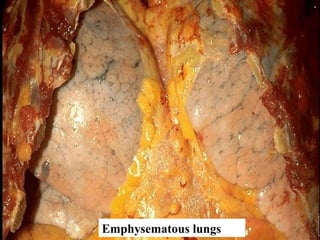
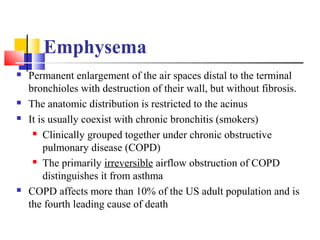
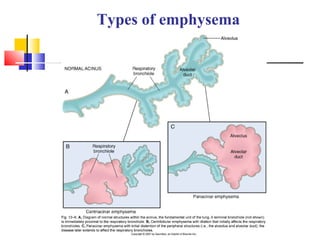
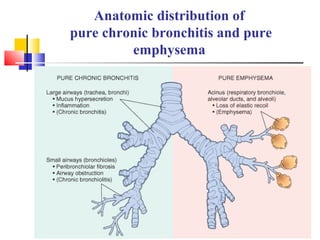
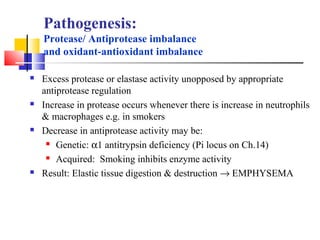
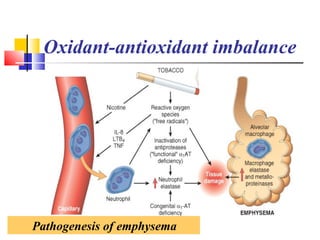
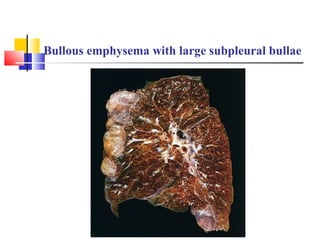
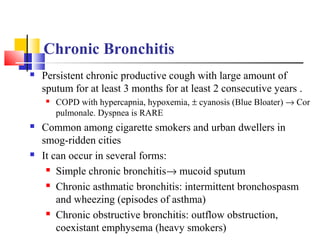
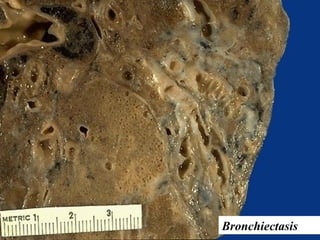
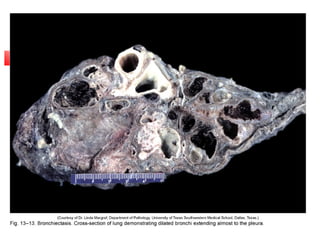
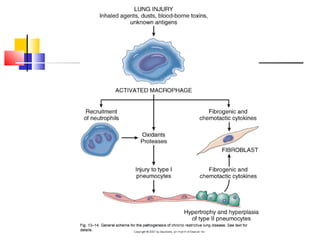
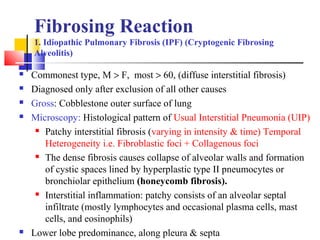
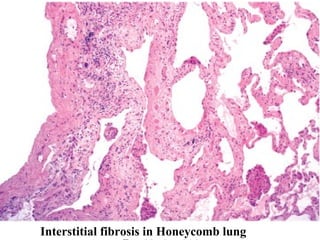
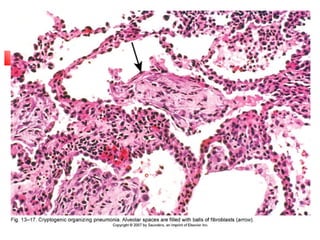
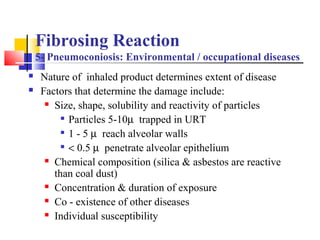
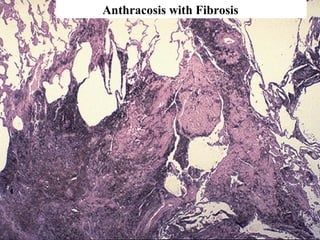
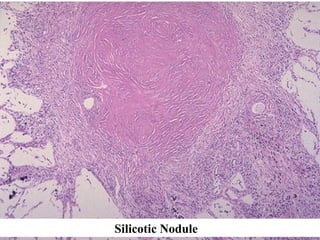
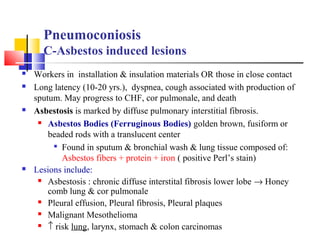
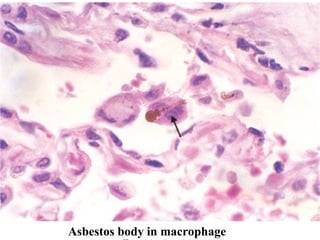
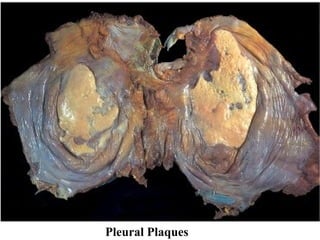
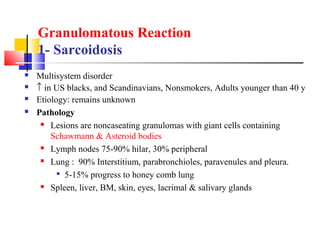
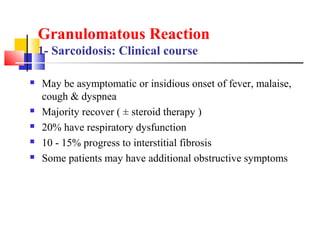
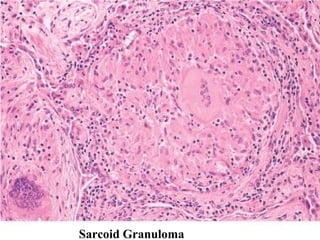
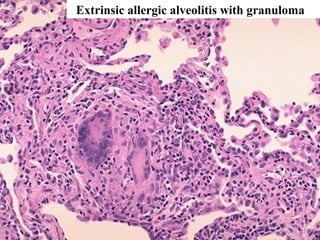
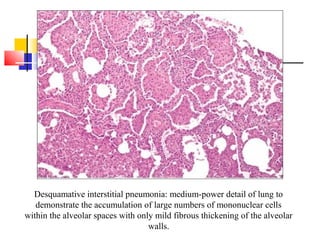
