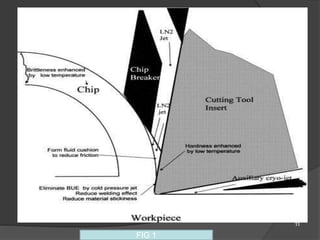
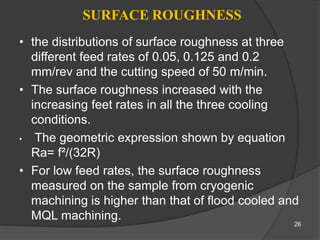
The document discusses cryogenic machining, which uses liquid nitrogen as a coolant instead of conventional cutting fluids. It provides background on the history and development of cryogenic machining. Key benefits identified include increased tool life, higher material removal rates, improved surface finish, and reduced manufacturing costs. The document outlines the cryogenic machining process and analyzes factors like tool wear, cutting forces, surface roughness, and economic impacts. Results showed that cryogenic machining yielded the best tool life and lower forces compared to other methods.