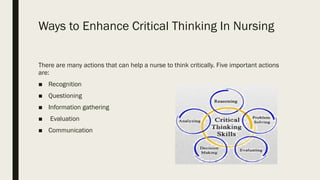
The document discusses the significance of critical thinking in nursing, emphasizing its role in clinical reasoning and decision-making. It outlines various skills, components, and processes that enhance critical thinking while addressing problem-solving strategies. Additionally, the text identifies factors influencing thought processes in nursing practice, providing a comprehensive guide for developing critical thinking abilities.