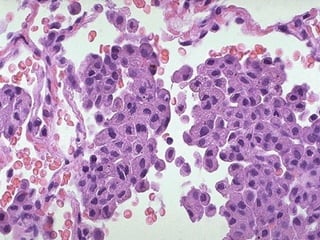
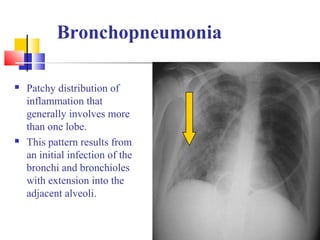
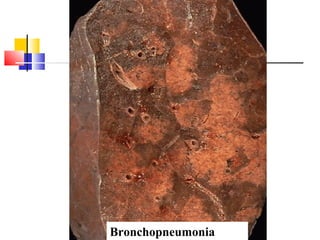
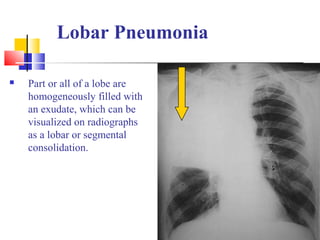
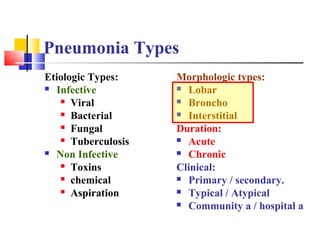
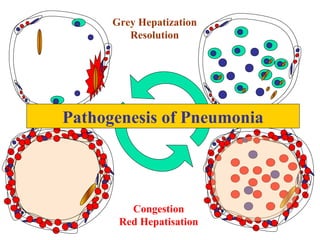
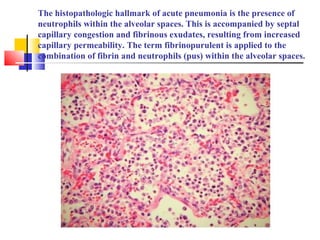
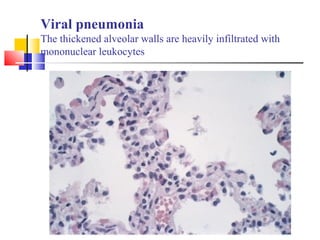
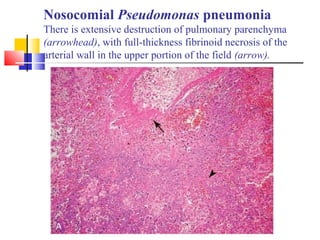
Diffuse pulmonary diseases can be classified as either obstructive or restrictive. Obstructive diseases involve increased airflow resistance and include emphysema, chronic bronchitis, and bronchiectasis. Restrictive diseases involve reduced lung expansion and decreased total lung capacity. Common restrictive diseases are interstitial lung diseases which involve fibrosis of the lung parenchyma, such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, sarcoidosis, and pneumoconiosis. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is characterized by a patchy interstitial fibrosis pattern known as usual interstitial pneumonia.