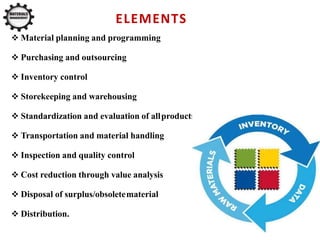
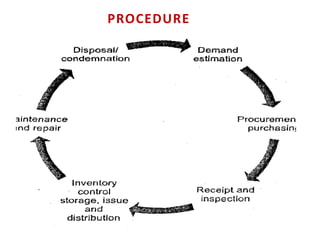
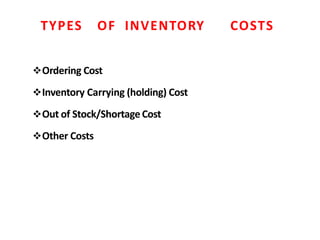
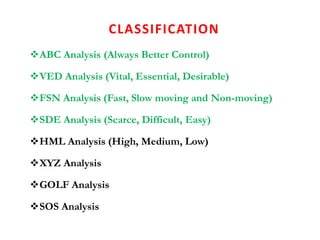
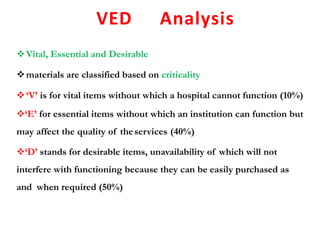
This document discusses material management in healthcare organizations. It defines materials as equipment, apparatus, and supplies procured and used by an organization. Material management involves planning, organizing, and controlling the flow of materials from procurement to use and disposal. It aims to ensure the right quality, quantity, time, place, and cost of materials. Key aspects of material management discussed include procurement, inventory control, classification techniques like ABC analysis, and establishing inventory levels. The overall goal is to efficiently manage materials and resources to meet organizational needs.