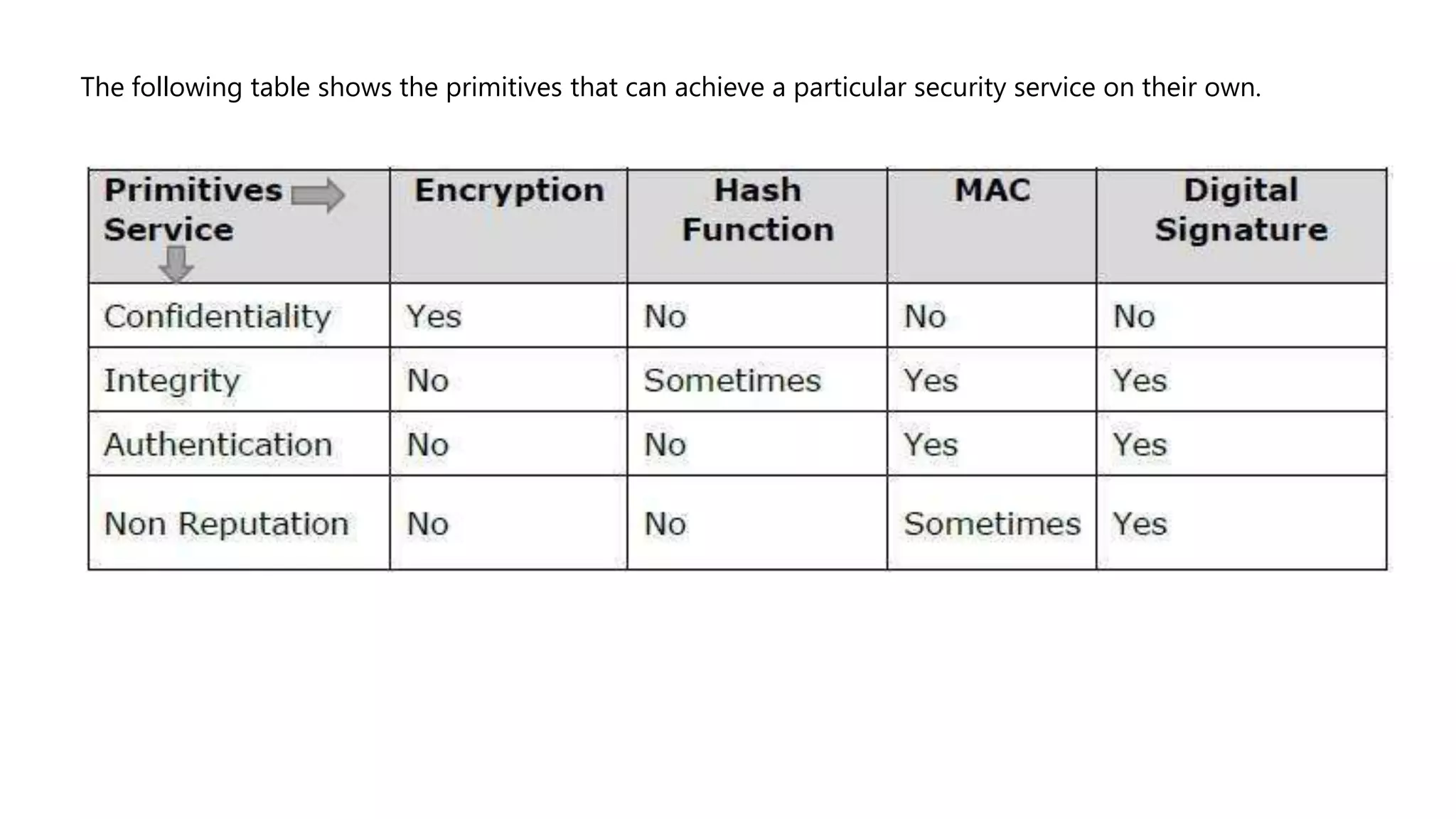
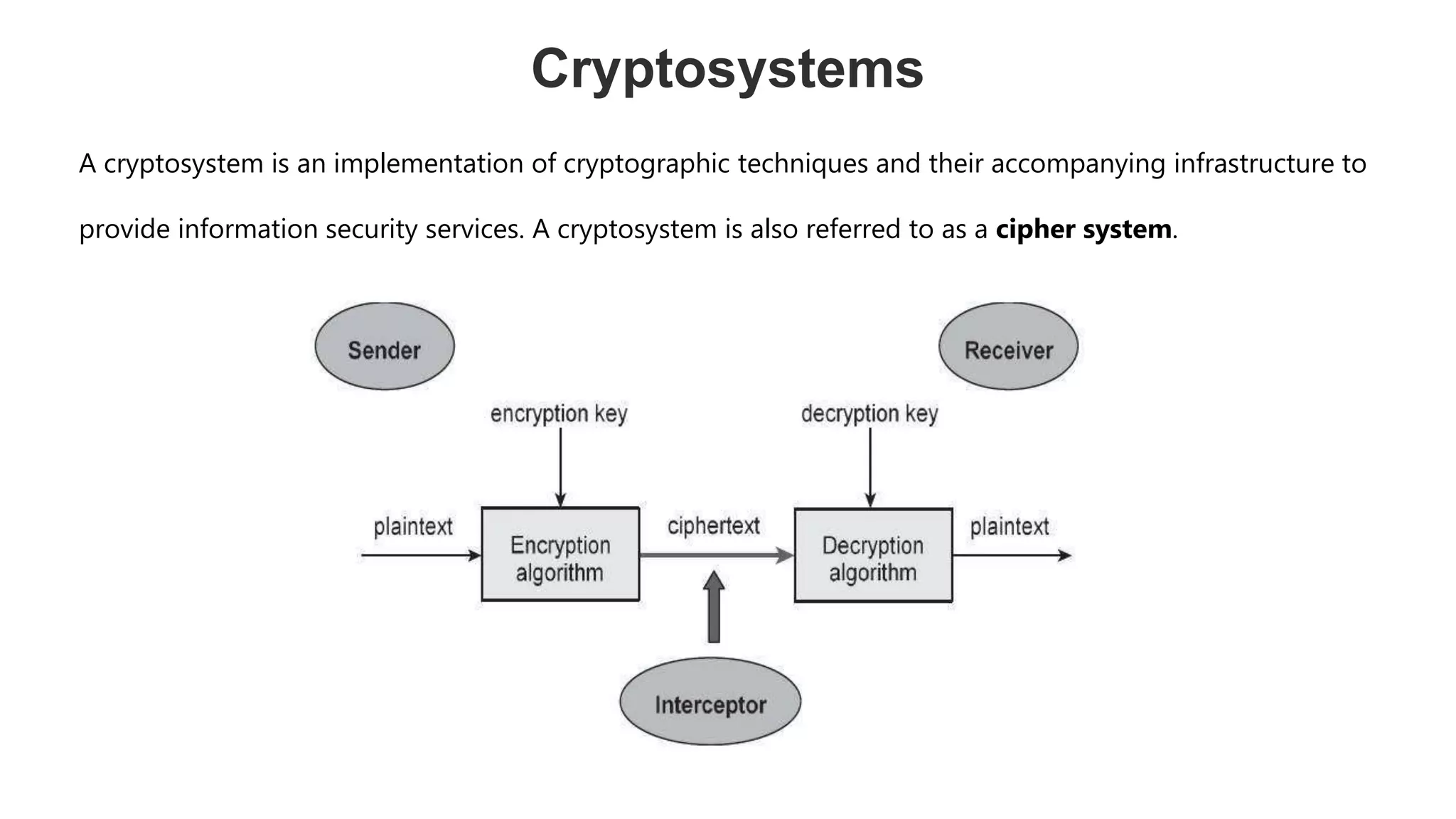
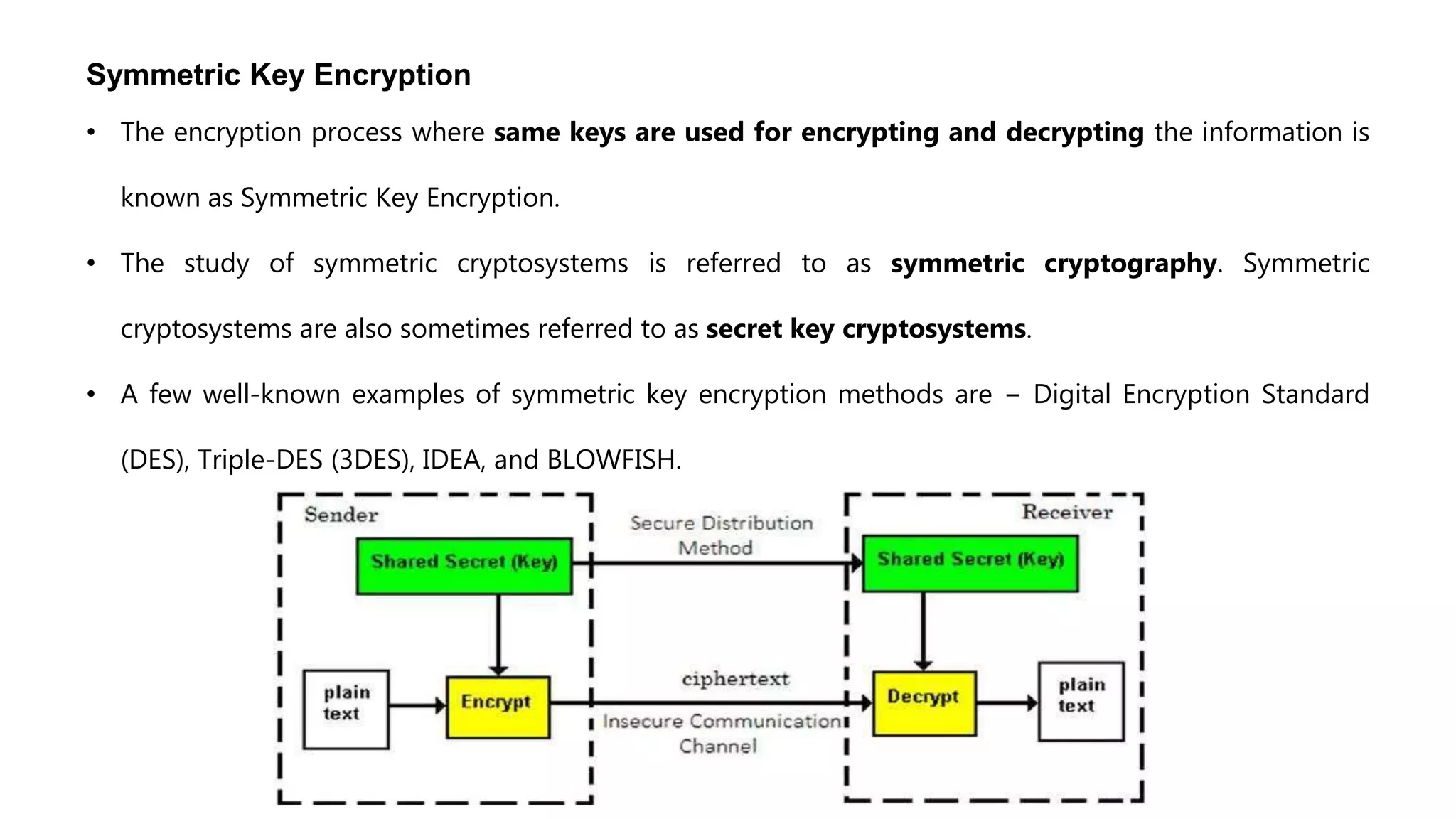
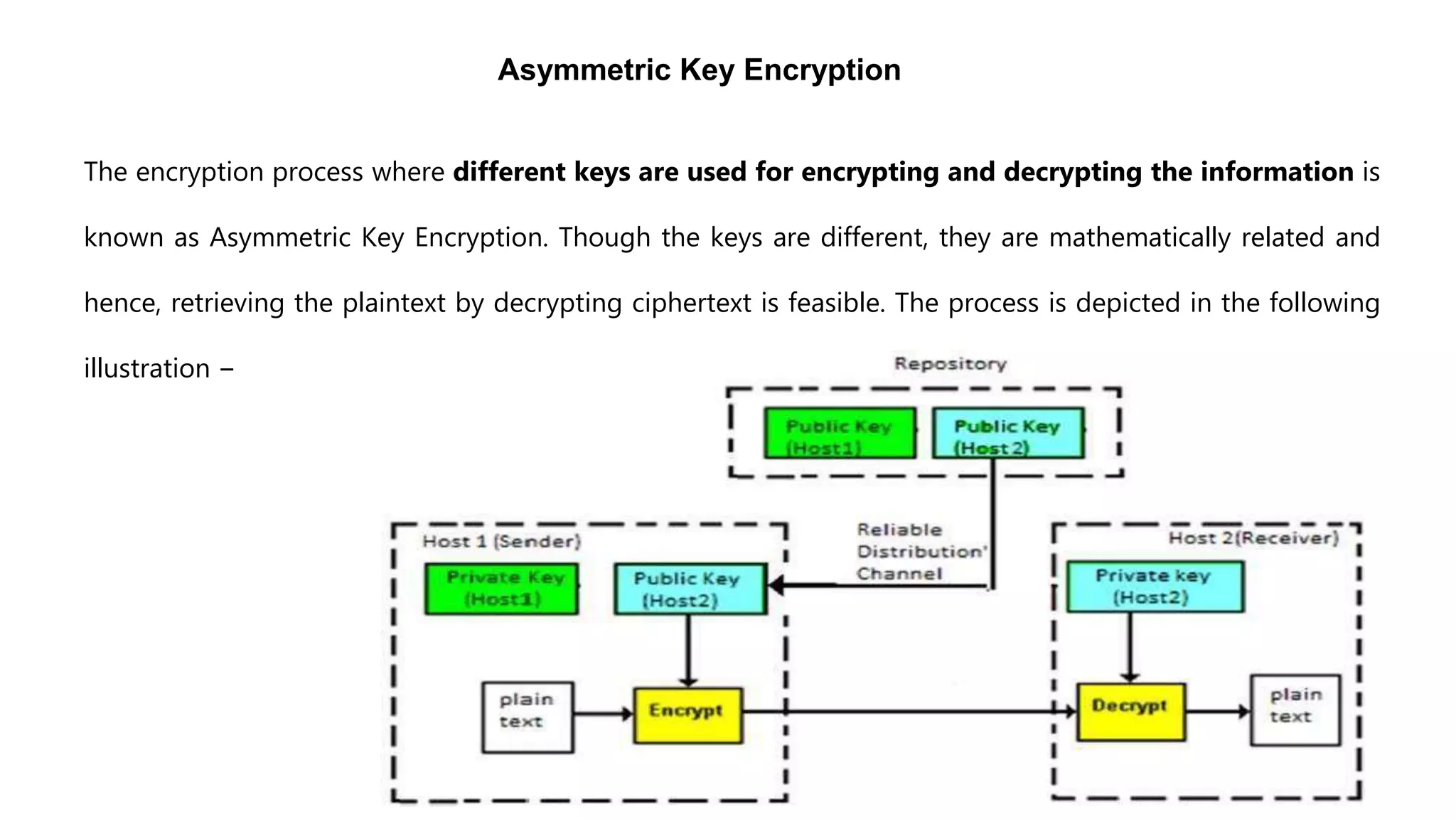
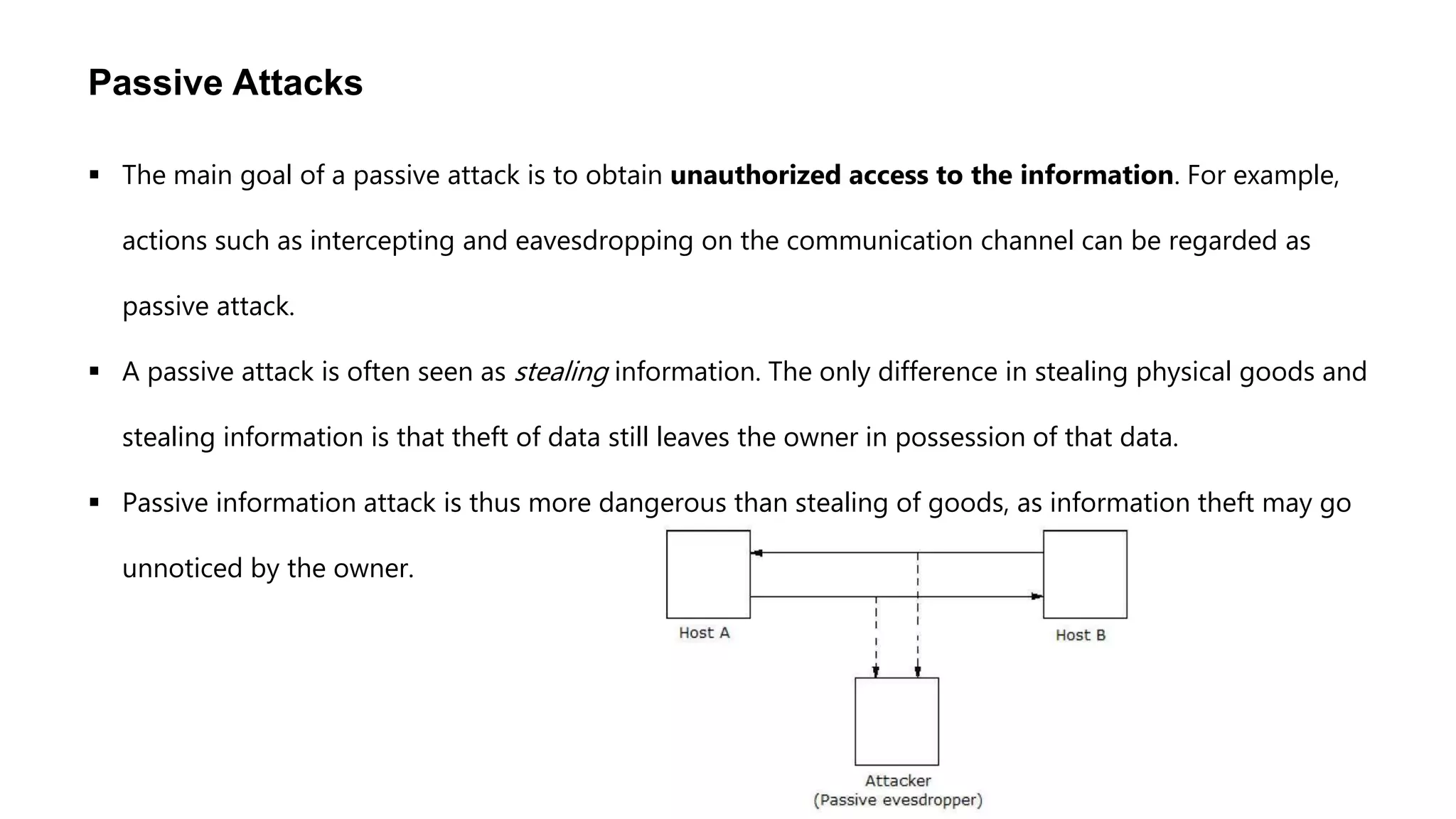
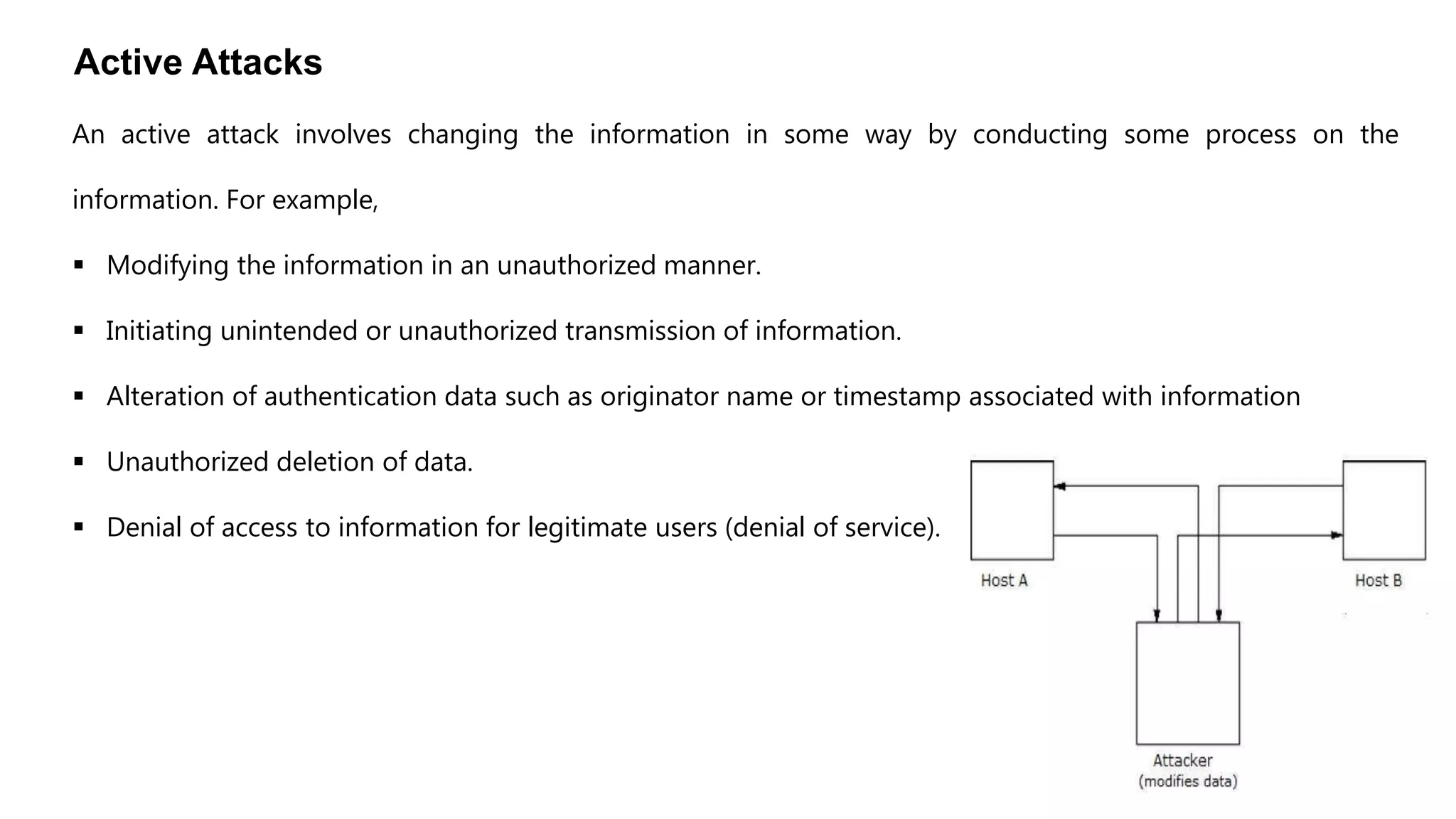
