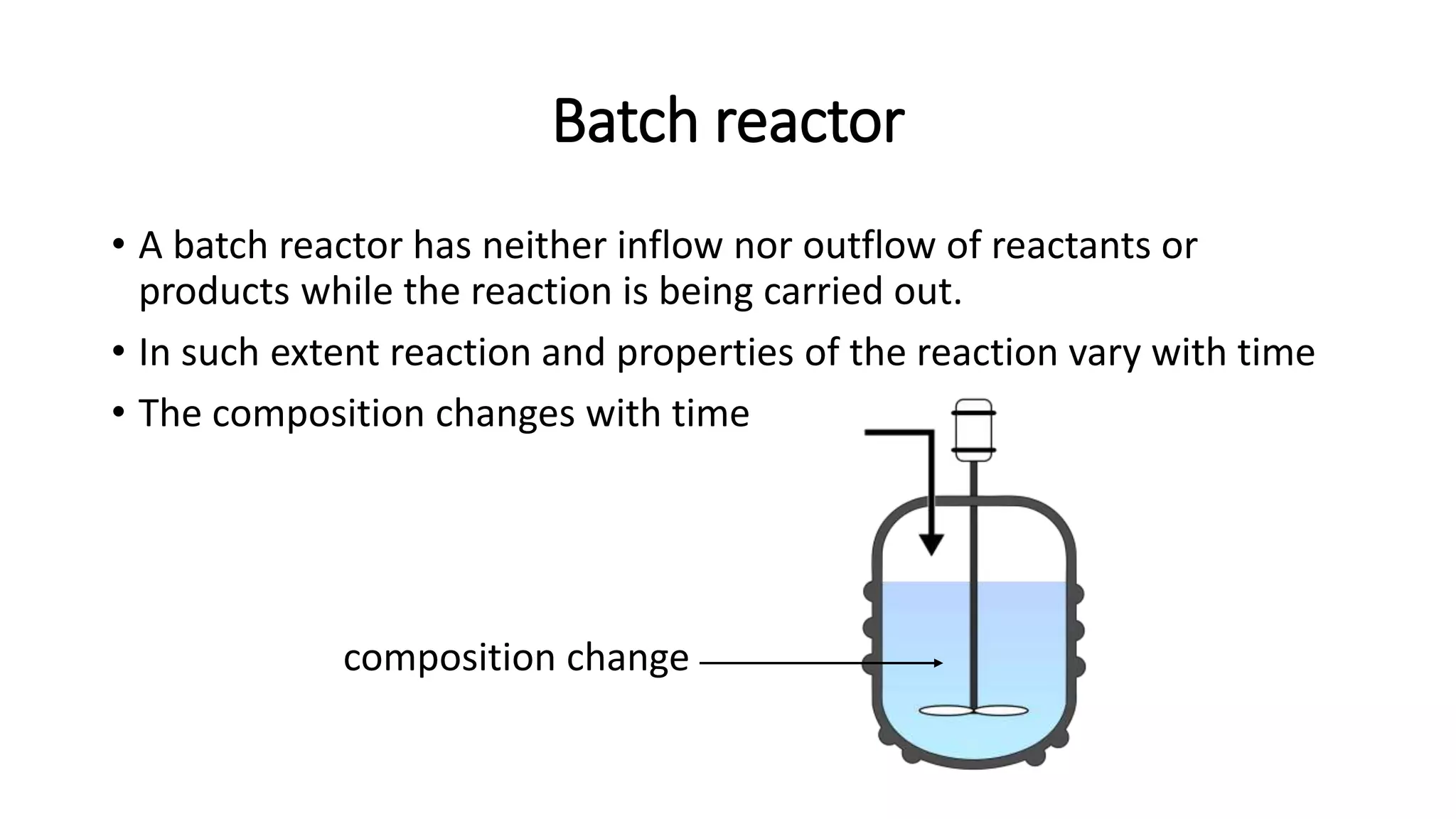
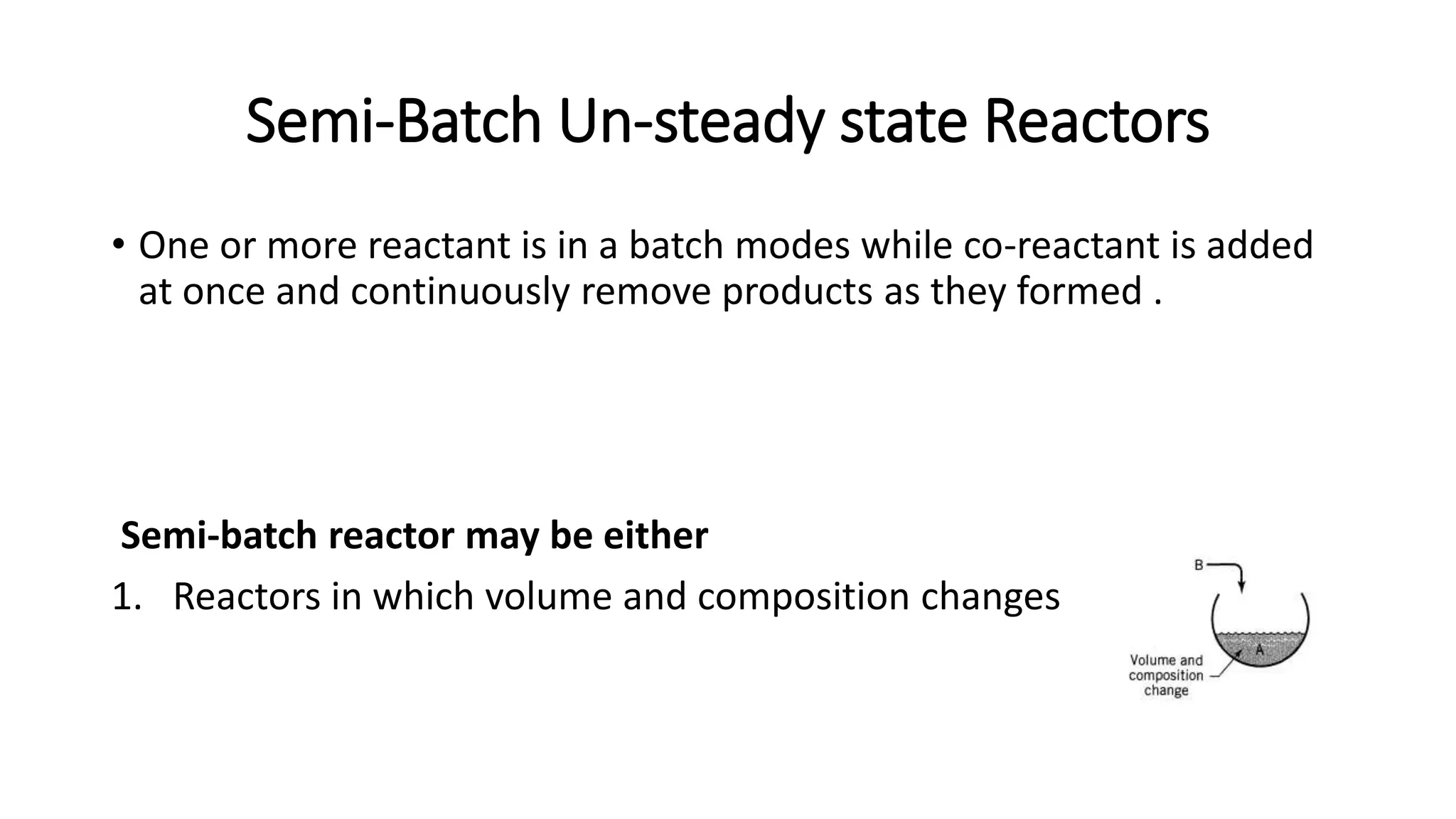
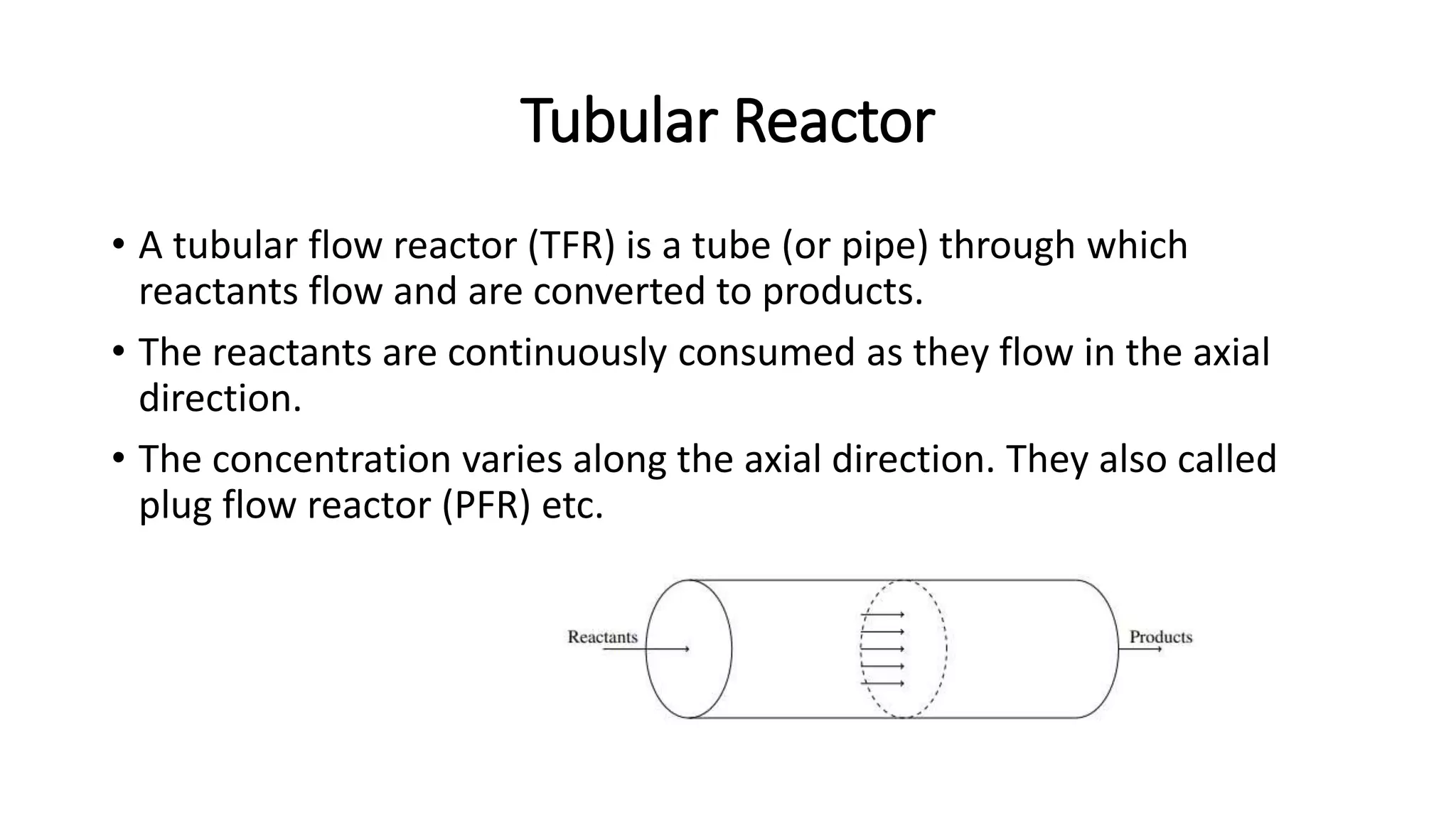
