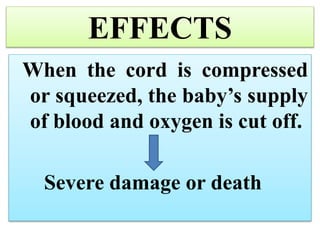
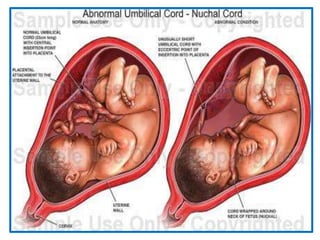
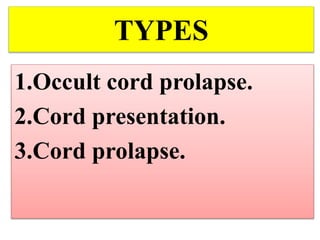
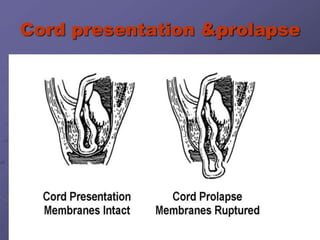
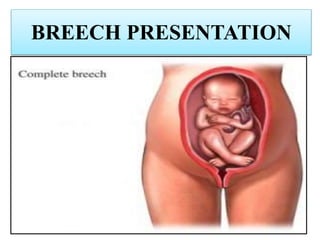
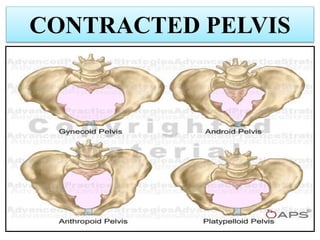
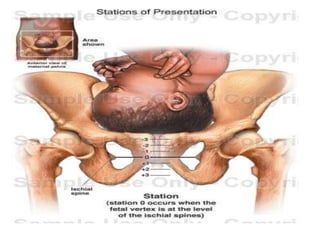
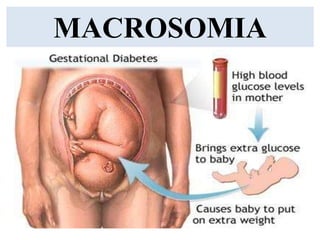
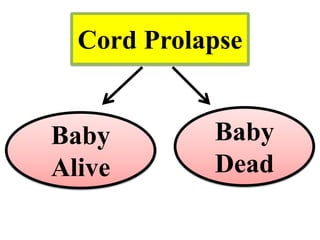
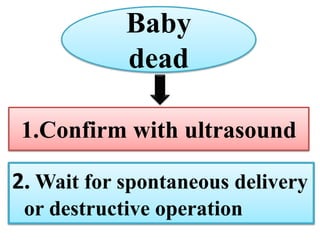
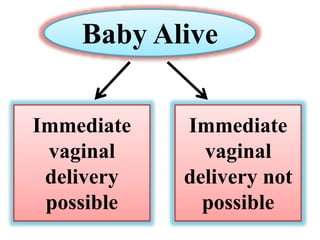
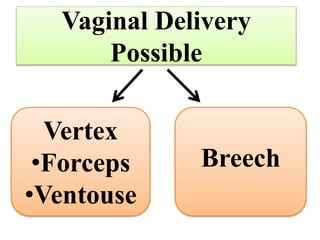
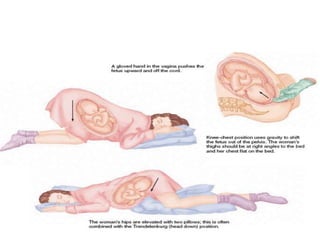
Umbilical cord prolapse occurs when the umbilical cord descends alongside or beyond the fetal presenting part during labor and delivery. It can cut off blood and oxygen supply to the fetus, potentially causing damage or death. Risk factors include prematurity, abnormal fetal position, polyhydramnios, and multiparity. Diagnosis is made through physical exam finding the cord in the vagina and a decreased fetal heart rate below 120 bpm. Immediate management depends on whether the baby is alive or dead, and involves vaginal delivery if possible or emergency c-section otherwise to prevent hypoxic injury or death.