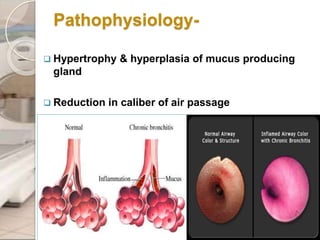
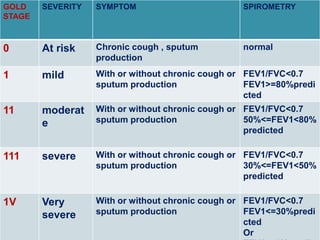
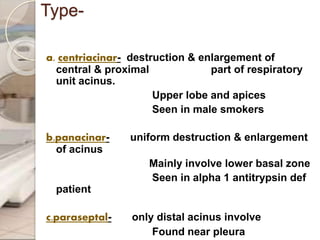
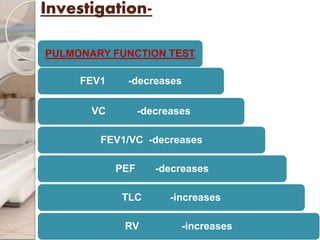
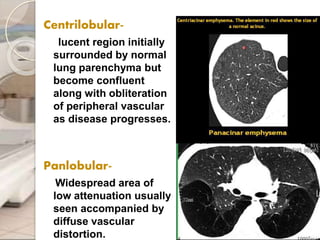
This document discusses chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), including chronic bronchitis and emphysema. It covers the definition, causes, pathophysiology, clinical presentation, investigations, management, and complications of COPD. Key points include that COPD is characterized by irreversible airflow limitation caused by chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Cigarette smoking is the primary risk factor. Symptoms include cough, sputum production, and shortness of breath. Pulmonary function tests can confirm the diagnosis and assess severity. Chest imaging shows hyperinflation of the lungs in emphysema. Treatment involves smoking cessation, bronchodilators, corticosteroids, oxygen therapy, and surgery in severe cases