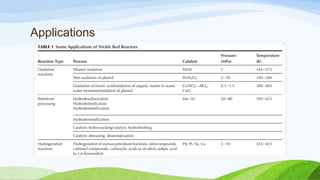
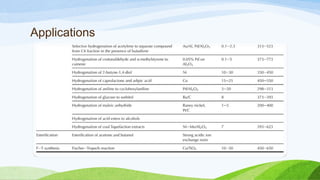
A trickle-bed reactor uses the downward movement of a liquid and upward or downward movement of gas over a packed bed of catalyst particles to facilitate catalytic reactions. There are three basic types - conventional trickle beds with randomly packed catalyst, semi-structured beds with structured or monolithic catalyst, and micro-trickle beds with catalyst in microchannels. In operation, the liquid trickles down while the gas flows concurrently up or down, with various flow regimes depending on flow rates and properties. Examples of uses include liquid-phase hydrogenation in refineries, oxidation of compounds in wastewater, and wastewater treatment using biofilm on the packed bed surface.