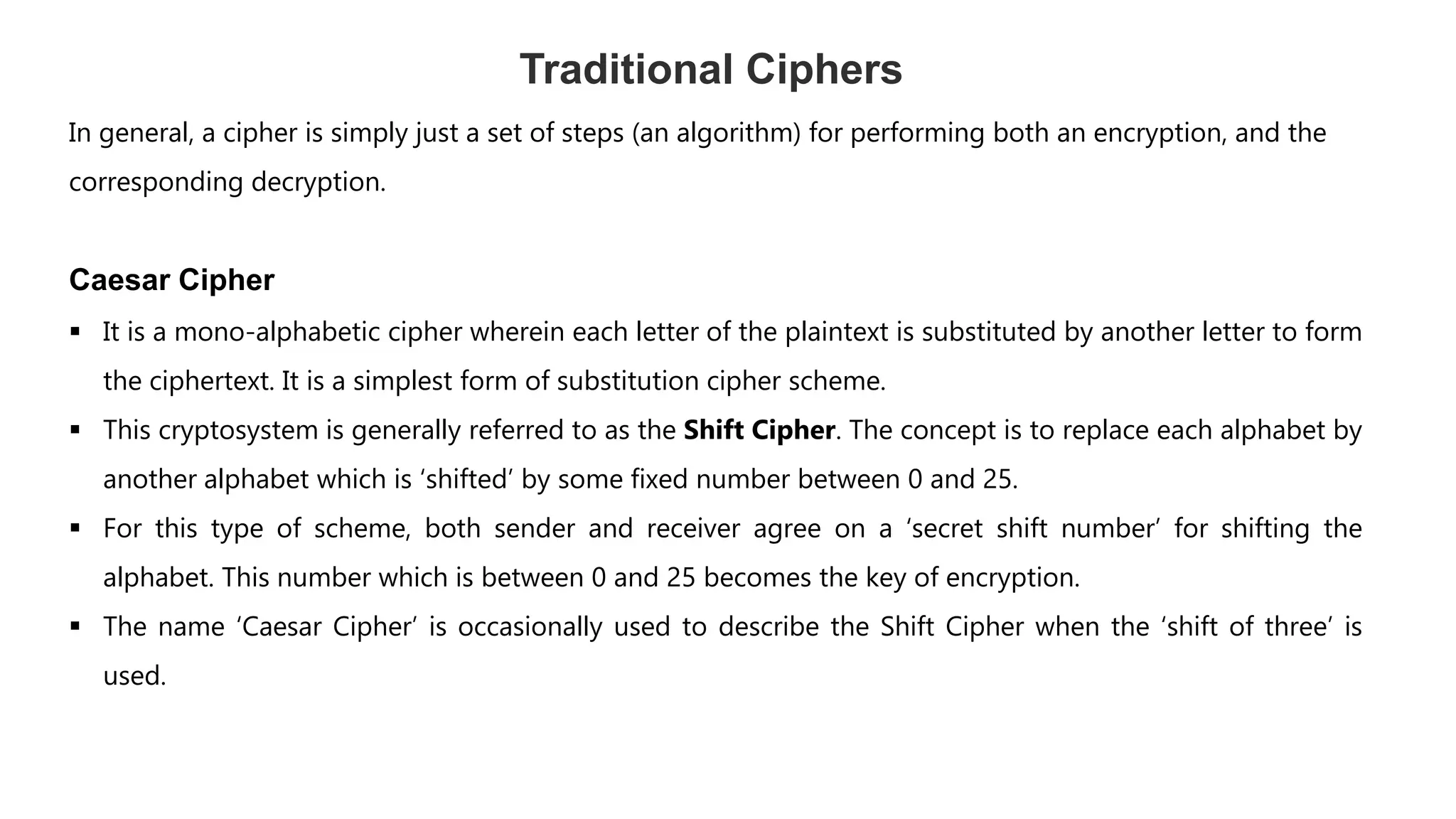
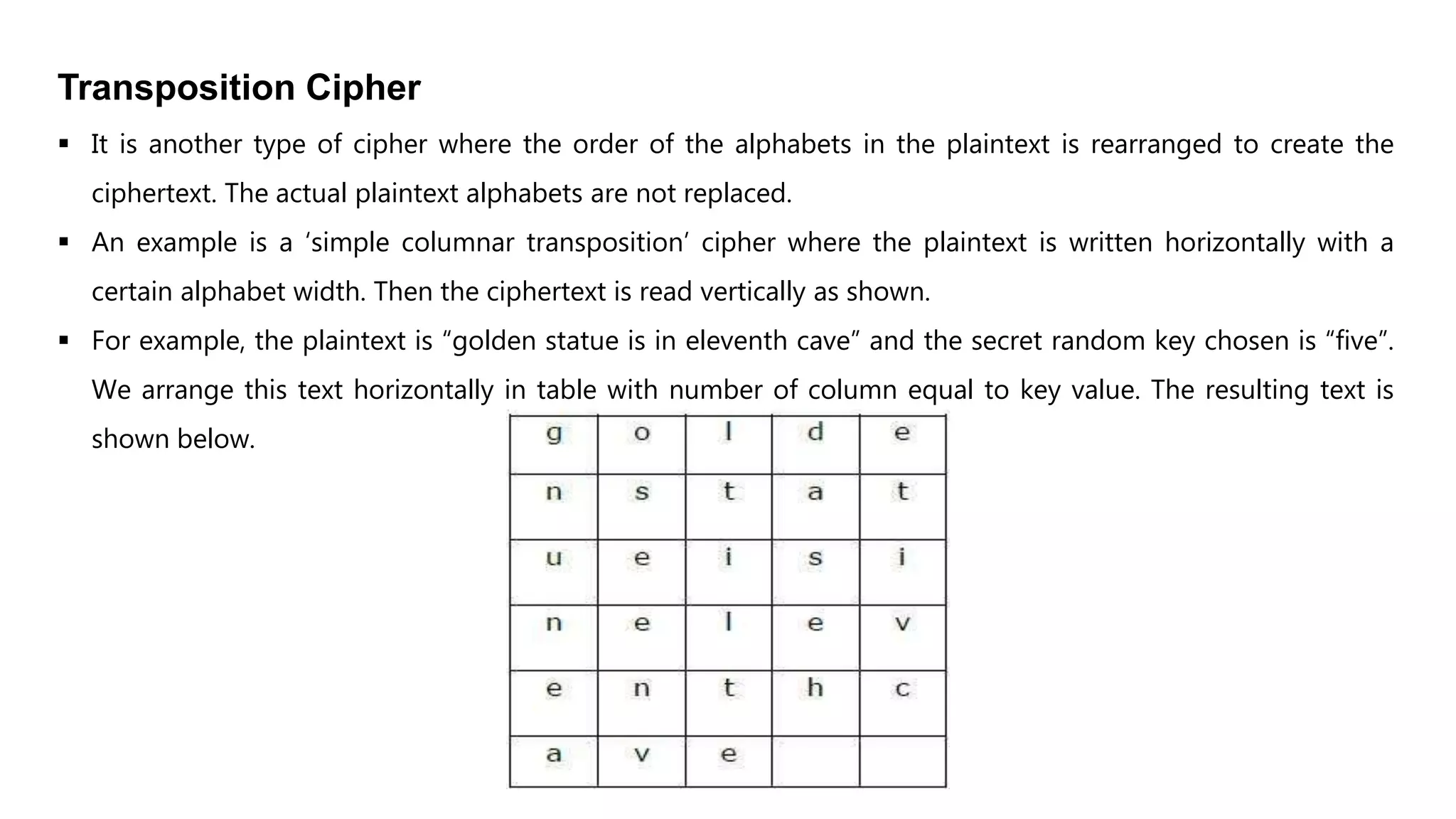
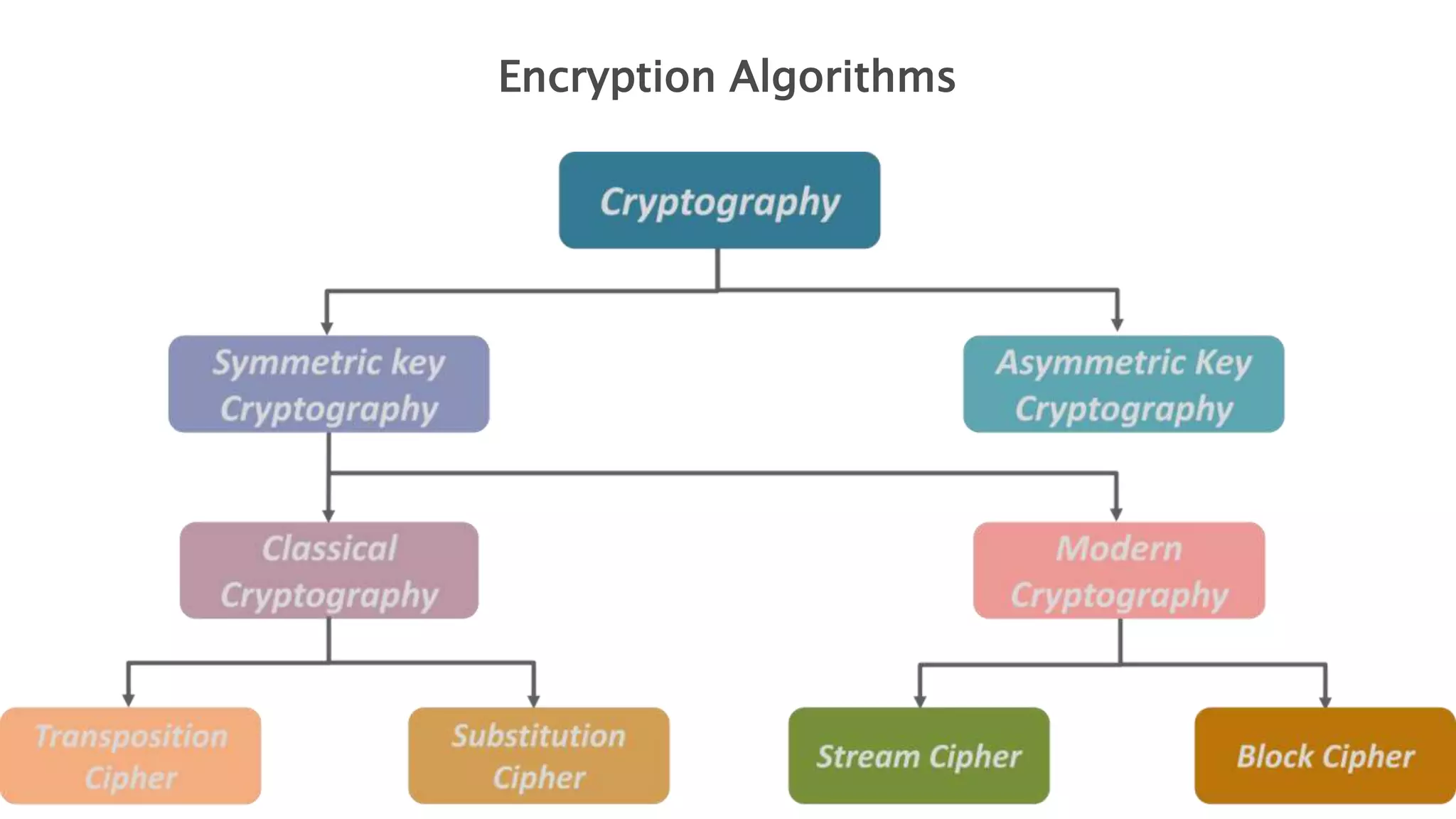
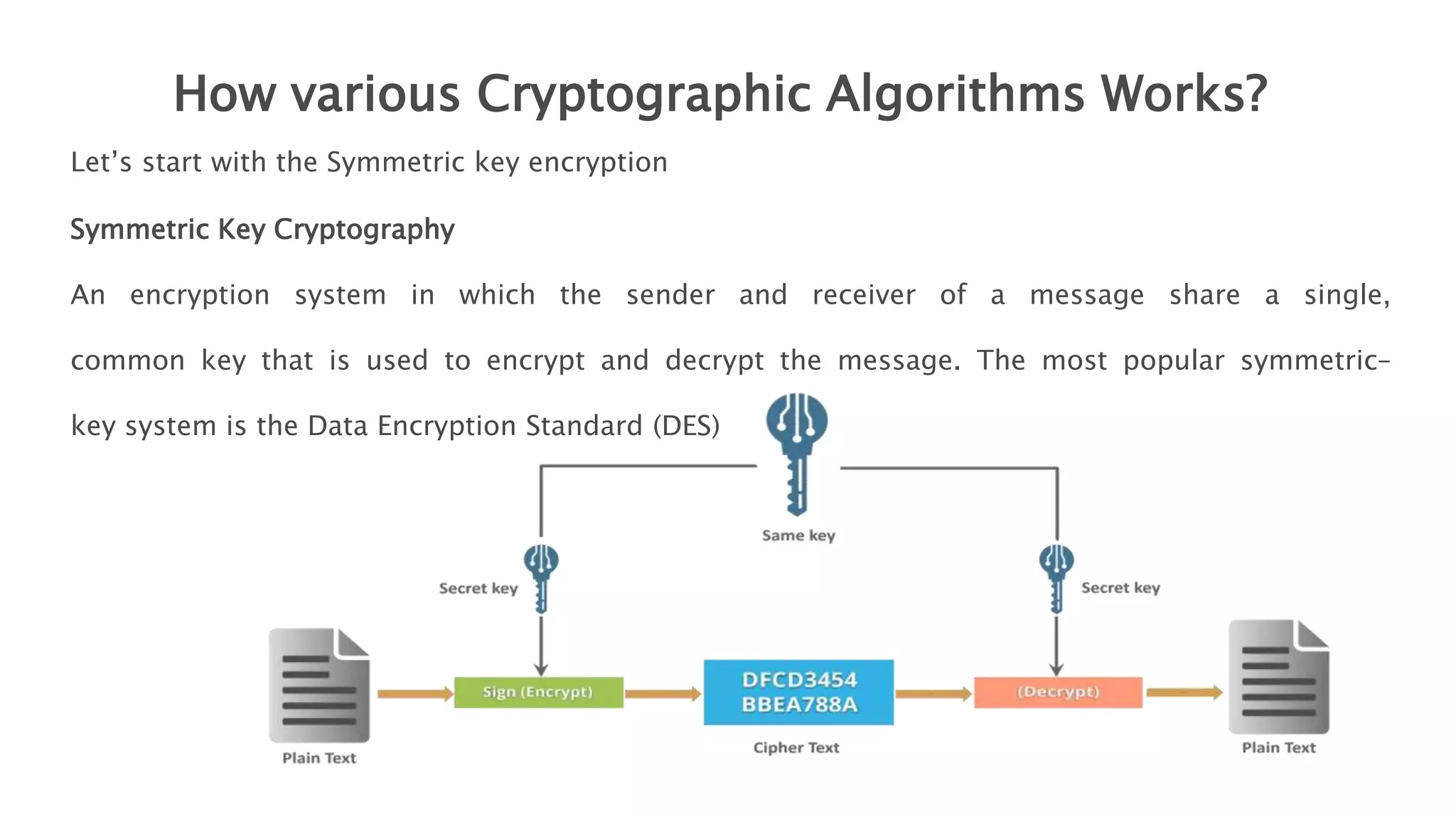
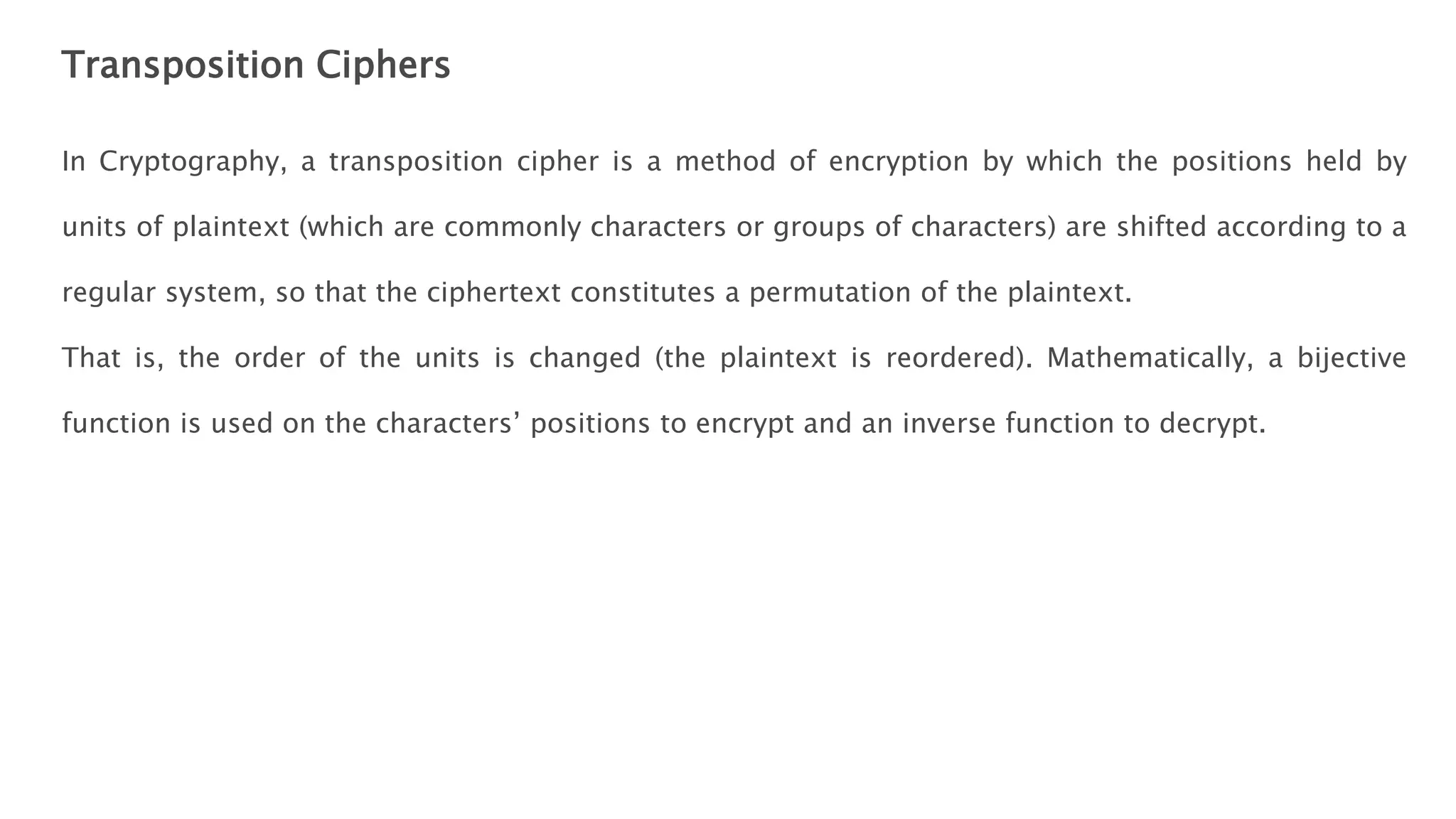
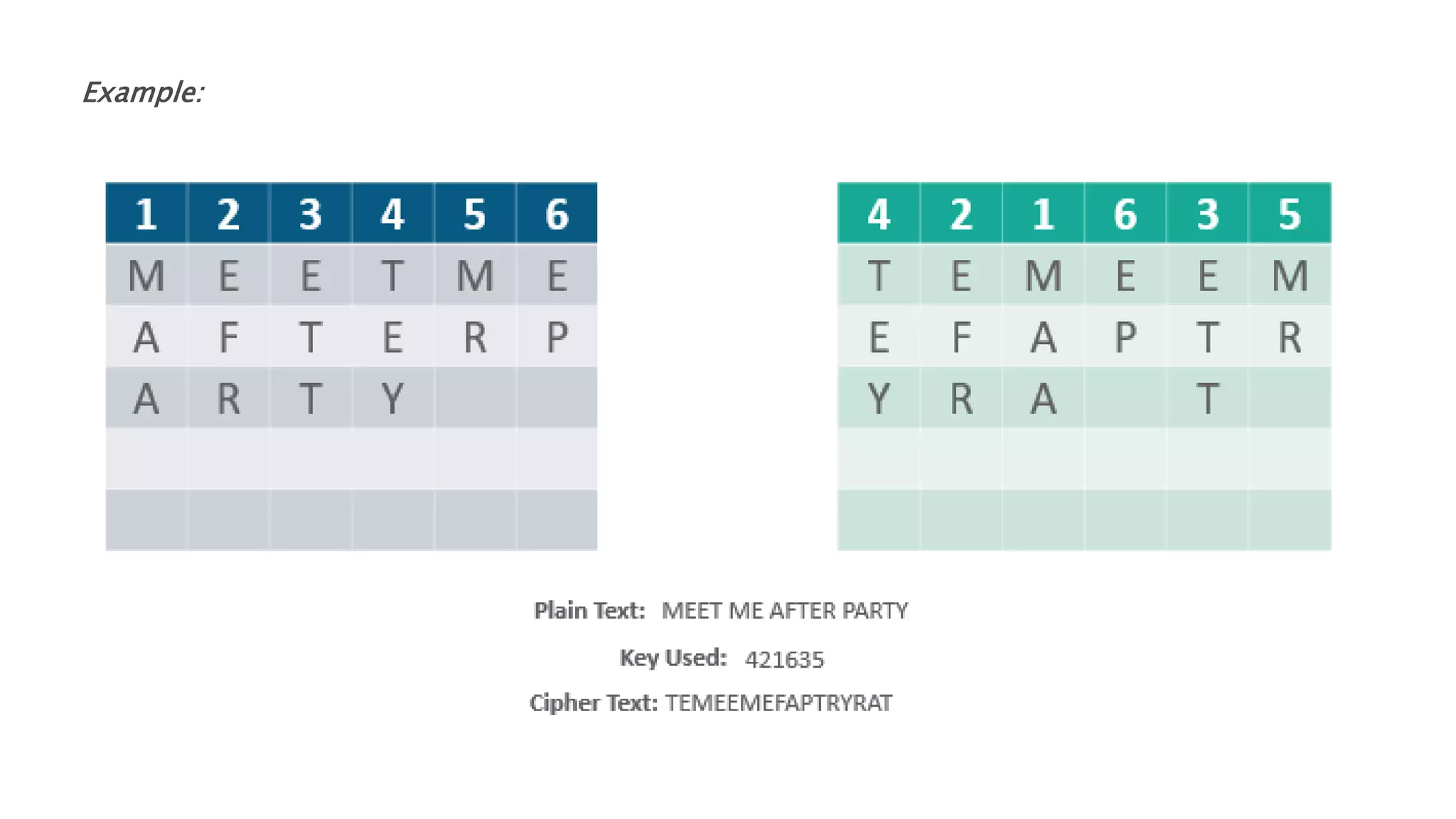
