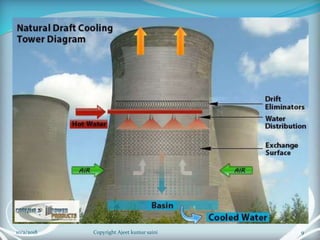
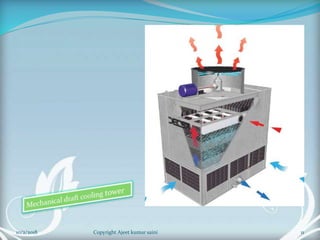
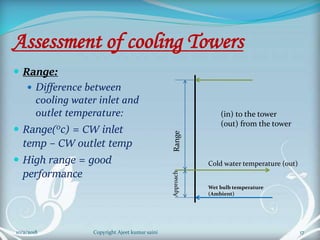
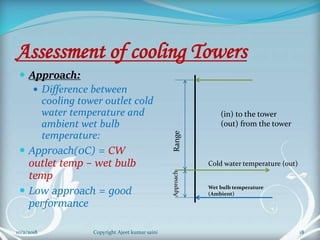
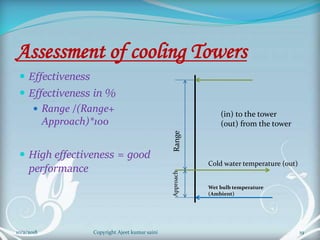
The document is a presentation on cooling towers. It discusses the components, types, and assessment of cooling towers. There are two main types - natural draft towers that use convection and mechanical draft towers that use fans. Mechanical draft towers can be forced draft, induced draft cross flow, or induced draft counter flow. The performance of cooling towers is assessed using parameters like range, approach, and effectiveness. Higher range and lower approach indicate better performance.