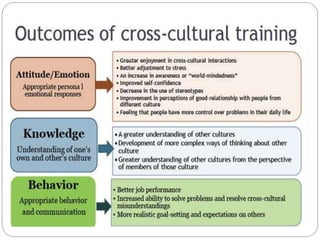
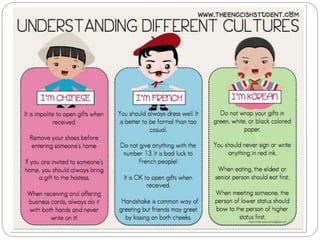
This document discusses cross-cultural communication and the importance of understanding cultural differences. Culture is defined as the ideas, customs, and social behaviors shared by a group. Cross-cultural communication looks at how people from different cultures communicate with each other and within their own culture. Barriers to effective cross-cultural communication include ethnocentrism, discrimination, stereotyping and cultural insensitivity. Understanding cultural differences like communication style, gestures, and values is key to overcoming these barriers. Being respectful and building trust across cultures helps improve cross-cultural communication.