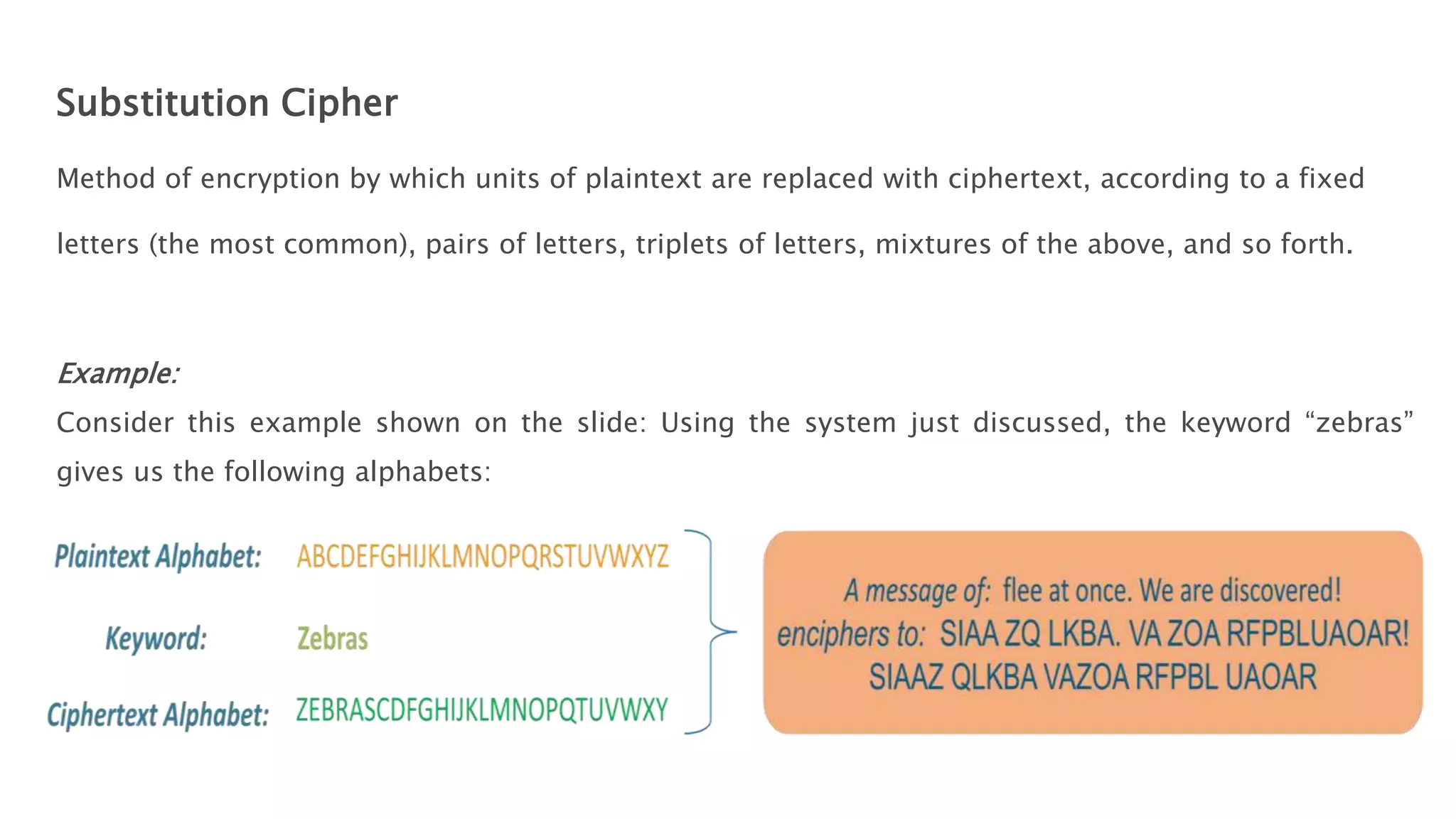
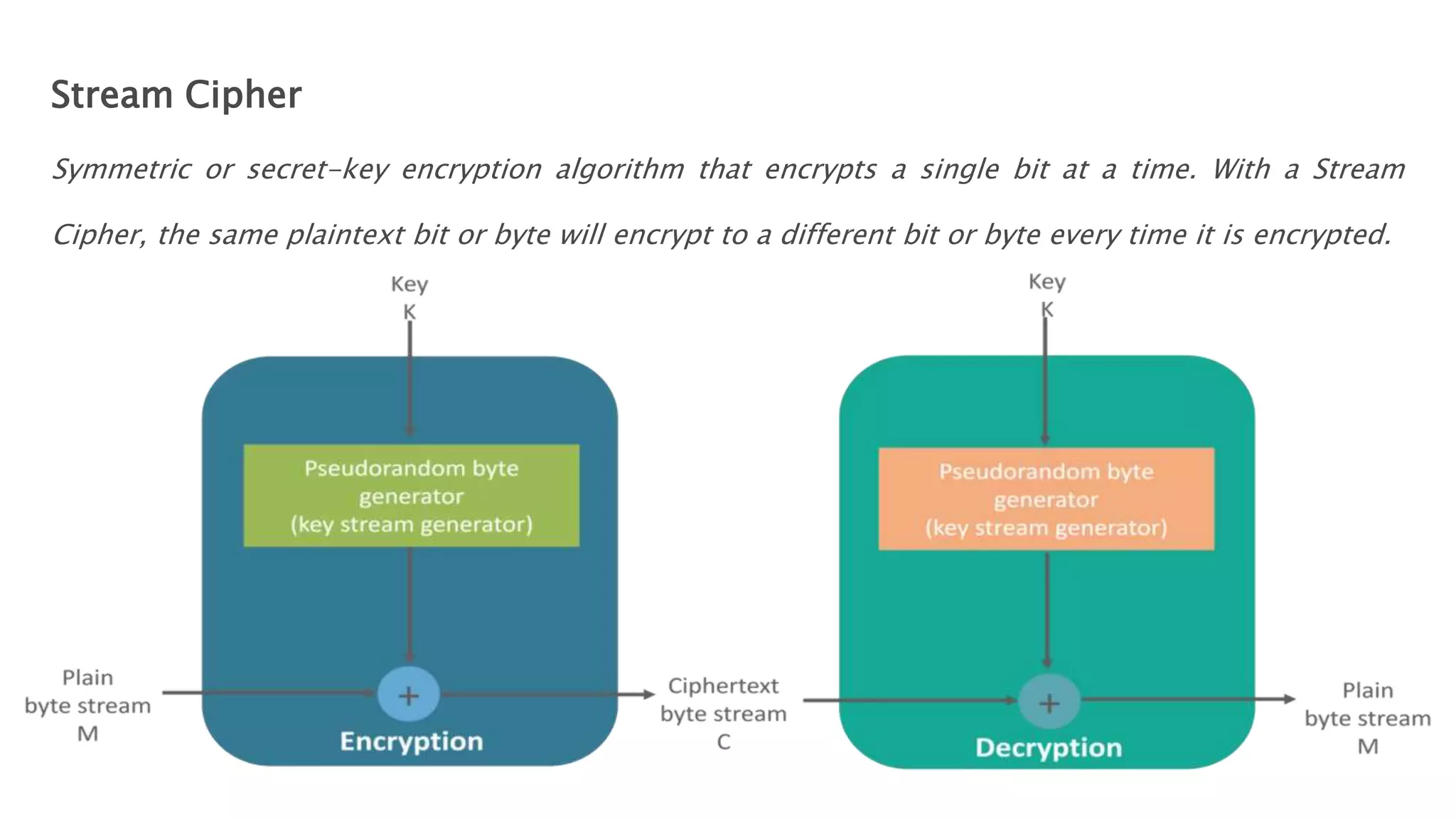
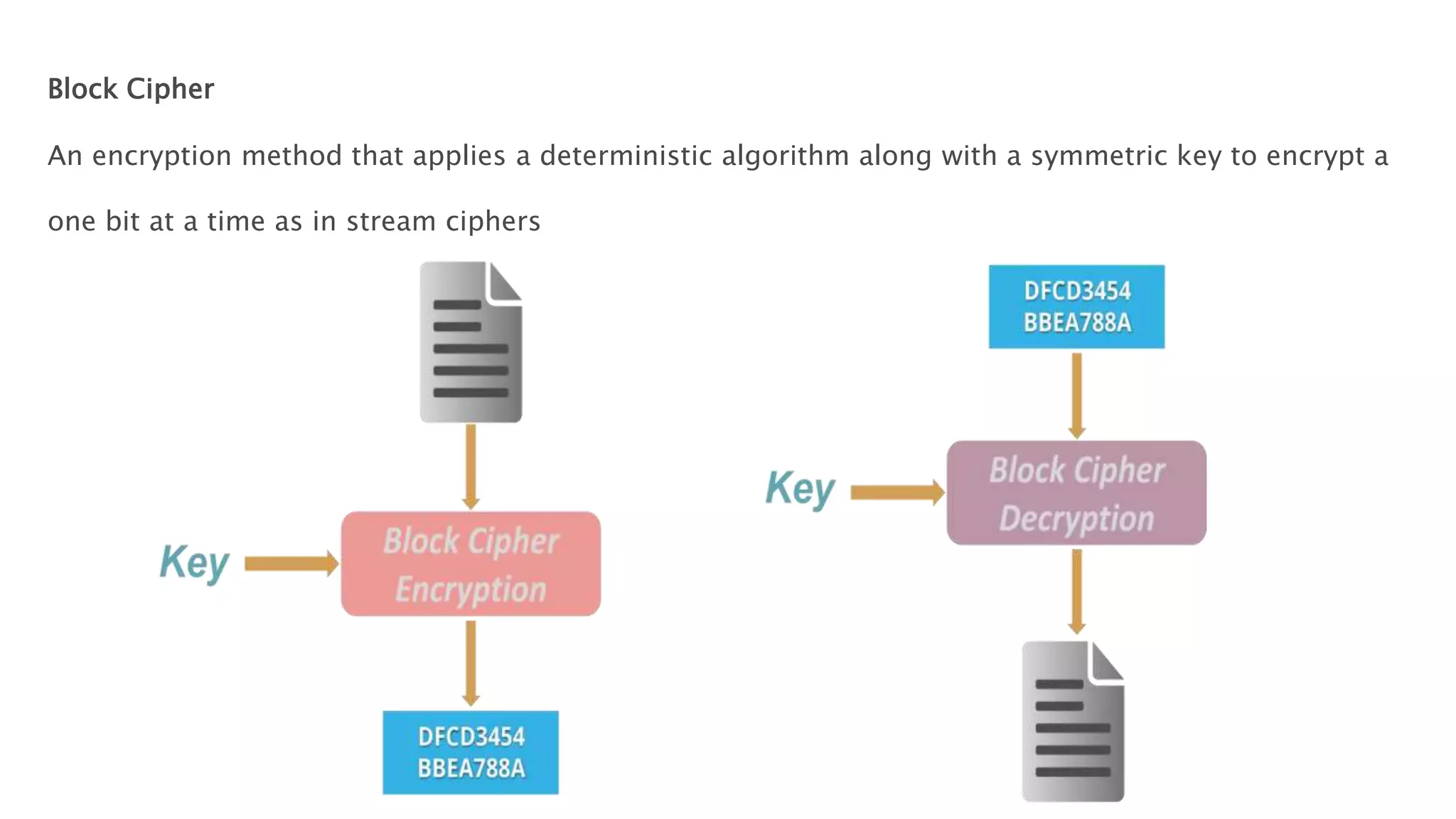
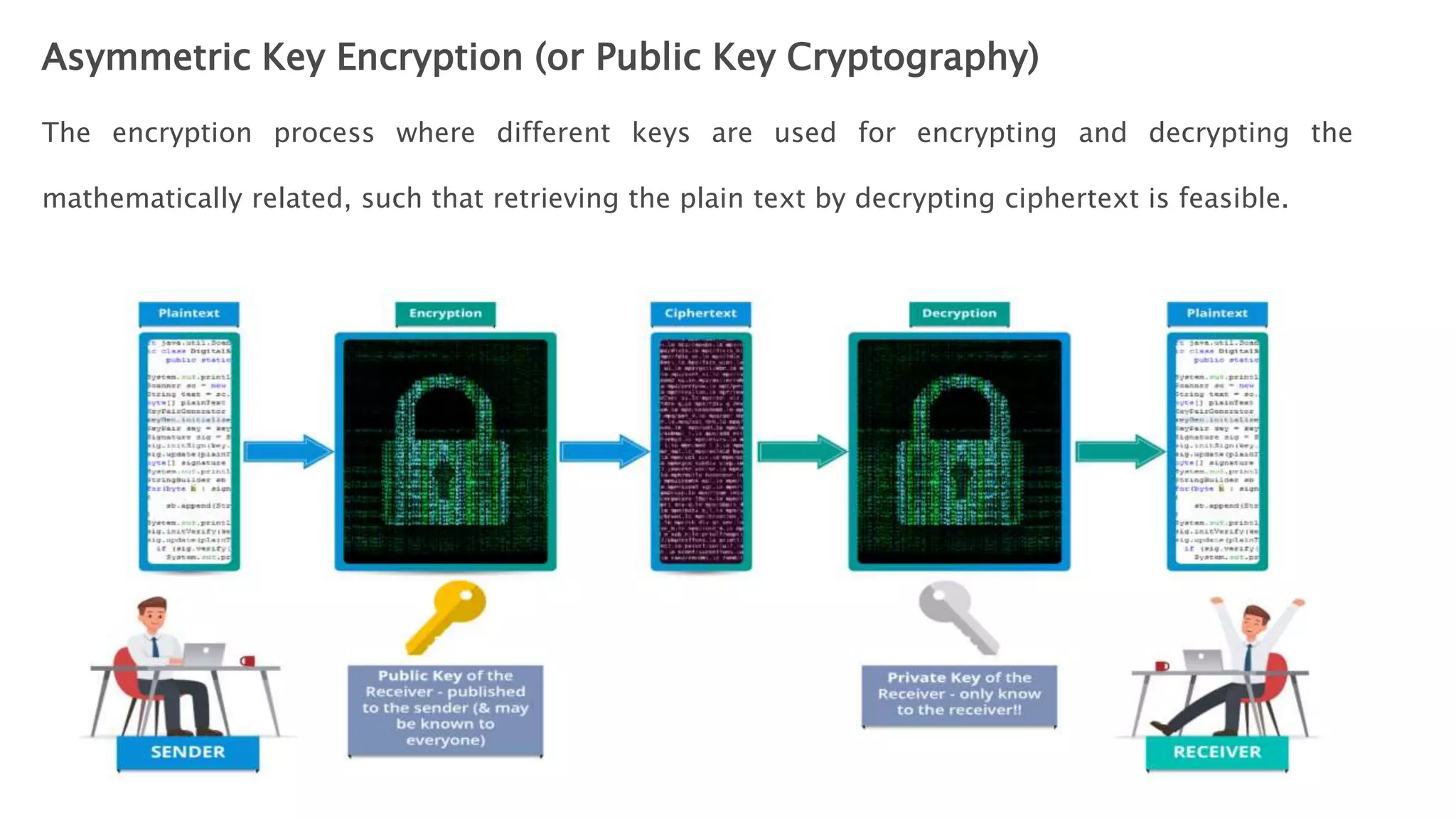
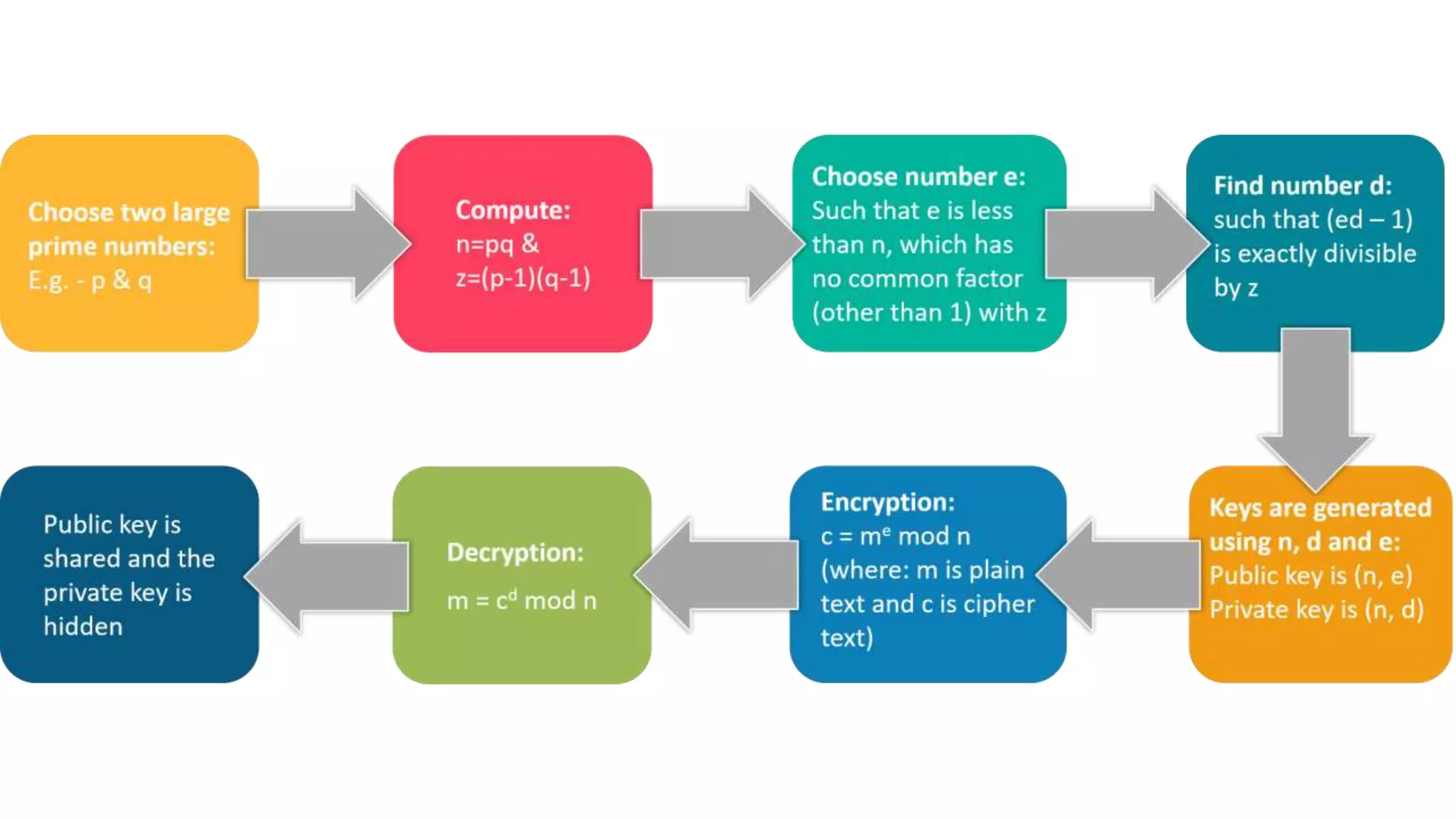
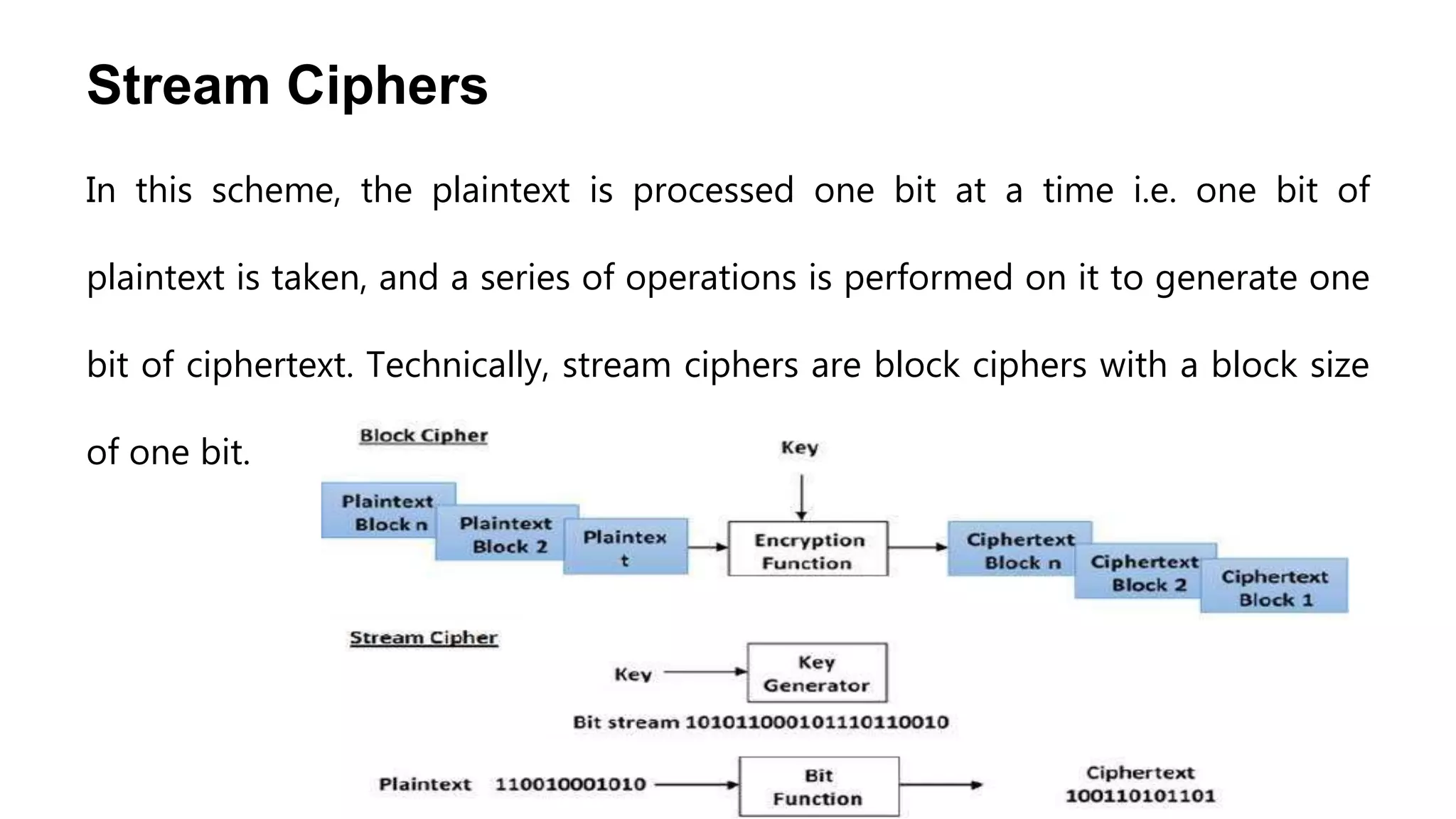
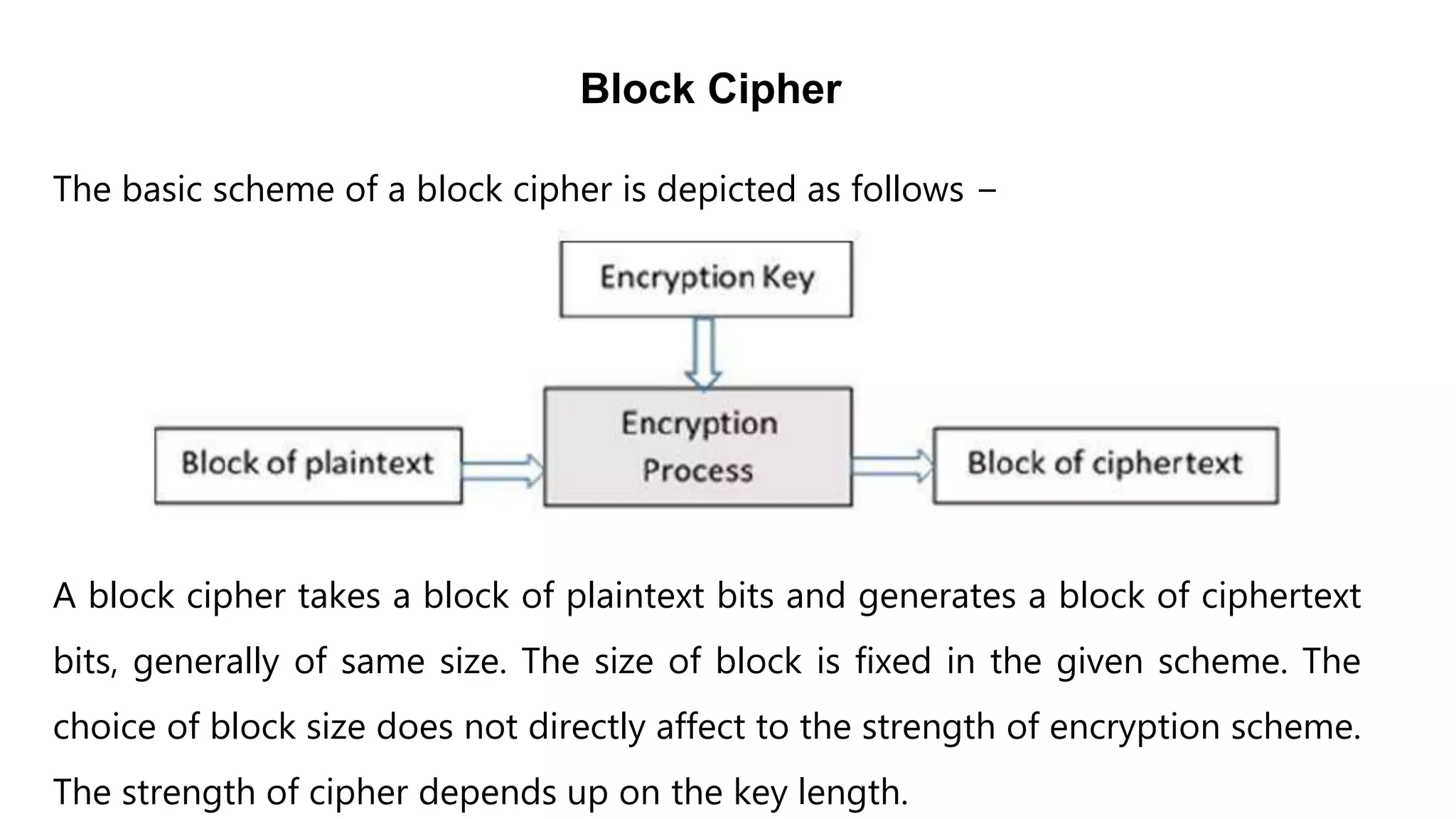
