Embed presentation
Download to read offline



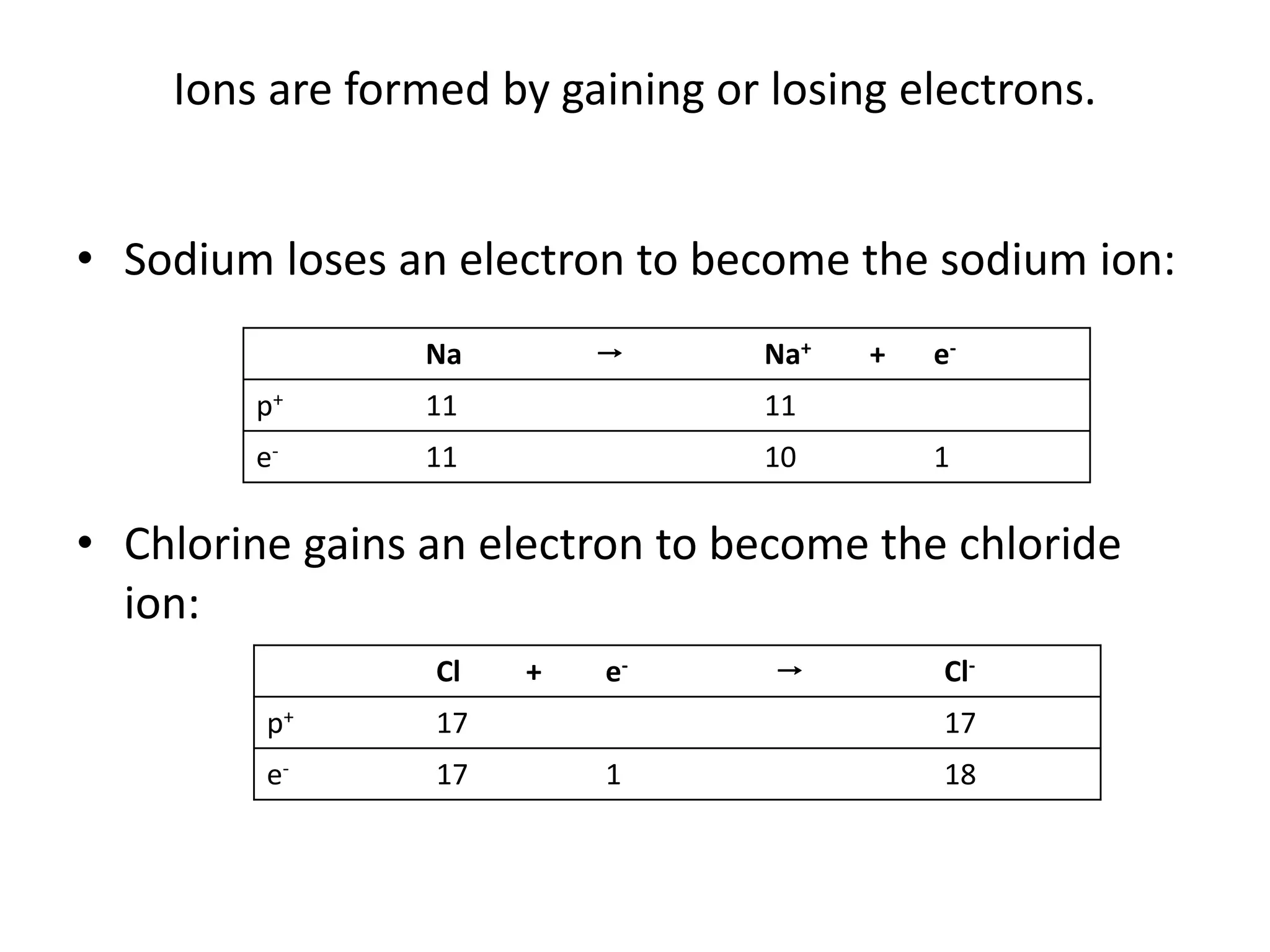

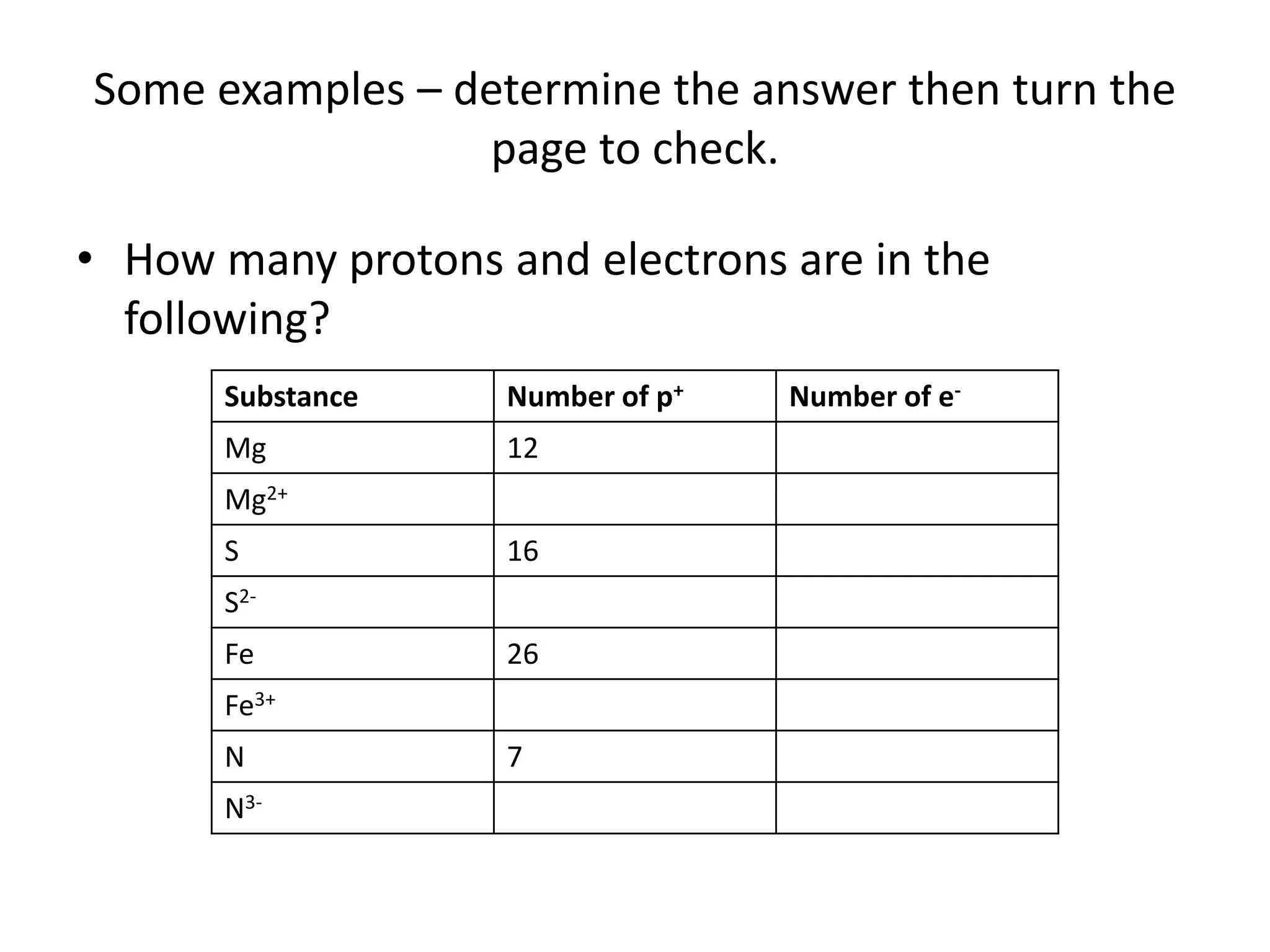
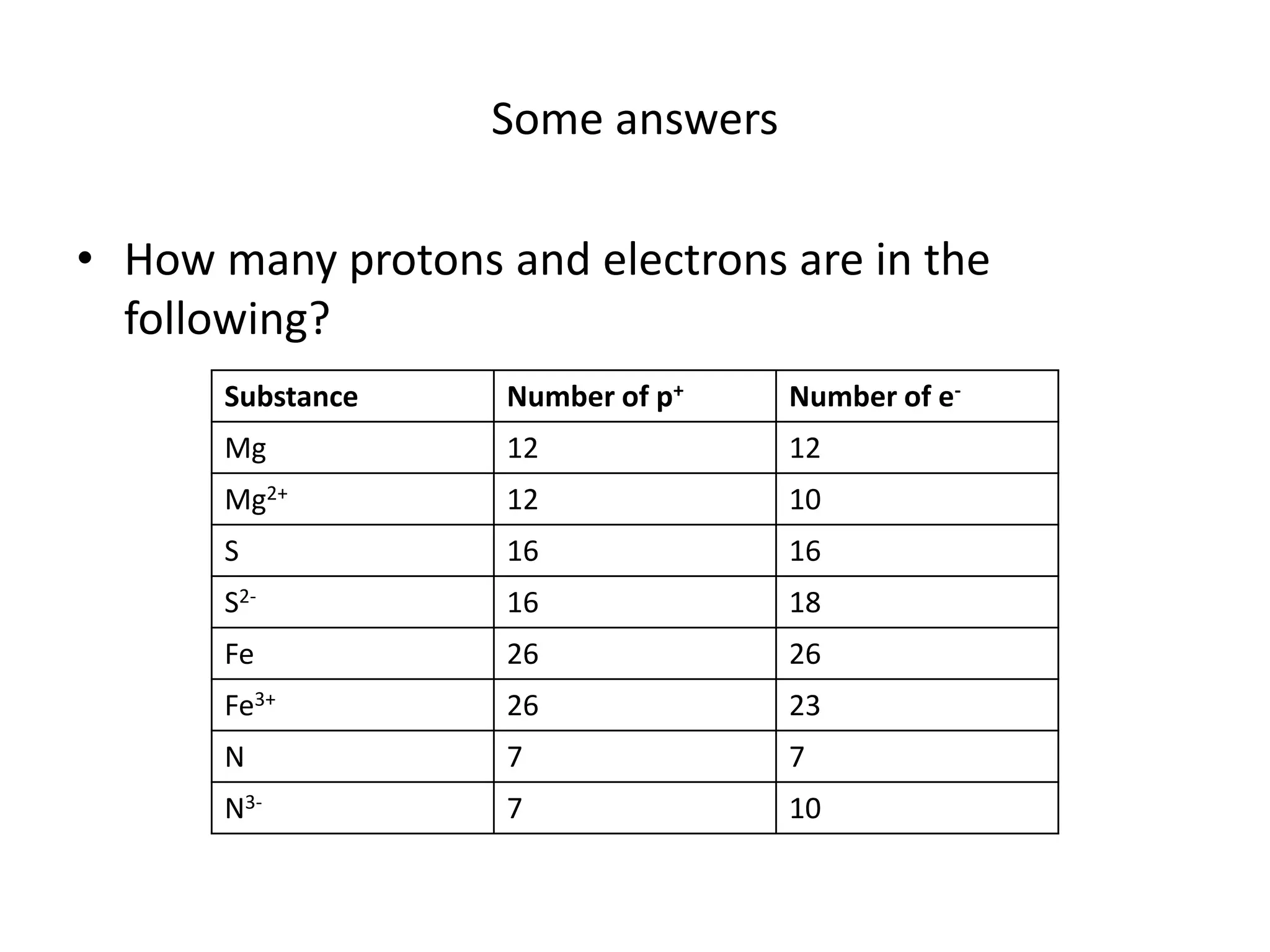
Ions are formed when atoms gain or lose electrons, giving them a positive or negative charge. Sodium loses an electron to become Na+, giving it 11 protons and 10 electrons. Chlorine gains an electron to become Cl-, giving it 17 protons and 18 electrons. Atoms only gain or lose electrons to become ions, keeping the number of protons the same. The document provides examples of ions formed from magnesium, sulfur, iron and nitrogen atoms and lists their number of protons and electrons.







