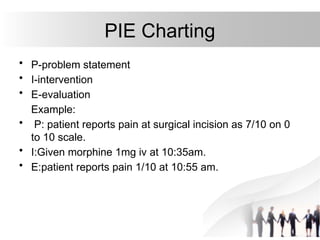
The document outlines the importance and principles of documentation and reporting in nursing, emphasizing the need for accurate and comprehensive records to ensure quality care and continuity. It details various types of records and reports, their purposes, and best practices for writing them, including the methods of documentation like narrative and problem-oriented charting. Additionally, it discusses the significance of incident reporting and the legal and communication roles of documentation in healthcare settings.