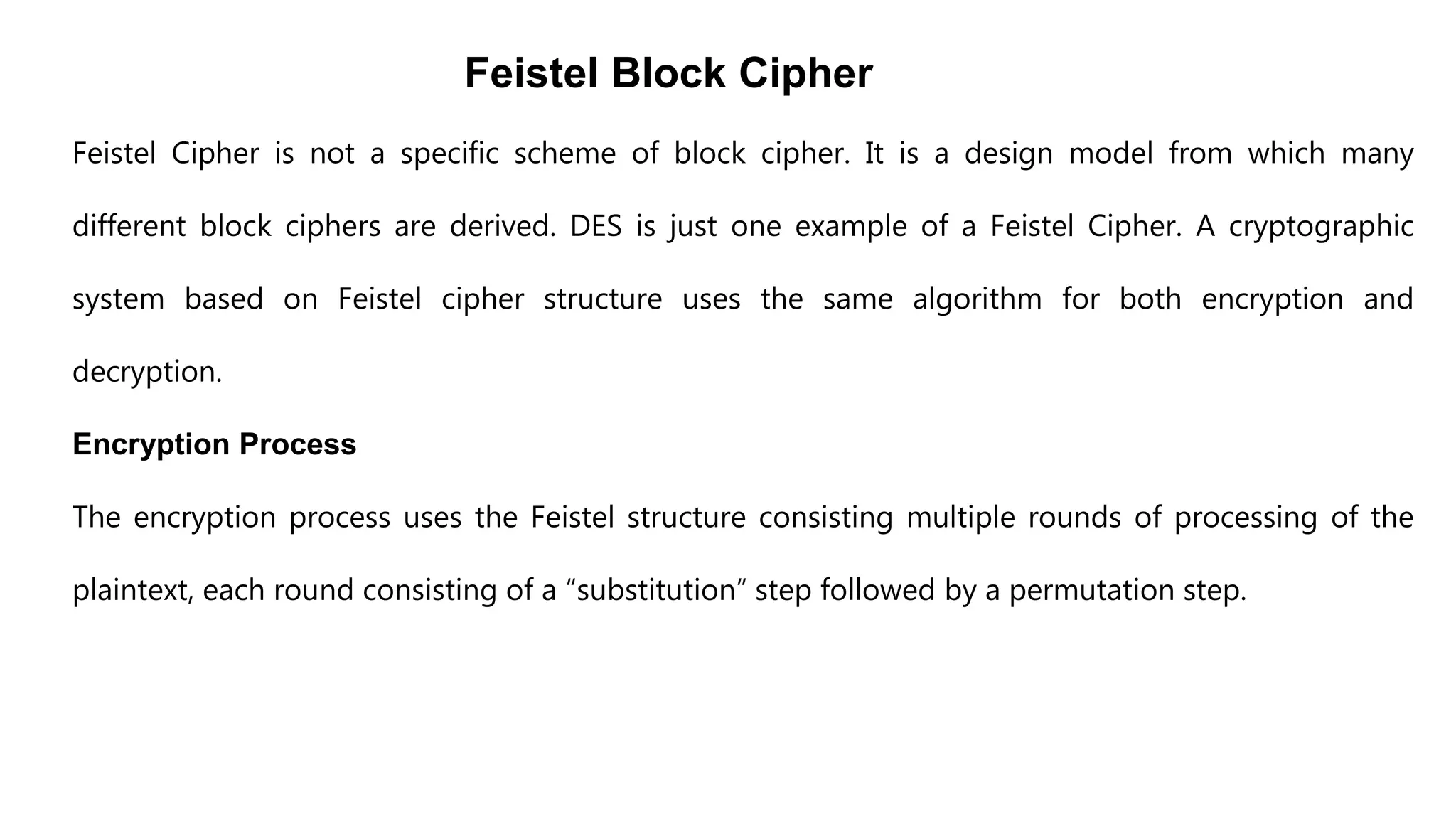
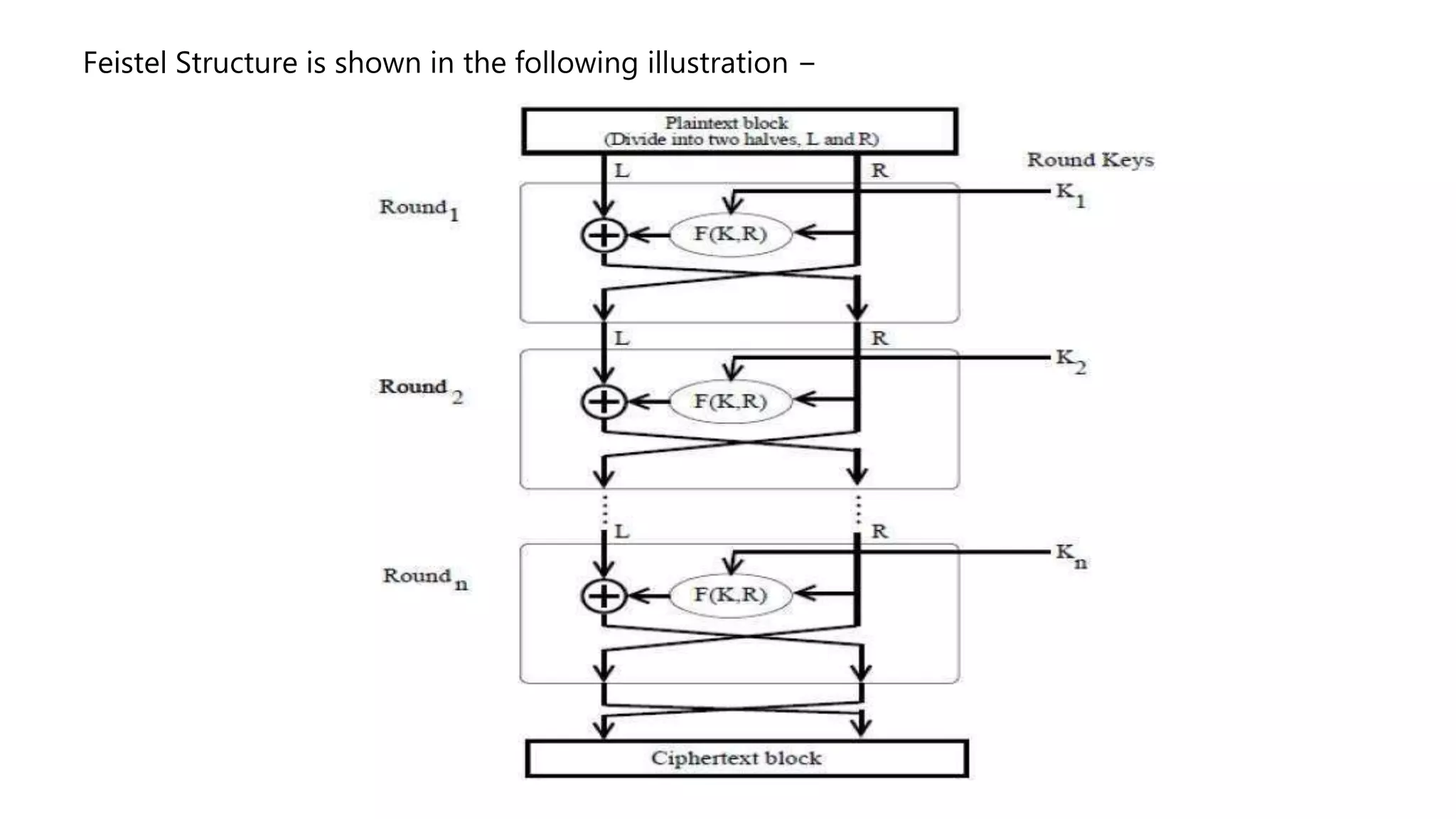
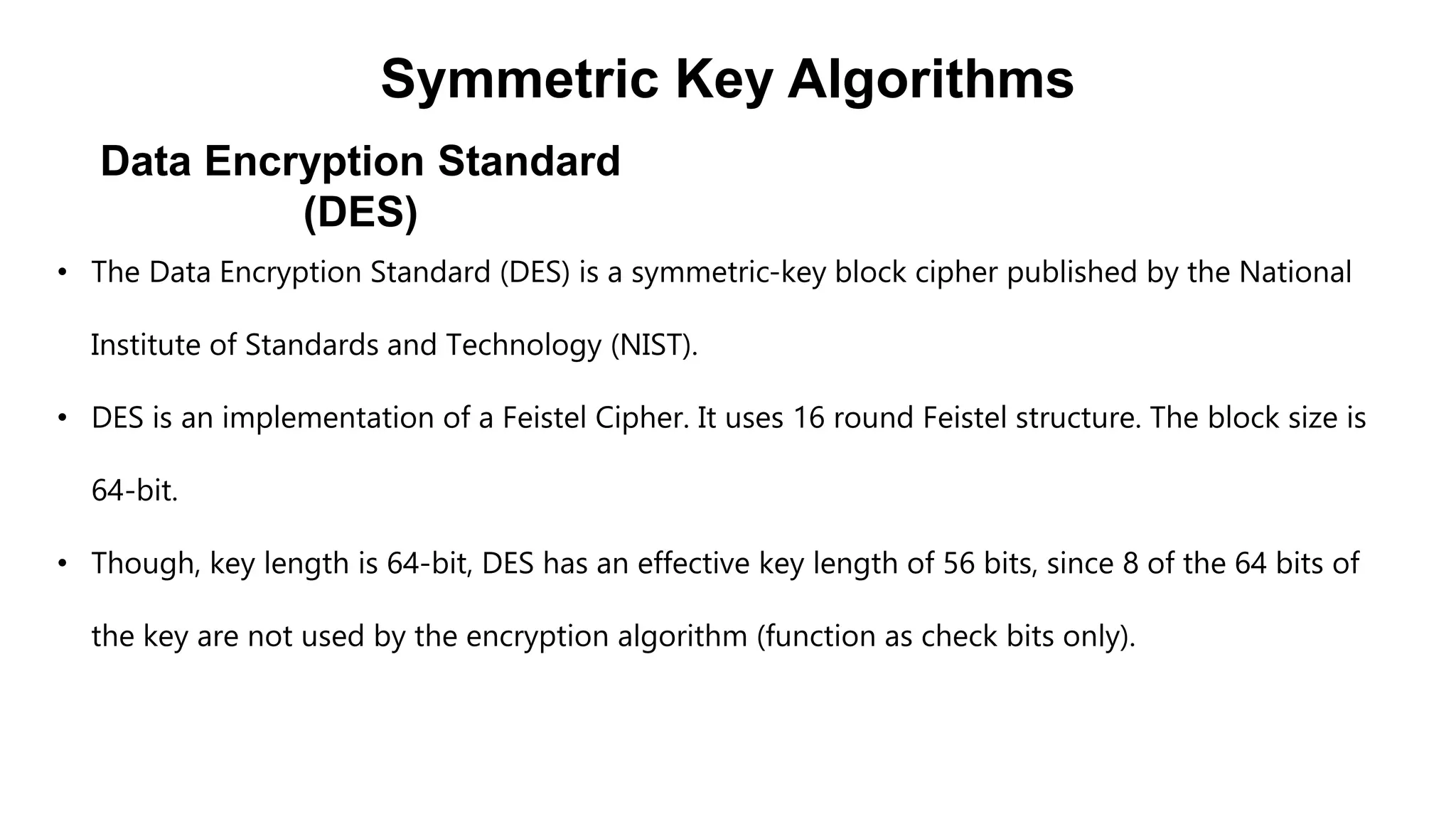
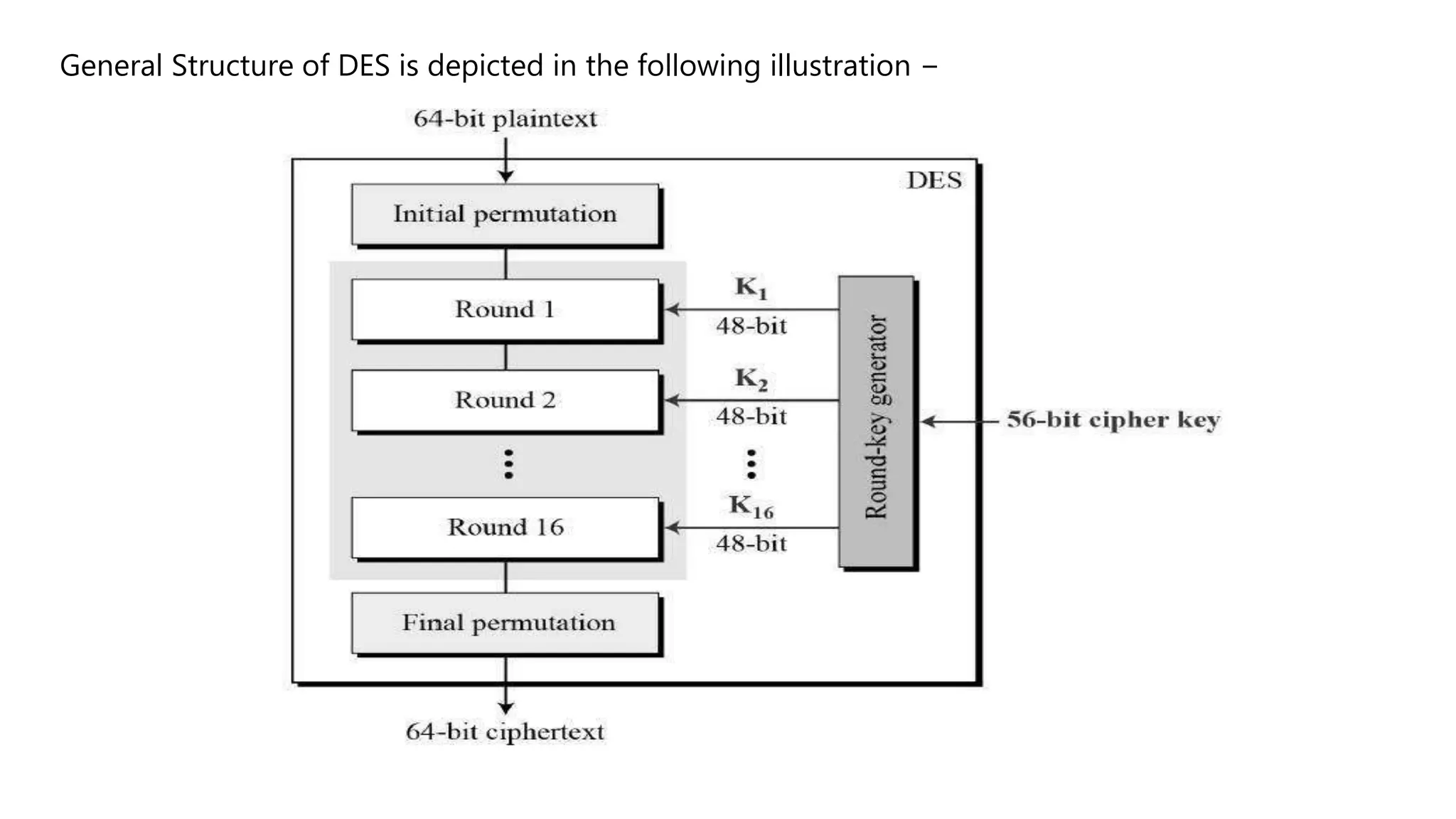
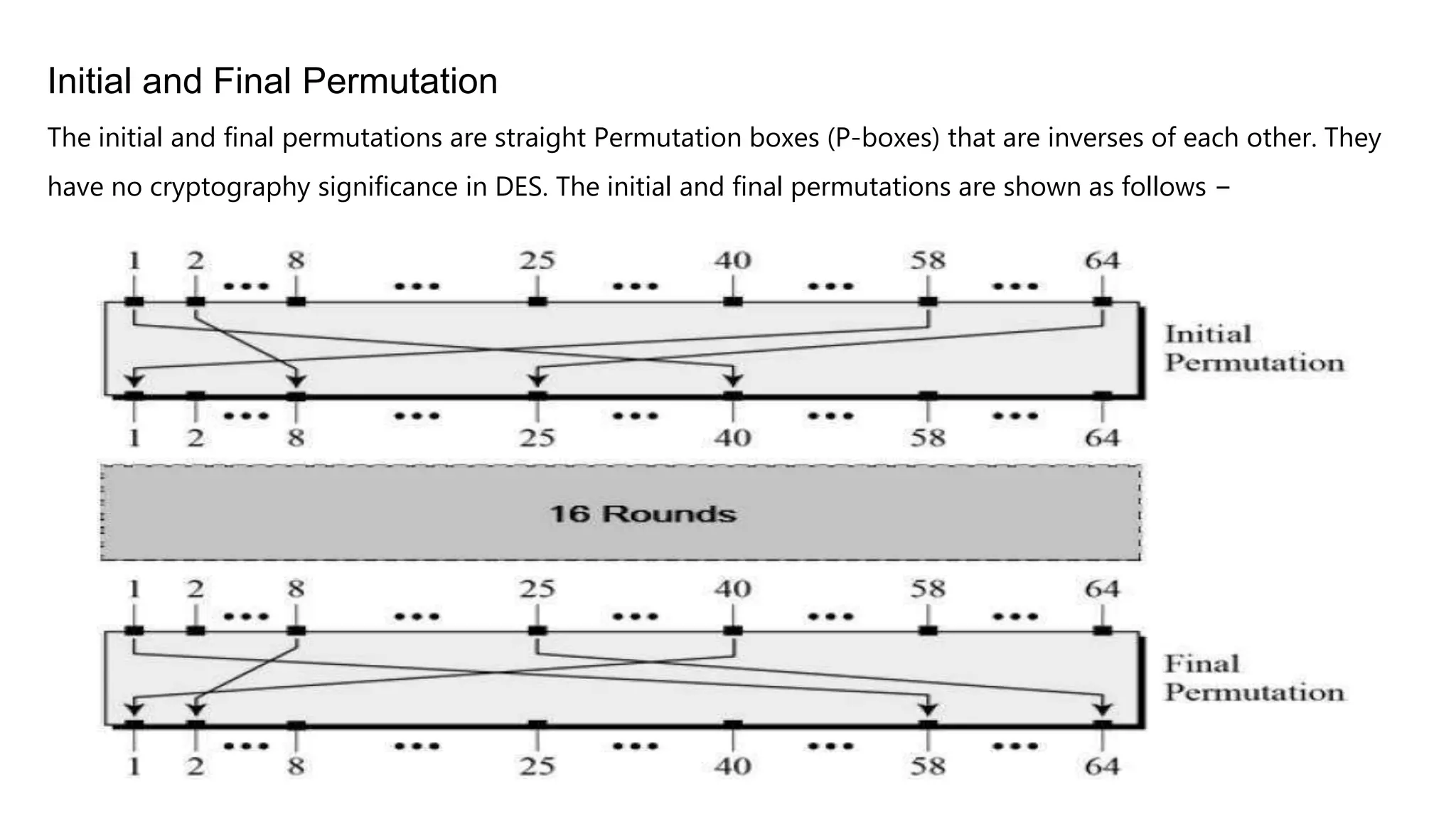
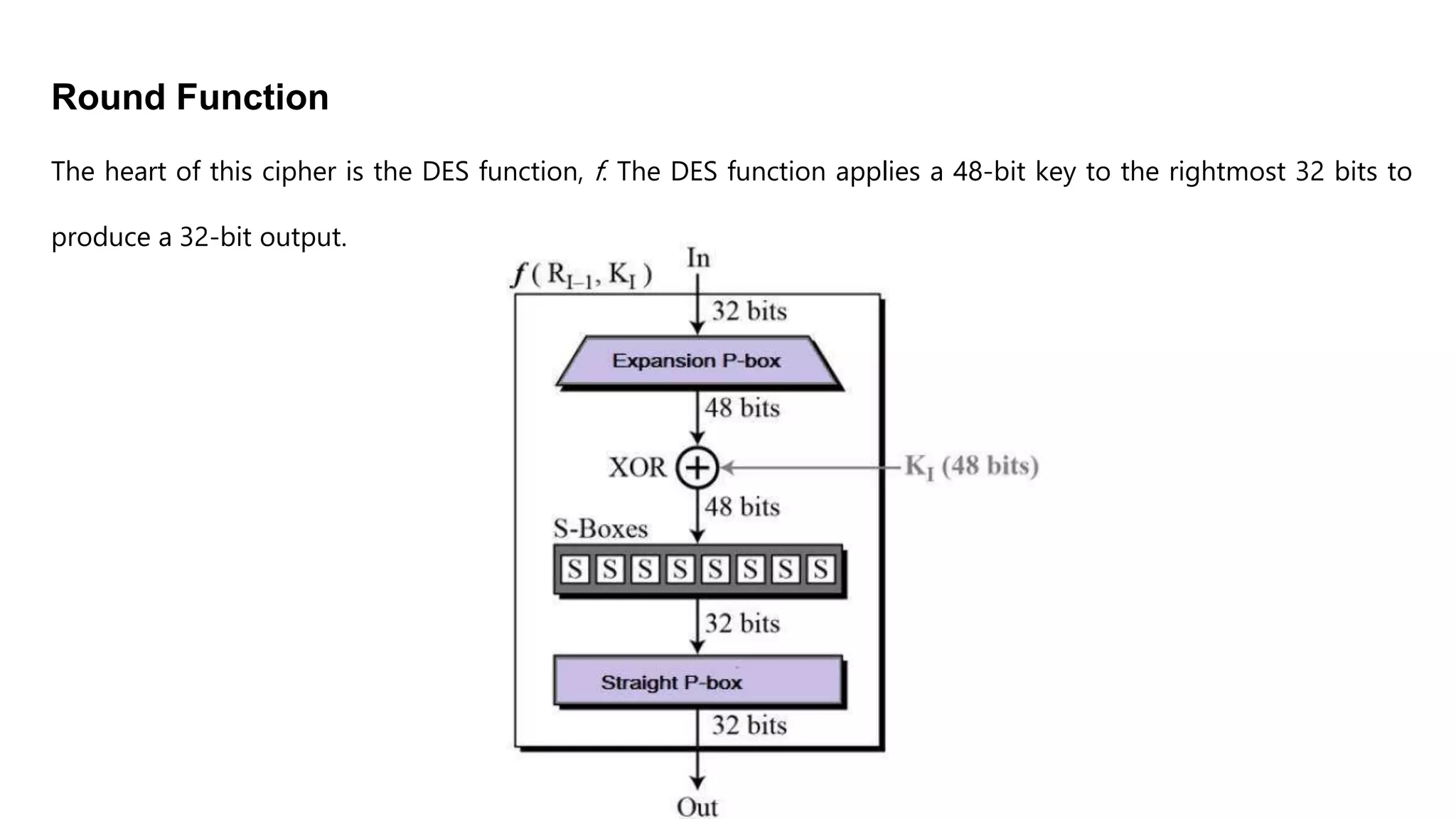
