Gfr factors. 17.02.13.
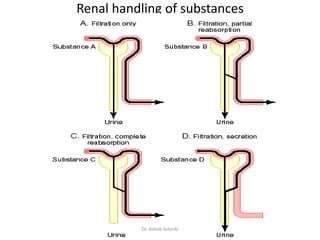
- 1. Renal handling of substances Dr. Ashok Solanki
- 7. Factors affecting G.F.R. Changes in renal blood flow Changes in glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure Changes in systemic blood pressure Afferent or efferent arteriolar constriction Changes in hydrostatic pressure in Bowman's capsule Ureteral obstruction Edema of kidney inside tight renal capsule Changes in concentration of plasma proteins: dehydration, hypoproteinemia, etc (minor factors) Changes in Kf Changes in glomerular capillary permeability Changes in effective filtration surface area Dr. Ashok Solanki
- 9. Glomerular fitration Substances in the blood are filtered through capillary fenestrae between endothelial cells (single layer). filtrate then passes across the basement membrane and through slit pores between the foot processes (also called pedicels) and enters the capsular space. From here, the filtrate is transported to the lumen of the proximal convoluted tubule. Dr. Ashok Solanki
- 11. Autoregulation of GFR • Afferent arteriolar feedback mechanism for regulating GFR • Efferent arteriolar feedback mechanism for regulating GFR • Myogenic mechanism regulating GFR- resist stretching during increase arterial pressure – stretch of vascular wall increase calcium ions entry from ECF into the cell – contract the cells – increase vascular resistance – decrease GFR and RBF Dr. Ashok Solanki
- 13. GFR = Kf . (PG – PB – pG + pB) The GFR is determined by the sum of the hydrostatic pressure colloid osmotic forces across the glomerular membrane Bowmens capsule hydrostatic pressure the glomerular capillary filtration coefficient, Kf GFR = Kf . Net filtration pressure Dr. Ashok Solanki
- 14. The 4 basic functions of the kidneys • Ultrafiltration by glomerular capillaries Dr. Ashok Solanki
- 15. glomerular filtration and tubular function. • bulk flow of fluid from glomerular capillary to Bowman’s space • volume = 20% of RPF (filtration fraction), ≈ 125 ml/min • barriers to filtration • endothelial fenestrae • basement membrane • Podocytes • GFR = Kf · NFP (filtration coefficient x net filtration pressure) Dr. Ashok Solanki
- 22. Junction- the JGA Blood flows into the glomerulus through the afferent arterioles and leaves the glomerulus through the efferent arterioles. The proximal tubule exits Bowman’s capsule. Dr. Ashok Solanki
- 23. Tubuloglomerular feedback o Alterations in GFR due to changes in glomerular perfusion pressure will lead to an alteration in the composition of the fluid delivered to the macula densa region of the nephron tubule o The macula densa senses these changes and acts to alter afferent arteriole tone to vary glomerular perfusion pressure to return the GFR to normal o Dr. Ashok Solanki
- 25. The structure of the filter 1. The glomerular capillary endothelium: • A highly specialised capillary endothelium with fenestrations (windows) to minimise the filter thickness; • This layer prevents cellular components of blood coming into contact with the basement membrane. 2. The glomerular basement membrane: • Made of connective tissue, it is negatively charged; • This is the layer that actually acts as the filter. 3. Bowman’s epithelial cells (podocytes): • Epithelial cells with multiple projections (foot processes) which interlink with each other • whilst still keeping a small gap between them creating a large surface area; • Act to maintain the basement membrane, and has phagocytic functions . Dr. Ashok Solanki
- 32. Tubuloglomerular feedback Dr. Ashok Solanki
- 37. Factors affecting GFR 1. Glomerular capillary hydrostetic pressure – - arterial pressure - afferent arterial resistance - efferent arterial resistance 2. Colloidal osmotic pressure of glomerulus – 3. bowmen’s capsular hydrostetic pressure – ureteric stone, obstruction of urinary tract 4. RBF – GFR directly related to RBF 5. Sympathetic stimulation Dr. Ashok Solanki
- 38. Factors affecting GFR • Decrease Kf decrease GFR • Increase Kf increase GFR • In some diss. Lower Kf by reducing the number of functional glo. Capillaries • Increase thickness of the glo. Capillaries • Chronic uncontrolled hypertension and diabetes mellitus Dr. Ashok Solanki
- 39. Autoregulation of GFR Afferent arteriolar feedback mechanism for regulating GFR Efferent arteriolar feedback mechanism for regulating GFR Myogenic mechanism regulating GFR- resist stretching during increase arterial pressure – stretch of vascular wall increase calcium ions entry from ECF into the cell – contract the cells – increase vascular resistance – decrease GFR and RBF Dr. Ashok Solanki
- 40. Glomerular capillary filtration coefficient - Kf The Kf is a measure of the product of the hydraulic conductivity and surface area of the glomerular capillaries Kf = GFR / Net filtration pressure GFR – 125 ml / min Net filtration pressure – 10 mm of Hg Kf – 12.5 ml / min /mm of Hg 4.2 ml/min/mm of Hg/100g of kidney wt. Dr. Ashok Solanki
- 42. Net filtration pressure • Forces favoring filtration (mm Hg) glomerular hydrostatic pressure - Pg 60 bowmen’s capsule colloid osmotic pressure – πb 0 • Forces opposing filtration (mm Hg ) bowmen’s capsule hdrostatic pressure - Pg 18 glomerular capillary colloid osmotic pressure – πg 32 Net filtration pressure = 60 – 18 – 32 = +10 mmof Hg Dr. Ashok Solanki
- 43. Forces promoting & opposesing filtration • Net filtration force is +ve causing filtration Dr. Ashok Solanki
- 44. GFR is sum of Kf x Net filtration pressure The amount of the glomerular filtrate by all the nephrons of both the kidneys in a one minute is called GFR GFR = filtration fraction x RBF In the average human adult, the GFR is about 125 ml / min. or 180 L / day Filtration fraction – the fraction of the renal plasma which becomes the filtrate Filtration fraction = GFR / RBF Dr. Ashok Solanki
