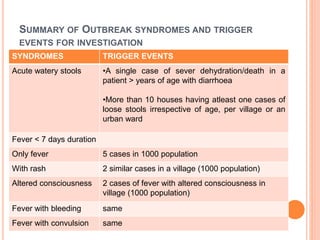
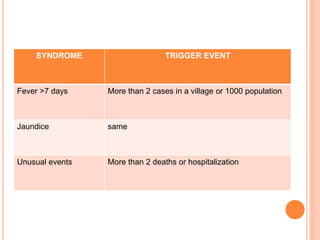
This document provides definitions and examples of outbreaks, epidemics, and pandemics throughout history. It defines an outbreak as a sudden increase in disease cases in a specific time and place. An epidemic occurs when there are more cases than normal within a community or region. A pandemic is an epidemic that spreads across multiple continents or worldwide. Several examples of devastating past pandemics are provided, including the Black Death which killed an estimated 75-200 million people in the 14th century, and the 1918 Spanish Flu pandemic which killed 20-50 million people. Causes and death tolls of other pandemics like the Plague of Justinian, cholera, and influenza outbreaks are also summarized.