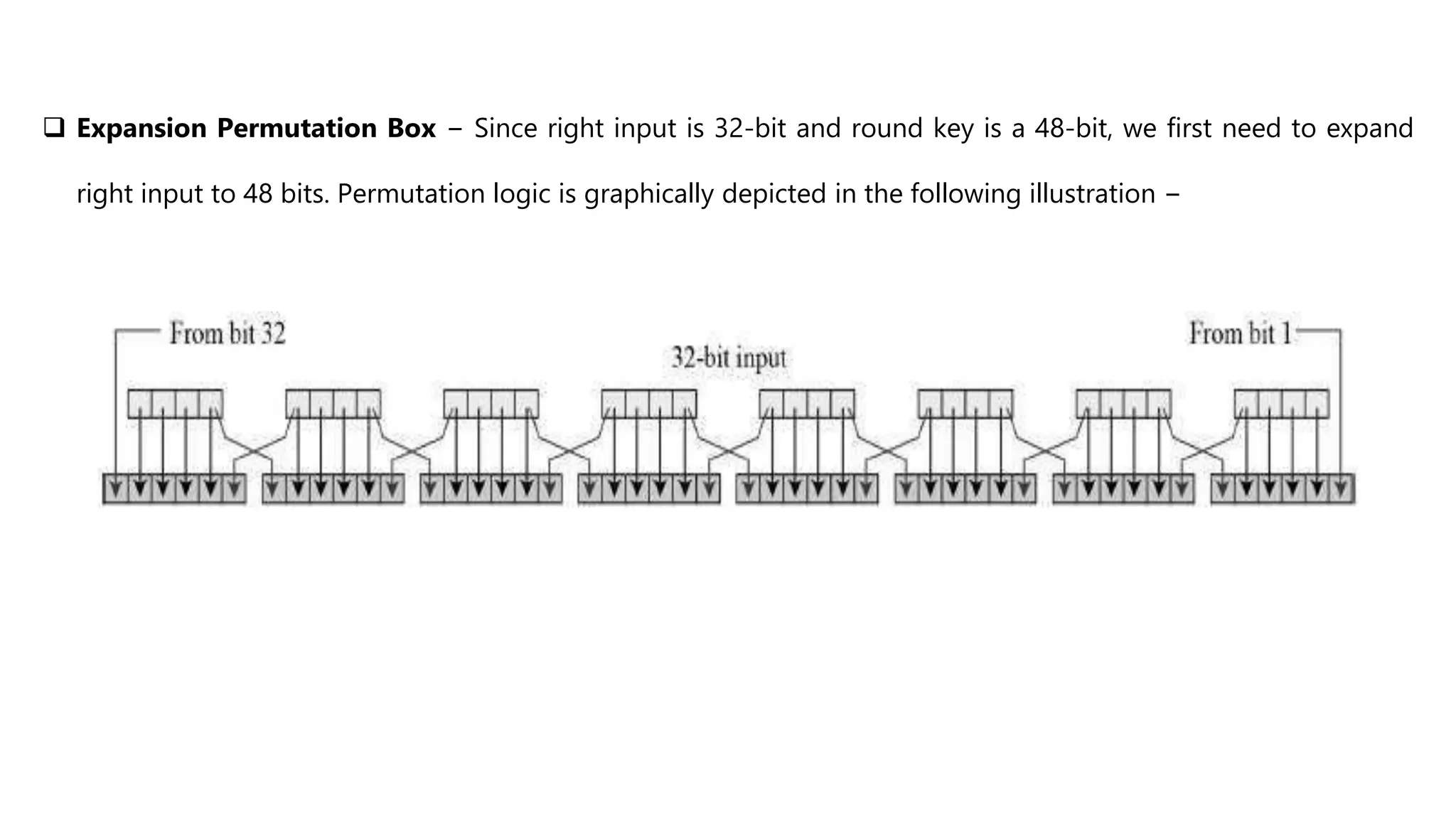
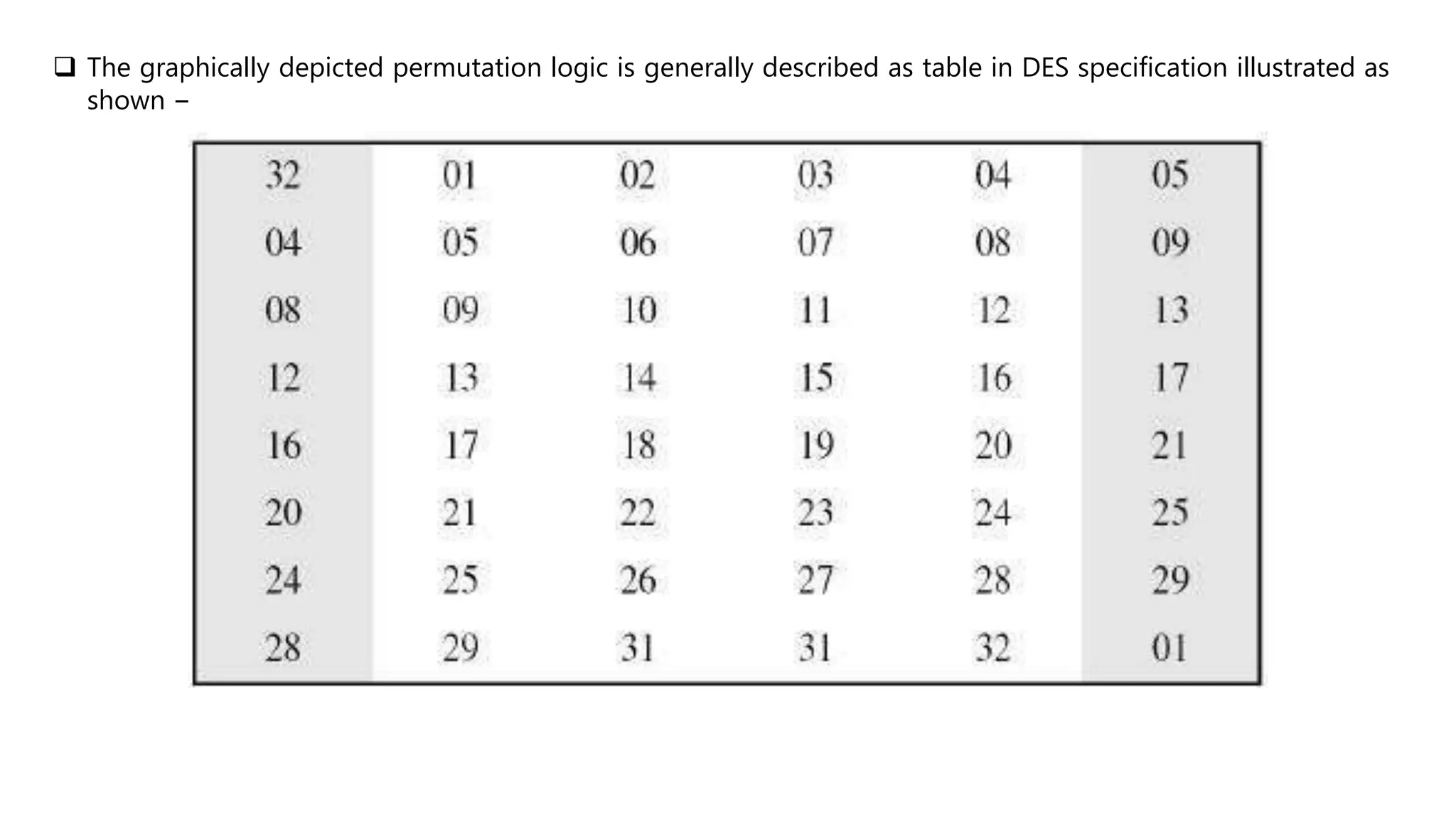
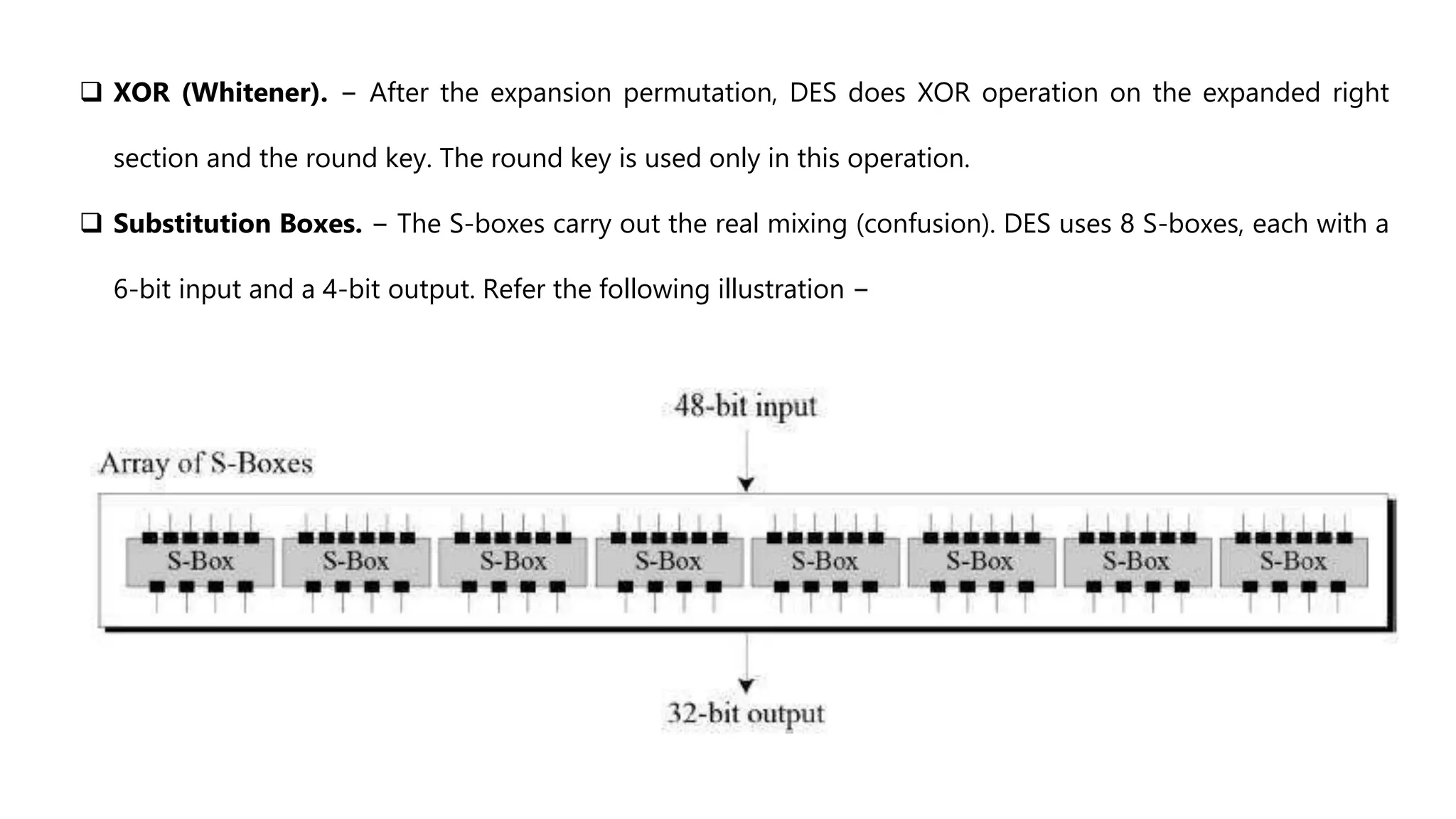
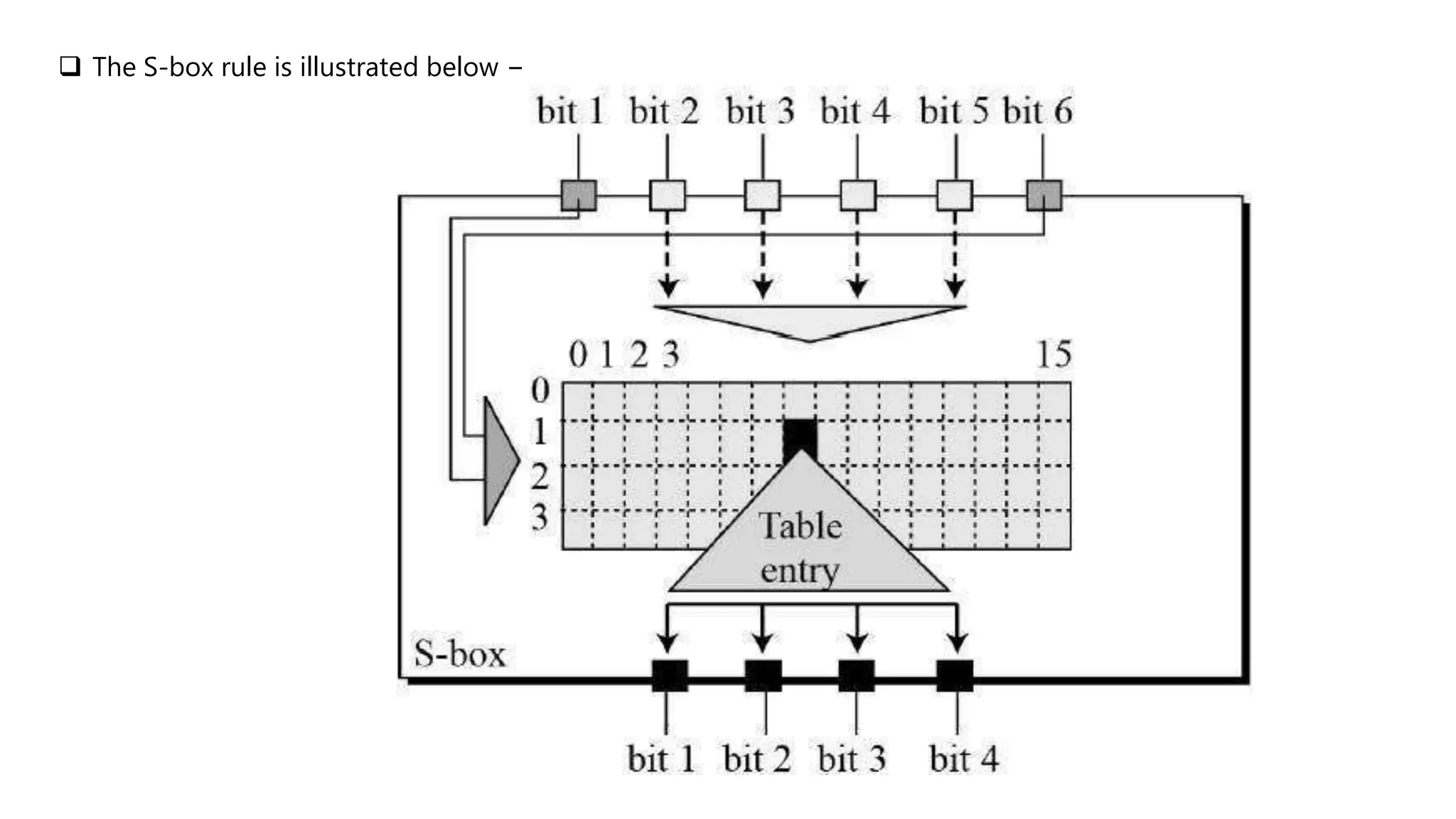
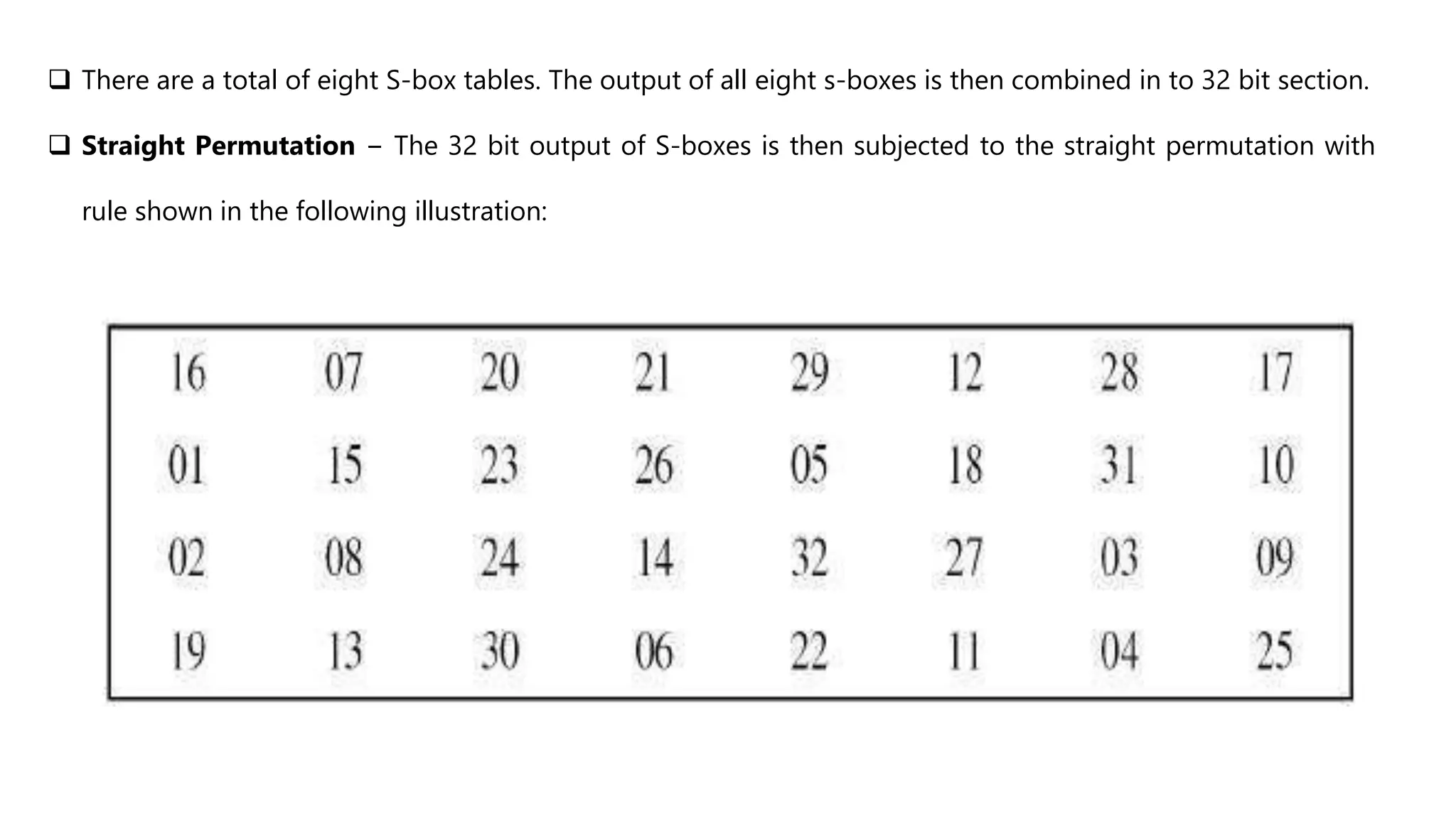
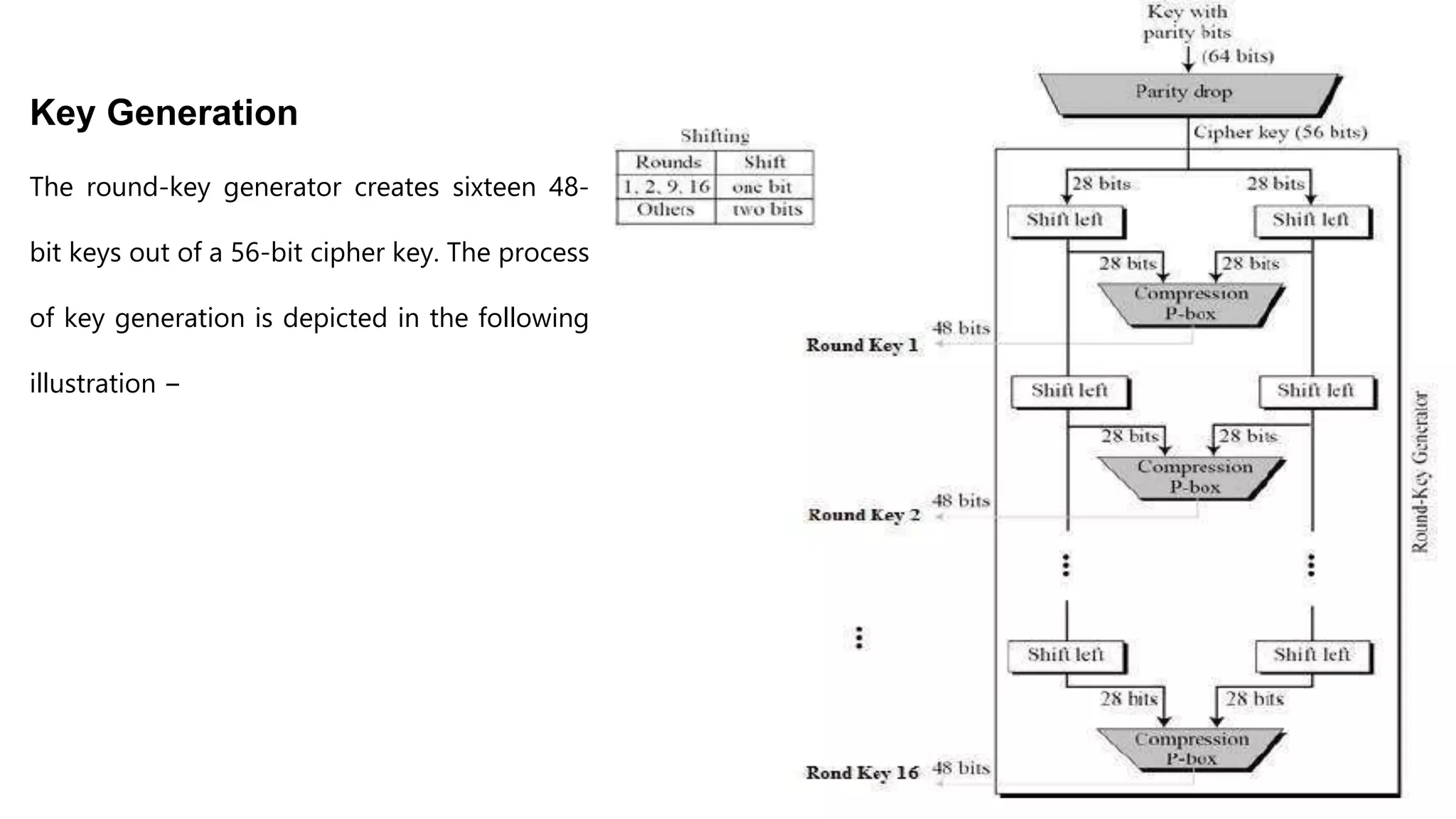
Cryptography originated from Greek words meaning "hidden writing". It involves concealing messages to add secrecy. The earliest techniques include hieroglyphs used by Egyptians and simple substitution ciphers later. Modern cryptography is based on mathematical concepts like number theory and relies on publicly known algorithms rather than secrecy. It aims to provide confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation. Cryptography tools include encryption, hash functions, message authentication codes, and digital signatures. A cryptosystem uses algorithms, keys, and infrastructure to encrypt plaintext into ciphertext and decrypt it back using the same or related keys. Cryptosystems can be symmetric, using one key, or asymmetric, using separate keys.