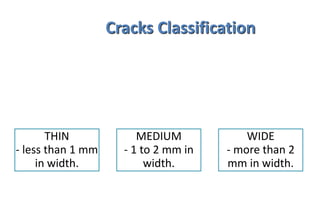
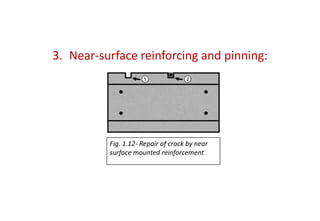
Cracks in concrete structures can be classified as thin (less than 1mm), medium (1-2mm), or wide (more than 2mm). Cracks are caused by factors like plastic shrinkage during curing, drying shrinkage due to moisture loss, thermal stresses from temperature changes, chemical reactions between aggregates and alkalis, and weathering from freezing and thawing. Cracks are evaluated based on their location, extent, and width. Repair methods include epoxy injection into cracks, routing and sealing cracks, reinforcing around cracks, and cement grouting of cracks. Left unrepaired, cracks can compromise the structural integrity and durability of concrete.