This document discusses column chromatography, a technique used to separate mixtures of compounds. It involves using a stationary phase, typically an adsorbent material like silica gel or alumina, packed into a glass column. A mobile liquid phase is passed through the column, carrying the sample mixture. Components of the mixture are separated based on differences in how strongly they interact with and adhere to the stationary phase. Key factors in column chromatography include selecting an appropriate stationary phase and mobile phase based on the compounds' properties. The document outlines experimental aspects like suitable adsorbents, packing techniques, and applications of column chromatography in separating mixtures.
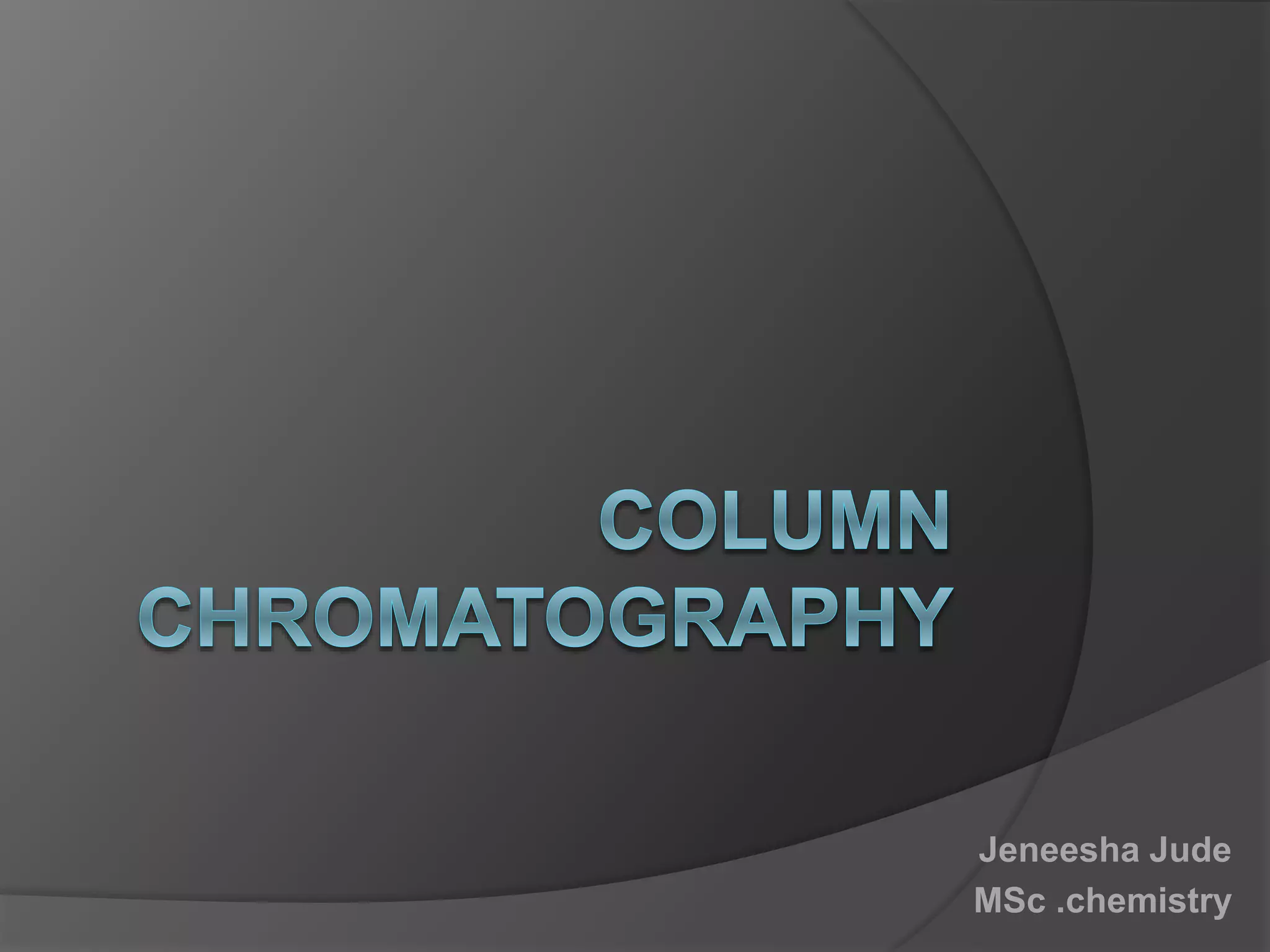




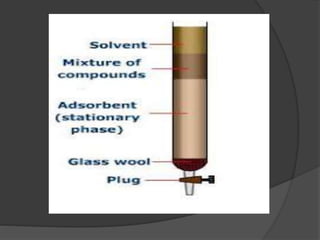








![ It percolates through the adsorbent column ,
different components adsorbed to different
extend .
Most readily adsorbed constituent(say a) is
held at the top .
Other (say b and c) of decreasing
adsorbabilities are held up at different zones
or bands down the column in the same order
[say b and then c]
This partial separation is improvised by
adding some amount of original solvent –
development of chromatogram.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/columnchromatography-191105015032/85/Column-chromatography-16-320.jpg)



