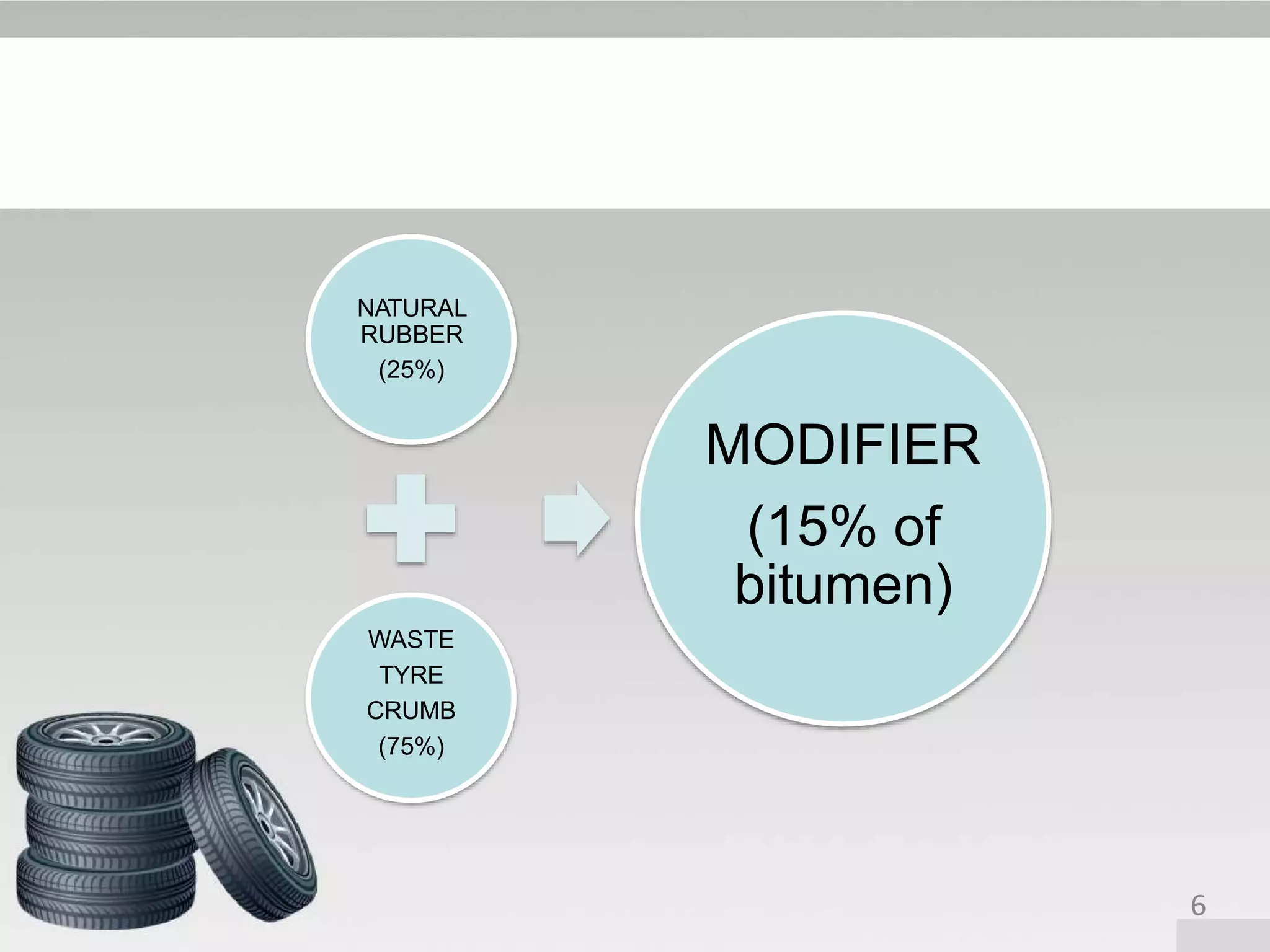
This document discusses crumb rubber modified bitumen (CRMB), which is a modified bitumen produced by mixing crumb rubber from shredded waste tires with conventional bitumen. The summary is as follows:
(1) CRMB was developed in the 1960s as a way to improve the performance of bituminous pavements and address issues like susceptibility to heat and water damage. (2) Crumb rubber is obtained from shredded truck and automobile tires and is mixed with bitumen using either a dry or wet process. (3) Compared to conventional bitumens, CRMB has benefits like lower temperature susceptibility, higher resistance to deformation, better adhesion between aggregates and binder, and improved performance under heavy traffic. However,