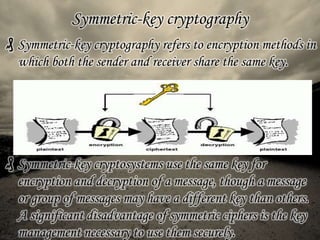
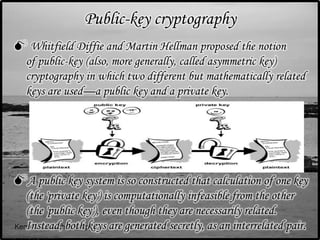
Cryptography is the art of securing information by converting it into an unreadable format, with decryption possible only for those with a secret key, addressing issues of confidentiality, authentication, authorization, data integrity, and non-repudiation. It has evolved from classic ciphers to modern techniques using digital computers, including symmetric-key cryptography, where both parties share a key, and public-key cryptography, which uses a pair of mathematically related keys. Cryptanalysis, the study of breaking encryption, plays a critical role in maintaining security in today's digital landscape.