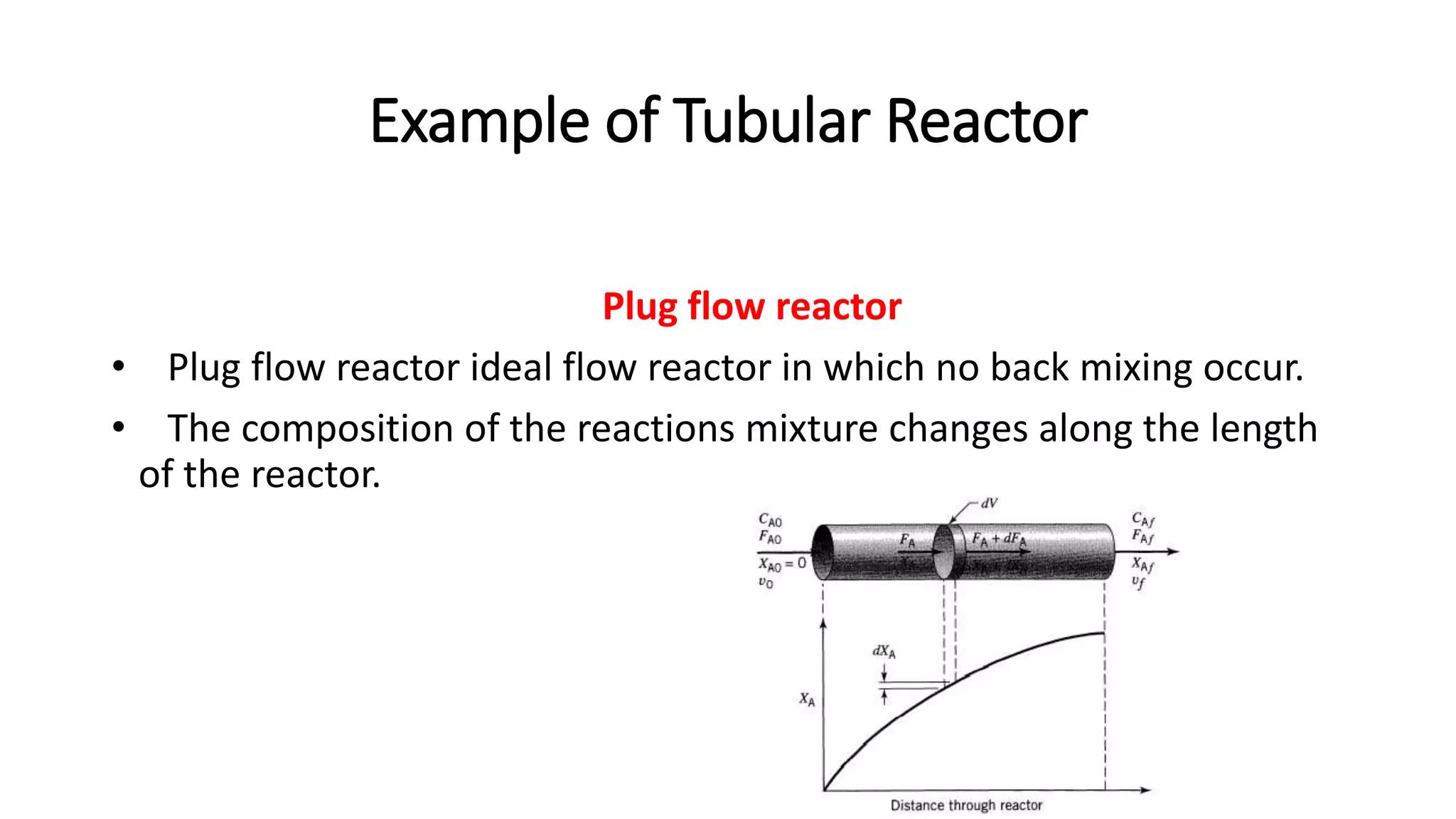
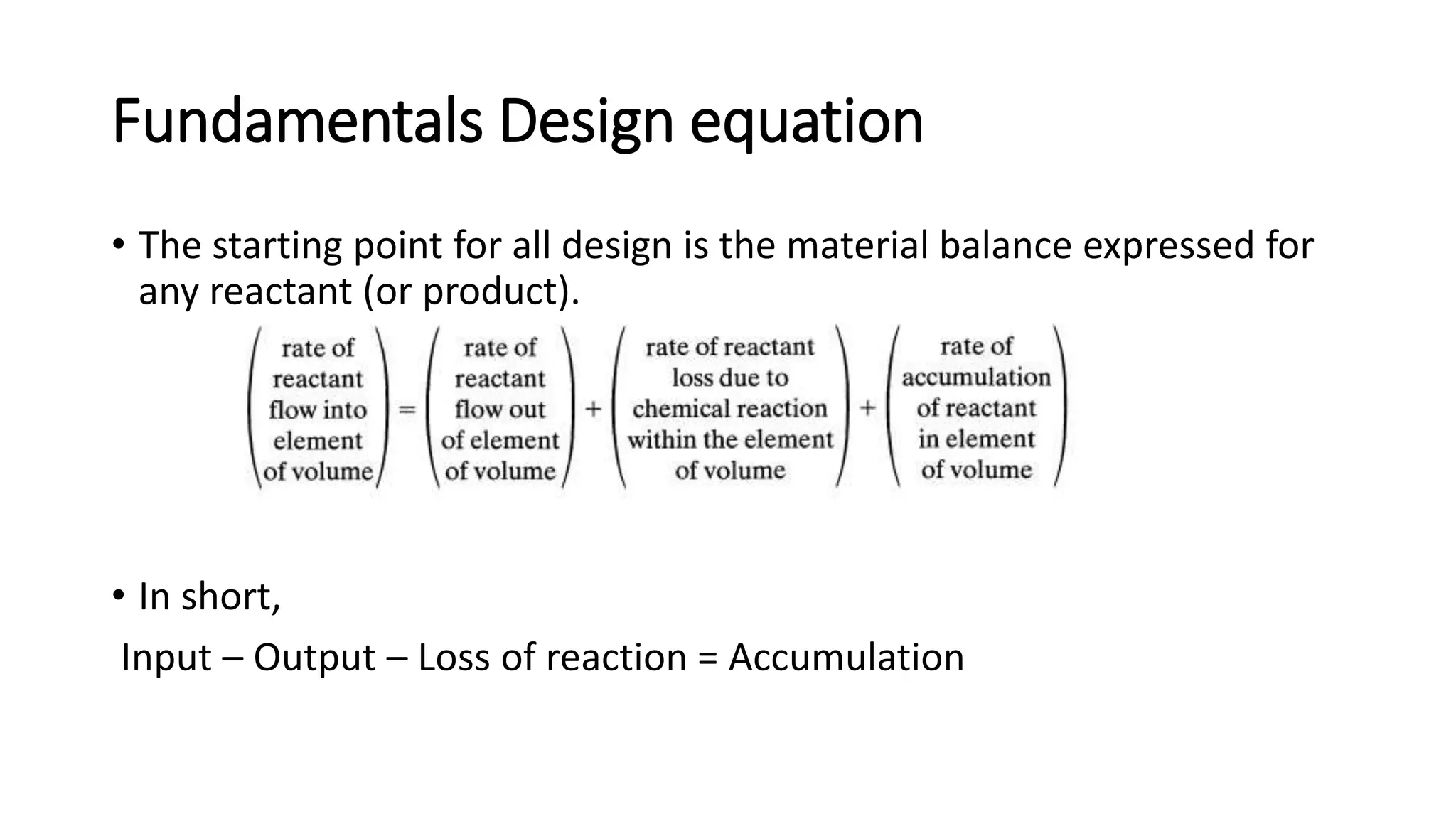
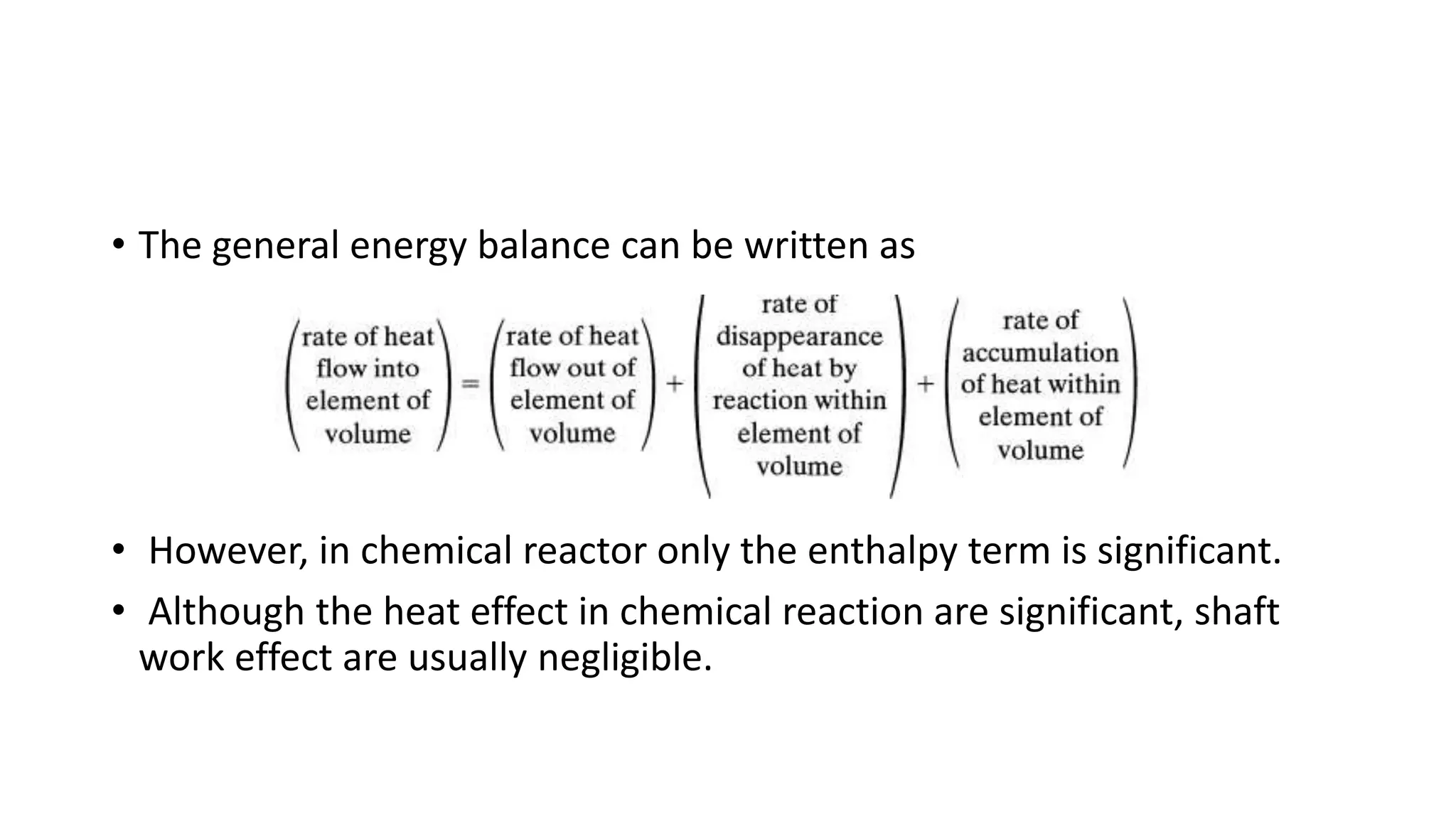
This document provides an introduction to reactor design in chemical reaction engineering. It discusses the key factors involved in reactor design, including size, type, temperature, and production rate. It also describes the main types of reactors based on operation (batch, continuous, semi-batch), shape (tank, tubular), and number of phases (homogeneous, heterogeneous). Material and energy balances are important design equations, taking into account input/output, reaction losses, and accumulation. Temperature effects must also be considered since reaction rates strongly depend on temperature.