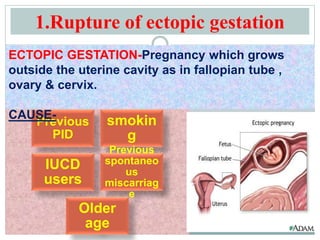
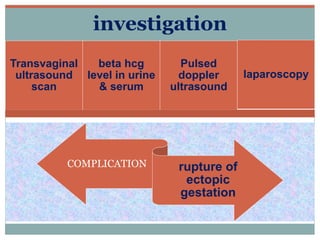
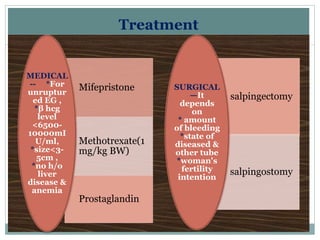
1. Ruptured ectopic pregnancy presents with sudden onset of severe abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding. Diagnosis is confirmed with transvaginal ultrasound and beta-hCG levels. Treatment depends on stability and may include medical or surgical options like salpingectomy.
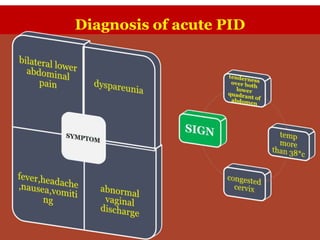
2. Acute pelvic inflammatory disease is caused by ascending bacterial infection and presents with abdominal pain and abnormal discharge. Diagnosis involves screening for infections and inflammatory markers. Treatment involves intravenous antibiotics.
3. Testicular torsion presents with sudden severe scrotal pain. Diagnosis involves physical exam showing a high-riding painful testicle. Immediate surgical detorsion is required to save the testis.

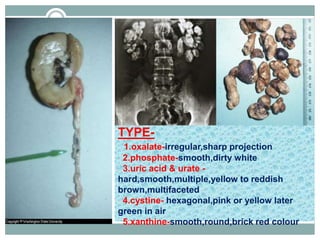
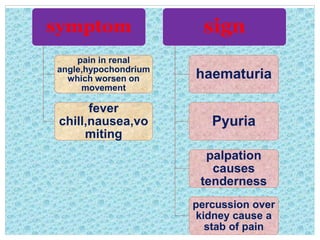
![….
[A].Gynaecological & obstetrical causes of acute abdomen….](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ravi-surgeryseminar-191217132540/85/Surgery-2-320.jpg)





















![Treatment
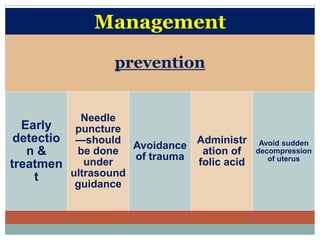
Shift the pt to an equipped maternity unit as early
as possible.
Blood examination-ABO,Rh typing,Hb% &
haematocrit estimation.
Immediate delivery-
a].pt is in labour-vaginal delivery
accelerated by low rupture of membrane.
amniotomy which accelerate the myometrial
contraction
b].pt is not in labour-
Induction of labour- inj. Oxytocin 10IU(slow) or
methergin 0.2mg i.v.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ravi-surgeryseminar-191217132540/85/Surgery-31-320.jpg)




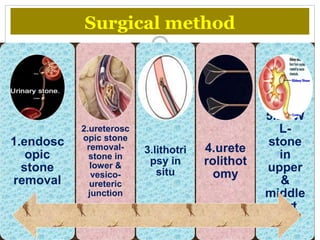
![[B]. Genitourinarycauses of acute
abdomen](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ravi-surgeryseminar-191217132540/85/Surgery-37-320.jpg)