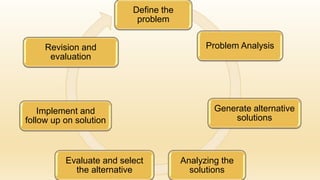
Problem solving is defined as finding solutions to problems in an orderly manner. It is a complex process that involves defining the problem, analyzing it, generating alternative solutions, evaluating those solutions, implementing the best one, and following up through revision and evaluation. Community health nurses address patients' problems using a variety of approaches including persuasion, enforcement, team approaches, and community involvement to find the best solutions.