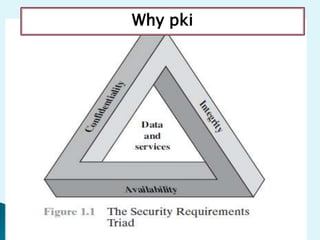
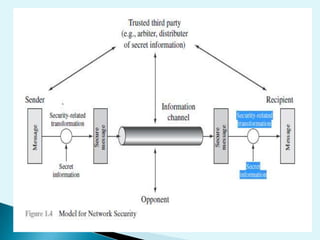
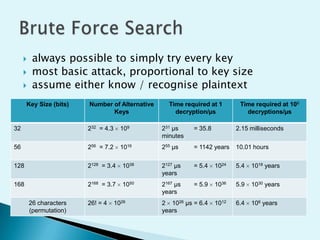
This document discusses the importance of cryptography and PKI for ensuring security, privacy, and authentication in digital communications. It addresses the three main goals of cryptography - confidentiality, integrity, and availability. The document then provides an overview of cryptographic algorithms, including symmetric and asymmetric encryption as well as hash functions. It also discusses common cryptanalytic attacks and how the strength of encryption increases exponentially with longer key sizes, making brute-force attacks infeasible for sufficiently long keys.